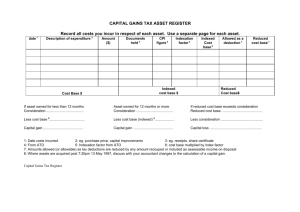
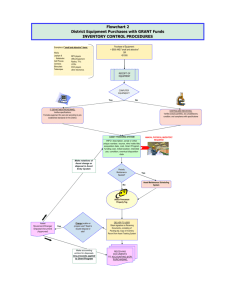
Presentation
advertisement

How to Conduct an Asset Lifecycle Study By Marla Williams, CPPM President, Integrated Asset Management, Inc. President, Federal Center Chapter 1 Typical Mission/Charter • • • • • • Improve Accuracy of Asset Records Streamline Processes Leverage Technology Reduce Costs Promote Reutilitization of Assets Improve the overall way the organization manages assets throughout their lifecycle. 2 Plan Dispose/ Donate Procure Redeploy Receive Use 3 Approach • Analyze Current State • Evaluate Gap – Regulatory and Accounting Requirements – Best Practices – Voluntary Consensus Standards • Determine Future State • Prepare Implementation Road Map 4 Identify Steering Committee • Varying Levels Within Organization • Varying Phases in Asset Lifecycle • Typically includes: – – – – – – – – Controller Capital Asset Accounting Purchasing Information Technology Facilities Management Warehouse/Receiving Fleet Property Management 5 Request Preliminary Data • Current Asset Record Data • Last Two Physical Inventories and Reconciliation Detail • Internal/External Audit Reports • Written Policies/Procedures • Sample Forms 6 Document Current State Composition of Capital Asset Values BUILDINGS BUILDING ADDITIONS LAND VEHICLES EQUIPMENT LAND IMPROVEMENTS CONTRIBUTED CAPITAL 7 Document Current State Moveable Equipment Vehicles $10,976,478 *360 Vehicles Equipment $10,586,561 940 Items 8 Document Current State 896 669 721 358 PC-DESKTOP 1255 MONITOR 1412 7646 MISC* PC-LAPTOP PRINTER PROJECTOR DVD PLAYER 4685 TELEVISION AMPLIFIER 7455 9 Identify Subject Matter Experts (SME) • Steering Committee Identifies SME’s (top to mid-level) in various departments • Include both small and large department property custodians – best property managers and the worst. 10 Kick-Off Meeting • Top Level Organizational Representative should explain mission, its importance and ask for cooperation • Consultant reviews approach and data requirements • SME’s sign up for back-to-back 2 hour interview slots • Consultant visits each SME at their office 11 SME Meetings • Consultant meets with each SME or group of SME’s in their work area • Assume nothing, ask open ended questions, document step-by-step processes verbally • Then ask for written policies/procedures, if any, sample forms – blank and completed -- expectation is to leave with this information. 12 SME Meetings • Make follow-up appointments with operational personnel for system and process demonstrations. • Document each meeting: – Additional action required – Distribute to all attendees – Solicit feedback but make no conclusions or recommendations. 13 Operational Personnel Meetings • Obtain sample completed forms, on the spot • Step-by-step demonstrations of each system • Watching how a custodian tags and “receives” a new asset into the system or seeing a demonstration of data collection and entry into the system can be most illuminating • Open-ended question – what is the most difficult thing you do, what would you change if you could. . . 14 Document Current State • Organization Structure – Roles and Responsibilities (official and unofficial) • Systems – – – – – – – Procurement Purchasing Fixed Asset Accounting Work Orders Help Desk Auto Discovery CAFM 15 Document Current State • Definitions – Capital Assets – Controlled Assets (Accountable or Sensitive Property) • Procurement – Purchase Requisitions – Issuing Purchase Orders (e.g. object/class codes, work flow approval) – Purchase or Credit Cards – Restricted Purchases • Grant Purchases • Federally Funded Purchases 16 Document Current State • Receiving – – – – – “Receiving” into Purchasing System to approve payment “Receiving” Assets -- tagging, describing and recording receipt Issuing Payment for Assets Identifying Capital Assets for General Ledger Recording Capital/Controlled Assets in Property Management System, if any. • Information Technology Equipment – Help Desk – Auto Discovery Tools – Software and Configuration Management • Facilities Management – Work Orders – Moves and Relocations 17 Document Current State • • • • • • • • Capital Leases (e.g. vehicles, copiers) Software License Management Maintenance of Non-IT Equipment Unique Fleet Requirements Unique Agency Systems or Processes Inter-Departmental Transfers Physical Inventory and Reconciliation Identification of excess or surplus property available for re-use – Updating status in Fixed Asset Accounting System 18 Capital Asset Definition • Outside Factors – GAAP – nothing specific – GFOA – minimum life is accounting period – GASB34 – one year minimum life – OMB A-87 - $5,000 for federally funded assets – Audit Findings 19 Capital Asset Definition • Conflicting Internal Definitions – Board Policy – Financial Statements – IT Department – Logistics 20 Controlled Asset Definition • Software (license tracking, transfers between departments, recovery of license information from refreshed equipment, justifying new purchases) • State and Federal EPA regulations require recycling or testing at end of life • GSA FMR B-34 Disposal of Federal Electronics • Look at ASTM E2608 Standard Practice for an Equipment Control Matrix (ECM) – need to discuss 21 Equipment Control Class ECC-1 ECC-2 ECC-3 ECC-4 ECC-5 Equipment Control Level Continuous Continuous While Mobile Event Tracking Containment No Tracking Highest Standard of Sensitivity Moderate Standard of Sensitivity Minimal Standard of Sensitivity Controllable Standard Non-Accountable 1 Consequences of loss of control is a societal safety/security impact, which is characterized by negative societal safety or security impact and would extensively damage the reputation of the organization. 2 Consequences of loss of control is a personal safety/security impact, which is characterized by negative personal safety or security impact that does not rise to the level of a societal safety or security impact. 3 Consequences of loss of control is a operational safety/security impact, which is characterized by negative operational or security impact that does not rise to the level of a personal or societal safety or security impact. 4 Consequences of loss of control is a compliance safety/security impact, which is characterized by negative compliance with applicable laws, regulations or other relevant internal or external guidance that does not rise to the level of an operational impact. 5 Consequences of loss of control is not discernible, which is characterized by having no visible or recognizable impact on the organization. Firearms (duty or training) Munitions or Explosives Destructive Devices Vehicles Software Secure Communications, Desktop/Laptop Secure Radios Equipment with Retainable Memory Stun Guns, Tasers not encrypted: Personal Computing Devices (i.e., PDA, Blackberry, etc) Cameras Portable, Easily Convertible to Private-use and/or High Potential for Theft: Tools, Satellite Phones Televisions, VCR/DVD, Projectors, Small Office Machines ASTM Description Examples Minimum: End of Life Control for monitors, copiers, fax, scanner, printer and other peripherals where improper disposal could result in hazardous materials being released into the environment or consider classifying as ECC-3. 22 Business Process Modeling • graphical representation for specifying business processes in a business process model • Cross Functional Flowcharting 23 No requirement to check Surplus before ordering new Review Quote, RFP if necessary, Selects Source Numbers Purchase Orders Send to Vendor Vendor Business Division Requestor selects proper object code Treasury Enter Purchase Request Ships Assets Accounts Payable Responsible Scan Invoice into Document Capture Logistics Department Requestor or Designated Purchaser Current Procurement and Receiving Process Physically Receives Assets Tags Asset and Completes Inventory Control Form Capital Assets Not Systematically Recognized on Financial Statements Approval Workflow Budget Check Mail Invoice Enter Invoice into Sungard A/P Send Form to Treasury Treasury files Inventory Control Form Pays Vendor Send Copies of Form to Business Division Title I Days or Weeks Deliver Assets to Requestor Business Division or Requestor Receives into Sungard to authorize payment 24 System Interface Diagram • Document all Related Systems – – – – – – – Procurement Purchasing Fixed Asset Accounting Facilities Work Orders IT Help Desk IT Auto Discovery CAFM • Existing Interfaces 25 Computer Altiris queries AD for user and computer info. Collects Hardware and Software Information from computers and users on network Computer Current Altiris Client Mgmt Suite Active Directory Centralized Data on Network Access, Logins, Passwords, End Users and Departments Computer Altiris Service Desk Logs and Tracks Calls, Generates and Updates Tickets to add/change hardware/software Teamworks Solution Sungard Facilities Work Order Purchasing/AP Procurement thru Accts Payable TPS Fueling Log Collects User, Dept, Location Fueled and Date FleetPro Fleet Mgmnt, parts inventory, procure supplies, and charge back labor costs End User Fixed Asset Module Receiving to Disposition Fuelman Collects User, Dept, Location Fueled and Date Treasury Spreadsheet Risk Management Spreadsheet Manual Excel spreadsheet for Financial Statements Title I Inventory Control Forms Manual Excel spreadsheet Manual Excel spreadsheet for Vehicles 26 Delivery Future State • Review Legal/Regulatory Requirements • Compare to Best Practices • Compare to Voluntary Consensus Standards like ASTM • Propose Alternatives • Analyze Cost/Benefits • Document New/Changed Processes 27 Check Surplus before ordering Requestor selects proper object code Numbers Purchase Orders Send to Vendor Vendor Review Quote, RFP if necessary, Selects Source Ships Assets Scan Invoice into Document Capture Logistics Physically Receives Assets Tags Asset and Collects Data in Handheld Approval Workflow Budget Check Accounts Payable Business Division Enter Purchase Request Treasury Requestor or Designated Purchaser Proposed Procurement and Receiving Process Mail Invoice Upload Data to Handheld Spreadsheet/ Database Enter Invoice into Sungard A/P Receive Assets to Authorize Payment in Sungard (Enter Tag No) Handheld Spreadsheet/ Database Pays Vendor Deliver Assets to Requestor Unload Data from Sungard to Handheld Spreadsheet/ Database Generates Financial “Skeleton” Records In Sungard Fixed Asset 28 Update Sungard Fixed Asset with Physical Data Sungard Fixed Assets Export Last Inventory Date Computer Altiris Client Mgmt Suite Altiris queries AD for user and computer info. Collects Hardware and Software Information from computers and users on network Computer Active Directory Centralized Data on Network Access, Logins, Passwords, End Users and Departments Computer Altiris Service Desk Logs and Tracks Calls, Generates and Updates Tickets to add/change hardware/software Teamworks Solution Sungard Facilities Work Order Purchasing/AP Procurement thru Accts Payable TPS Fueling Log Collects User, Dept, Location Fueled and Date FleetPro Export Last Fueled Date Fixed Asset Module Receiving to Disposition Download Assets, Upload Inventory Data Upload Receivng Data Handheld Interface Treasury Capital Asset Listing for Financial Statements Title I Asset Listing Fleet Mgmnt, parts inventory, procure supplies, and charge back labor costs Fuelman Collects User, Dept, Location Fueled and Date Risk Management Spreadsheet Manual Excel spreadsheet for Vehicles 29 Proposed Delivery Analyze Impact on Organization • • • • • • Changes to Roles and Responsibilities New Staffing Job Descriptions Employee Performance Objectives Communications Training 30 Implementation Roadmap • Present Study to Steering Committee and SME • Keep SME’s Involved and Informed -- Part of the Solution, Organizational Buy-In • Develop Phased Implementation Approach -- baby steps • Determine New Systems and Interface Requirements • Obtain Approvals • Document New Policies/Procedural Documentation • Create Change Management/Communication Plan – Communicate New Roles/Responsibilities – Design and Provide Multiple Training Opportunities 31 Monitor • Maintain User Groups to Solicit Feedback and Refine Processes • Determine and Track Performance Metrics – Loss Rate by Number and Value – Overage/Shortage Rates by Number and Value • Investigate Lost, Damaged or Destroyed Assets – Establish Independent Review Committee to investigate and recommend action 32 Adjust • • • • Review Re-evaluate Refine Re-train 33 Questions Marla Williams, CPPM President Integrated Asset Management, Inc. marla@weinventoryassets.com (800) 731-9569 Severna Park, Maryland and President, Federal Center Chapter 34