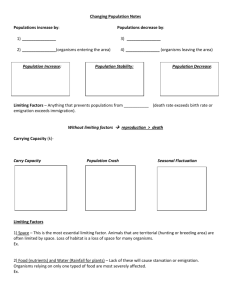
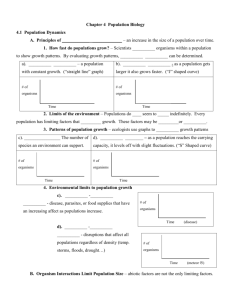
Lesson 2
advertisement

Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Populations Lesson 2 Changing Populations Lesson 3 Communities Chapter Wrap-Up How do populations and communities interact and change? What do you think? Before you begin, decide if you agree or disagree with each of these statements. As you view this presentation, see if you change your mind about any of the statements. Do you agree or disagree? 1. Some life exists in the ice caps of the North Pole and South Pole. 2. A community includes all organisms of one species that live in the same area. 3. Some populations decrease in numbers because of low birthrates. Do you agree or disagree? 4. An extinct species has only a few surviving individuals. 5. No more than two species can live in the same habitat. 6. A cow is a producer because it produces food for other organisms. Populations • What defines a population? • What factors affect the size of a population? Populations • biosphere • population • community • competition • limiting factor • population density • biotic potential • carrying capacity The Biosphere and Ecological Systems The parts of Earth and the surrounding atmosphere where there is life is called the Earth’s biosphere. The Biosphere and Ecological Systems (cont.) • The biosphere includes all the land of the continents and islands, all of the earth’s oceans, lakes, and streams, as well as the ice caps at the North Pole and the South Pole. • Parts of the biosphere with large amounts of plants or algae often contain many other organisms as well. What is a population? • An ecosystem is a group of organisms that lives in an area at one time, as well as the climate, soil, water, and other nonliving parts of the environment. • The study of all ecosystems on Earth is ecology. What is a population? (cont.) A community is all the populations of different species that live together in the same area at the same time. What is a population? (cont.) A population is all the organisms of the same species that live in the same area at the same time. What is a population? (cont.) A species is a group of organisms that have similar traits and are able to produce fertile offspring. What defines a population? Competition • Competition is the demand for resources, such as food, water, and shelter, in short supply in a community. • When there are not enough resources available to survive, there is more competition in a community. Population Sizes • Changes in environmental factors can result in population size changes. • A limiting factor is anything that restricts the size of a population. • Available sunlight is a limiting factor for most organisms. • Without sunlight, green plants cannot make food, which effects animals that eat plants. Population Sizes (cont.) • Temperature is a limiting factor for some organisms. • When the temperature drops below freezing, many organisms die because it is too cold to carry out their life functions. • Disease, predators, and natural disasters such as fires or floods are also limiting factors. Population Sizes (cont.) What factors affect the size of a population? Population Sizes (cont.) • Population density is the size of a population compared to the amount of space available. • One way of estimating population density is by sample count. Population Sizes (cont.) population from Latin populus, means “inhabitants” density from Latin densus, means “thick, crowded” Population Sizes (cont.) • A population’s biotic potential is the largest number of offspring that can be produced when there are no limiting factors present. • No population on Earth ever reaches its biotic potential because no ecosystem has an unlimited supply of natural resources. Population Sizes (cont.) • The largest number of individuals of one species that an environment can support is the carrying capacity. • A population grows until it reaches the carrying capacity of an environment. Carrying capacity is determined in part by limiting factors. Population Sizes (cont.) • Disease, space, predators, and food are some of the factors that limit the carrying capacity of an ecosystem. • The carrying capacity of an environment is not constant because it increases and decreases as the amount of available resources increases and decreases. • When the size of a population becomes larger than the carrying capacity of its ecosystem, overpopulation occurs. • The population density of organisms, including green plants and algae, varies throughout the world. • A community is all the populations of different species that live together in the same area at the same time. • The number of individuals in a population varies as the amount of available resources varies. Which term refers to all the populations of different species that live together in the same area at the same time? A. a population B. a biosphere C. a community D. an ecosystem Which of these refers to anything that restricts the size of a population? A. population density B. limiting factor C. carrying capacity D. biosphere Which of these increases when there are not enough resources available in a community for all its organisms to survive? A. competition C. organisms B. population D. food Do you agree or disagree? 1. The biosphere includes all parts of Earth and the surrounding atmosphere that support life. 2. A community includes all organisms of one species that live in the same area. Changing Populations • How do populations change? • Why do human populations change? Changing Populations • birthrate • death rate • extinct species • endangered species • threatened species • migration How Populations Change • A population change can be measured by the population’s birthrate and death rate. • A population’s birthrate is the number of offspring produced over a given period of time. • The death rate is the number of individuals that die over the same period of time. How Populations Change (cont.) • If the birthrate is higher than the death rate, the population increases. • If the death rate is higher than the birthrate, the population decreases. • When a population is in ideal conditions with unlimited resources, it grows in a pattern called exponential growth. How Populations Change (cont.) exponential Science Use a mathematical expression that contains a constant raised to a power, such 3 2 as 2 or x . Common Use in great amounts How Populations Change (cont.) • During exponential growth, the larger a population gets, the faster it grows. • E coli bacteria are microscopic organisms that undergo exponential growth; the population doubles in size every half hour. How Populations Change (cont.) • Disease and natural disasters such as floods, fires, or volcanic eruptions can decrease populations. • Predation—the hunting of organisms for food—also reduces population size. How Populations Change (cont.) • If populations continue to decrease in numbers, they disappear. • An extinct species is a species that has died out and no individuals are left. • Extinctions can be caused by predation, natural disasters, or damage to the environment. How Populations Change (cont.) extinct from Latin extinctus, means “extinguish” How Populations Change (cont.) • An endangered species is a species whose population is at risk of extinction. • A threatened species is a species at risk, but not yet endangered. Tom Brakefield/Getty Images How Populations Change (cont.) • Populations also change when organisms move from place to place. • Migration is the instinctive seasonal movement of a population of organisms from one place to another. • Ducks, geese, and monarch butterflies are examples of organisms that migrate annually. How Populations Change (cont.) List three ways populations change. Human Population Changes • Human population, like all other populations, are affected by birthrate, death rate, and movement. • Unlike other species, humans have developed ways to increase the carrying capacity of their environment. • Scientists estimate that there were about 300 million humans on Earth a thousand years ago. Human Population Changes (cont.) • Today there are more than 6 billion humans on earth. • As human population grows, people need to build more houses and roads and clear more land for crops, which means there is less living space, food, and other resources for other species. • Human energy use contributes to pollution that affects other populations. Human Population Changes (cont.) • Factors that keep the human birthrate higher than its death rate include food, resources, sanitation, and medical care. • Advances in agriculture have made it possible to produce food for billions of people. • Today people have access to more resources because of better transportation methods. Human Population Changes (cont.) • Modern water treatment and more effective cleaning products help prevent the spread of disease-causing organisms that can lead to death. • Human populations in some parts of the world are decreasing in size because of factors like disease, drought, and natural disasters. Human Population Changes (cont.) Like other organisms, populations of humans might move when more resources become available in a different place. Human Population Changes (cont.) What makes human populations increase or decrease in size? • The birthrate and the death rate of any population affects its population size. • The giant moa is classified as an extinct species because there are no surviving members. • A population that is at risk but not yet endangered is a threatened species. Tom Brakefield/Getty Images Which term refers to a species that is at risk, but not yet endangered? A. an extinct species B. a threatened species C. an endangered species D. a migrating species What happens to a population if the birthrate of a species is higher than the death rate? A. it decreases B. it remains the same C. it increases D. it disappears Which of these is the only species capable of developing ways to increase the carrying capacity of an environment? A. ducks B. zebras C. monarch butterflies D. humans Do you agree or disagree? 3. Some populations decrease in numbers because of low birthrates. 4. An endangered species is at risk of becoming extinct. Communities • What defines a community? • How do the populations in a community interact? Communities • habitat • symbiosis • niche • mutualism • producer • commensalism • consumer • parasitism Communities, Habitats, and Niches • A community is made up of all the species that live in the same ecosystem at the same time. • The place within an ecosystem where an organism lives is its habitat. • A habitat provides all the resources an organism needs, including food and shelter. Communities, Habitats, and Niches (cont.) A habitat has the right temperature, water, and other conditions the organism needs to survive. habitat from Latin habitus, means “to live, dwell” Communities, Habitats, and Niches • A niche is what a species does in its habitat to survive. (cont.) • Different species have different niches in the same environment. What is a community? Communities, Habitats, and Niches (cont.) • All living things use energy to carry out life processes such as growth and reproduction. • How an organism obtains energy is an important part of its niche. • Almost all the energy available to life on Earth originally came from the sun. Communities, Habitats, and Niches (cont.) • Producers are organisms that get energy from the environment, such as sunlight, and make their own food. • Consumers are organisms that get energy by eating other organisms. • Herbivores get their energy by eating plants. Communities, Habitats, and Niches • Carnivores get their energy by eating other consumers. (cont.) • Omnivores, such as most humans, get their energy by eating producers and consumers. • Detritivores get their energy by eating dead organisms or parts of dead organisms. Energy Flow A food chain is a way of showing how energy moves through a community. A food web shows many food chains within a community and how they overlap. Energy Flow (cont.) Identify a food chain in a community near your home. List the producers and consumers in your food chain. Relationships in Communities • The populations that make up a community interact with each other in a variety of ways. • Some species have feeding relationships, meaning they either eat or are eaten by another species. Relationships in Communities (cont.) • Predators help prevent prey populations from growing too large for the carrying capacity of the ecosystem. • The members of some populations, like meerkats, work together in cooperative relationships for their survival. Relationships in Communities (cont.) • A close relationship between two or more organisms of different species that live in direct contact is called symbiosis. • A symbiotic relationship in which both partners benefit is called mutualism. Relationships in Communities (cont.) A symbiotic relationship that benefits one species but does not harm or benefit the other is commensalism. Carol & Don Spencer/Visual Unlimited/Getty Images Relationships in Communities (cont.) • A symbiotic relationship that benefits one species and harms the other is parasitism. • In parasitism, the species that benefits is the parasite, and the species that is harmed is the host. Relationships in Communities (cont.) List five ways species in a community interact. • Each organism in a community has its own habitat and niche within the ecosystem. • Within a community, each organism must obtain energy for life processes. Some organisms are producers and some are consumers. • Some organisms have cooperative relationships and some have symbiotic relationships. Carol & Don Spencer/Visual Unlimited/Getty Images What type of organism gets energy from the environment to make its own food? A. consumers B. carnivores C. producers D. herbivores Which type of organism gets energy by eating both producers and consumers? A. omnivores B. detritivores C. herbivores D. carnivores A food chain helps illustrate how which of these moves through a community? A. food B. water C. life D. energy Do you agree or disagree? 5. No more than two species can live in the same habitat. 6. A cow is a producer because it produces food for other organisms. Key Concept Summary Interactive Concept Map Chapter Review Standardized Test Practice A community contains many populations that interact in their energy roles and in their competition for resources. Populations can increase, decrease, and move, affecting the community. Lesson 1: Populations • A population is all the organisms of the same species that live in the same area at the same time. • Population sizes vary due to limiting factors such as environmental factors and available resources. • Population size usually does not exceed the carrying capacity of the ecosystem. Lesson 2: Changing Populations • Populations of living things can increase, decrease, or move. • Populations can decrease until they are threatened, endangered, or extinct. • Human population size is affected by the same three factors as other populations— birthrate, death rate, and environment. Tom Brakefield/Getty Images Lesson 3: Communities • A community is all the populations of different species that live together in the same area at the same time. • The place within an ecosystem where an organism lives is its habitat and what an organism does in its habitat to survive is its niche. • Three types of relationships within a community are predator-prey, cooperative, and symbiotic. Carol & Don Spencer/Visual Unlimited/Getty Images What term refers to all the organisms of the same species that live in the same area at the same time? A. biosphere B. population C. community D. limiting factor Which term refers to the largest number of offspring that can be produced when there are no environmental factors restricting the size? A. limiting factor B. population density C. carrying capacity D. biotic potential Which term refers to the instinctive seasonal movement of a population of organisms from one place to another? A. movement B. extinction C. migration D. predation What do scientists call a species whose population is at risk of extinction? A. an endangered species B. an extinct species C. a threatened species D. a dying species Which term refers to everything a species does in its habitat to survive? A. population B. niche C. symbiotic relationship D. parasite What is the name for the parts of Earth and the surrounding atmosphere where life exists? A. community B. population C. biosphere D. ecosystem Which of these refers to the size of a population compared to the amount of space available? A. population density B. biotic potential C. limiting factor D. carrying capacity What term refers to the number of offspring produced by a population over a given period of time? A. death rate B. exponential growth C. birthrate D. migration What general term do scientists use to describe the close relationship between two or more organisms of different species that live in direct contact? A. mutualism C. parasitism B. commensalism D. symbiosis In parasitism, which species benefits? A. parasite B. host C. partner D. predator