Morphology
advertisement

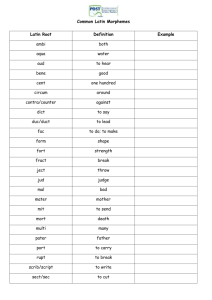
Morphology The Structure of Words Morphemes • Defined as, “a minimal unit of meaning” • Not the same as a syllable, which is a unit of sound (e.g., tuxedo has one morpheme and three syllables, while sixths has three morphemes and one syllable) • Not the same as a word, although a word can contain only one morpheme (e.g., tree, tuxedo) • Some morphemes are bound, meaning they can only appear attached to some other morpheme (e.g., -s, -ly, -un). Free morphemes can appear by themselves as words Allomorphs • Defined as “a variant of morpheme;” variant can be in pronunciation and/or spelling • Examples: – – – – Hymn, hymnal -ible, -able, gullible/gullibility, usable Electric/electricity Condemn/condemnation Inflectional vs. Derivational Morphology • Derivational Morphemes form new words, often changing the word class (part of speech) - E.g., bake/baker, legal/legalize • Inflectional Morphemes make a different form of the same word, such as plural or past tense. The eight inflectional morphemes in English will be shown on the next slide. English Inflectional Morphemes • On Nouns: – Plural – Possessive -s -’s • On Verbs: – – – – 3rd person singular present tense Past tense Part participle Present participle -s -ed -en -ing • On Adjectives: – Comparative – Superlative -er -est Types of Morphology • Affixation - adding an affix (prefix or suffix) to a root (e.g., en-list-ed) • Compounding - combining two or more roots in a single word (e.g., eggplant, greenhouse) • Internal Change - changing part of the root (e.g., sit/sat, foot/feet, mouse/mice) • Suppletion - changing the root completely (e.g., good/better, is/am) • Zero-Change - changing nothing (e.g., fish/fish, hit/hit) Some Adjective Affixes GENERAL ADJECTIVE SUFFIXES -al normal -an urban -ane urbane -ant pliant -ar solar -ary customary -ate ornate -ent fluent -ic phonic -id fluid -ile senile -ine saline -it implicit -ite definite -ive active -ory savory -ose comatose -ous anxious -y hefty -some handsome -ful peaceful -ward backward -able fixable -ly -like SIMULATIVE ADJECTIVE SUFFIXES manly -oid asteroid, humanoid egglike -ish sixish, boyish Some Noun Affixes -a -i -m -on -um alga fungi poem carbon album GENERAL -ae algae -ice notice -men specimen -ory accessory -ure fracture -em -in -ment -t -us ABSTRACT -age damage -dom wisdom -em problem -hood manhood -ion action -is basis -ship friendship -th width -y democracy emblem toxin pigment cult fungus -e -ine -ness -tude importance saline kindness magnitude Some More Noun Affixes -an -ast -eer -ine -or -ster -ess -ix -ary -ory -orium AGENTIVE physician -ant assistant gymnast -ate delegate auctioneer -ent president libertine -ist dentist actor -t poet jokester -eroo stinkeroo -ar -e -er -ite -yer templar misanthrope astrologer Israelite lawyer FEMINI NE AGENTIVE poetess -ette usherette aviatrix -a alumna LOCATIVE granary -arium dormitory -ery auditorium -eria planetarium cemetery cafeteria Still More Noun Affixes -ee -endum -andum -cle -ette -il -let -y PATIENTIVE SUFFIXES employee -acle spectacle agendum -end dividend, reverend memorandum -and multiplicand DIMINUTIVE muscle -cule molecule cigarette -icle particle pupil -isk asterisk piglet -ling gosling baby -el -ie -le -ule morsel doggie candle capsule Some Verb and Negative Affixes be-ize -(i)fy CAUSATIVE befriend en- encode legal -ate liberate beautify re- aantidisinnon- apathetic antipathy dishonest inhuman nonsense ITERATIVE redo NEGATIVE ananemic dedefoliate imimpossible -less careless unundo Word Classes (Parts of Speech) • Form Class Words – Also known as “Content Words” and “Open Class Words” – Have Semantic Content – Nouns, Verbs, Adjectives, and Adverbs • Structure Class Words – Also know as “Function Words” and “Closed Class Words” – Have a Grammatical Function – Pronouns, Articles, Prepositions, Auxiliaries…