Earth Science First Semester Final Exam Study Guide
advertisement

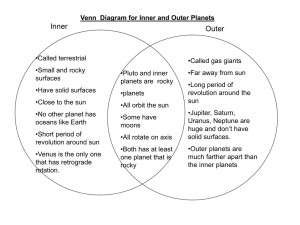
Name: Period: Earth Science First Semester Final Exam Study Guide 1. What is created at mid-ocean ridges? What type of plate boundary do these occur at? 2. What happens at subduction zones? What 3. Describe the relationship between the mid-ocean ridge and the age of sea floor rocks. (As you move away from the ridge what happens to the age of the rocks?) 4. What is geothermal energy? 5. Why does California have lots of geothermal energy? 6. Complete the table below. Plate Boundary Transform fault Convergent Divergent Movement of Plates Geologic Formations Created 1. At what type of plate boundary are trenches formed? What type of Earth’s crust is involved? 2. What was Wegener’s main evidence for continental drift? 3. What aspect of continental drift was Wegener unable to explain? 4. What is the San Andreas Fault? Which direction are the plates moving? 5. What is a tectonic plate? 6. How does plate density affect convergent boundaries? 7. Describe the difference between a theory and a hypothesis. 8. How is the inner core of earth different from the outer core? 9. What caused the earth to have different layers? 10. What caused earth to be very hot when it first formed? 11. What are the 5 inner layers of the earth? (Start with the lithosphere.) 12. What are convection currents and what layer of the Earth are they found? How do they relate to plate tectonics? 13. Describe the differences between rock that makes up with lithosphere and the asthenosphere. 14. Name the planets in order. Circle the inner planets. Put a box around the outer planets. 15. Fill in the ‘differences and similarities between the inner and outer planets’ table. (For most, just circle the correct response.) Planet Fact Moon #? Thickness of atmosphere? Time of formation? Volcanoes? Rings? Rate of rotation? Rate of revolution? Planet composition? Planet core? Other names for the planets? Density of planets? Inner Planets Many/ Few Thick/ Thin Outer Planets Many/ Few Thick/ Thin Present/ Not present Present/ Not present Slow/ Fast Long/ Short Rocky/ Gaseous Present/ Not present Present/ Not present Present/ Not present Slow/ Fast Long/ Short Rocky/ Gaseous Present/ Not present More dense/ Less dense More dense/ Less dense 16. The age of Earth’s moon led to the discovery of the age of our __________ ___________. 17. What is a nebula? 18. What is the nebular theory? 19. Draw the Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram. What is on the X-axis? The y-axis? What is plotted on the diagram? Where are the four groups of stars located? (Main sequence, white dwarf, red giant, and super giant.) 20. What is type of star is our sun? 21. How do stars generate energy? 22. What is the source of fuel for the sun? What is created in the process of hydrogen fusion? 23. How is the life cycle of a low mass different from a high mass stars? 24. What are the first three stages of a star’s life? 25. All stars begin as a ______________. 26. What is the main sequence stage of a star’s life? 27. How are different elements created in the cores of stars? 28. What are impact craters? How do they form? 29. What are constellations? 30. What is a galaxy? 31. Draw a picture of each type of galaxy. Galaxy Type Drawing 32. What type of galaxy is the Milky Way galaxy? 33. How big across is Milky Way in light years? 34. From earth, what tools can be used to differentiate stars from planets? 35. What is a spectroscope and why is it used?