Third Marking Period Social Studies Learning Guide Vocabulary
advertisement

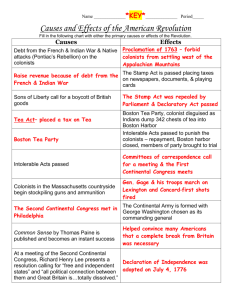
Third Marking Period Social Studies Learning Guide Vocabulary Leader – the person who directs or controls a group, organization, or country Parliament - a group of leaders that govern England Tax - money that you must pay to the government according to your income, property, goods, etc. that is used for public services Revolution - fighting for a change in government Nation – a country Independence – freedom from another country’s control – the ability to make your own decisions in life without having to ask others for permission, help, or money Surrender – to say officially that you want to stop fighting because you realize you cannot win Treaty - a formal, written agreement between two countries or governments Events to Know: French and Indian War - The French and Indian War began in 1754. The war was not between the French and Indians. Instead, the conflict was between the British and the French. Native Americans played a role in the war because they fought for both the British and the French. Why would the British and the French fight? The French Explorers came through North America looking for a shortcut to Asia. This would allow for faster trading. The explorers began to claim land for France. Eventually, the French owned more land in American than the English owned. The difference was the English had more people living in the colonies. The English did not want the French to own land in America. The fighting began and lasted for seven years. The English won the war, which lasted seven years. As a result of the war, the French owned land north of the United States now known as Canada. Proclamation of 1763 – The Proclamation of 1763 closed lands north and west of the Appalachian Mountains to settlement. The goal of the British was to put a stop to conflicts that had arisen between the Native Americans and the colonists due to the French and Indian War. Stamp Act – The Stamp Act was the first direct British tax on American colonists. Every newspaper, pamphlet, and other public and legal document had to have a Stamp, or British seal, on it. The Stamp cost money, and the colonists didn't think they should have to pay for something they had been doing for free for many years. Tea Act – The Tea Act kept the tax on tea in place. The act also gave one British company control of all the tea trade, threatening the business of American tea merchants. Quartering Act – The Quartering Act was a law that required colonists to provide housing, candles, bedding, and beverages to British soldiers stationed in the colonies. Boston Massacre – A small group of colonists in Boston were taking out their frustration with the British troops stationed in Boston by taunting and throwing snowballs at the soldiers. In retaliation, these soldiers opened fire, killing four of the Bostonians. Boston Tea Party - In 1773, a group of colonists, angered by the Tea Act, disguised themselves as Native Americans and boarded a British ship in Boston Harbor. They dumped 343 crates of valuable tea into the harbor. Intolerable Acts – In response to the Boston Tea Party, the British closed Boston Harbor and forced colonists to house and feed British soldiers. Lexington and Concord - The war began here when British soldiers and the colonists exchanged fire. Battle of Bunker Hill - Battle of Bunker Hill, which actually took place on Breed’s Hill, was won by the British. It was not a huge lose to the Americans, because although they actually lost the battle many British soldiers were injured or killed during the fight. It also showed that the less experienced Continental Army was willing and able to stand up again more highly trained British forces. Meeting of Continental Congress - After the Boston Tea Party, the 13 colonies held a meeting in Philadelphia to talk about creating a new country where people rule themselves. They sent a letter to King George III. This meeting was called the Continental Congress. o Other meetings that followed were: Sept. 1774 - 1st meeting – A group of colonial leaders, called the First Continental Congress met in Philadelphia. They wrote angry letters to the king and parliament. May 1775 – 2nd meeting – Washington named Commander-in-Chief July 4, 1776 – 3rd meeting – The Declaration of Independence was signed Declaration of Independence – A document that said “All men are created equal.” Signed on July 4, 1776. Everyone had the right to life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness. The main writer was Thomas Jefferson. John Hancock signed his name extra large so King George III could read it without his glasses. Also, it was dangerous to sign this document, because signing the document was considered treason. Washington crossing the Delaware River (Battle of Trenton) - Washington’s troops crossed the Delaware River and surprised the British at Trenton, NJ, giving the Continental Army its first major victory. Battle of Saratoga - Americans beat the British. France enters the war to aid the Americans. The Battle of Saratoga is considered a turning point of the Revolutionary War, because the battle shows the American’s ability to fight and win. France joined the colonists fight against the British as a result of this battle. Encampment at Valley Forge - Washington’s troops spend a cold winter camped at Valley Forge, PA. The conditions of Valley Forge were poor. Soldiers had little food, shelter, clothing, shoes, etc. Battle of Yorktown - British General Cornwallis surrenders to General Washington at Yorktown, VA. Battle of Yorktown is known as the last big battle of Revolutionary War. The Treaty of Paris was signed as a result of this battle. Treaty of Paris - An agreement signed by representatives of the US and British governments, officially ending the Revolutionary War. The Treaty of Paris guaranteed peace between British and Americans. Following the treaty, the colonies were a new nation, the United States of America. People/Groups to Know: George Washington - The Commander-in-Chief of the American army. He was a great leader. Soldiers called him General Washington. He was fair to the soldiers, lost many battles, but never gave up. He later became our first president. John Adams - A representative from Massachusetts who recommended Washington for commander of the American forces in the Continental Army. He was a member of the Sons of Liberty. John Hancock – He served as president of the Continental Congress from 1775 to 1777. As president, he was the first to sign in HUGE print the Declaration of Independence adopted by the Congress. He wanted his name to be clearly read by King George III. Thomas Jefferson - He had a leading role in the Continental Congress and American’s movement toward independence and wrote the Declaration of Independence. Ben Franklin – He helped write the Declaration of Independence. Ben went to Paris, France, and asked the French king to help the Americans. King Louis said he would give him clothing, soldiers, guns and ships because France wants them to beat England. General Cornwallis – He led the British army throughout the American Revolution. A British General who surrendered to General Washington at Yorktown, Virginia. Known for the Battle of Yorktown when the British decided to strike southern colonies. Washington rushed his army south. French ships blockaded the British and kept them from escaping. Baron von Steuben - He came from Germany to help Americans fight and specifically to train the soldiers. He taught Americans how to become better soldiers. Thomas Paine – Thomas Paine began working on the cause of independence. He published a pamphlet, Common Sense, which demanded complete independence from England. George Washington, Thomas Jefferson and other colonial leaders read the pamphlet and it became the most widely circulated pamphlet in American history at that time. Hessians - German soldiers hired by the British to fight the Americans. Minutemen - Minutemen were colonists/farmers (in Massachusetts) who trained themselves to be soldiers and promised to be ready to fight at a minute’s notice. Paul Revere – Patriot rider who warned that “The Redcoats are coming.” Sons of Liberty – Secret group that instigated the Boston Tea Party and other acts of rebellion. King George III – British King who taxed the colonists unfairly. Parliament – British government officials who made decisions about taxes. There were no colonial representatives in Parliament from colonies. Sides of the Revolution o Loyalists – loyal to the British King o Patriots – Fought for colonists independence from the British o Undecided or no side – People who were undecided and did not side with the loyalist or patriots