Earth Science Study Guide Semester 2 Exam
advertisement
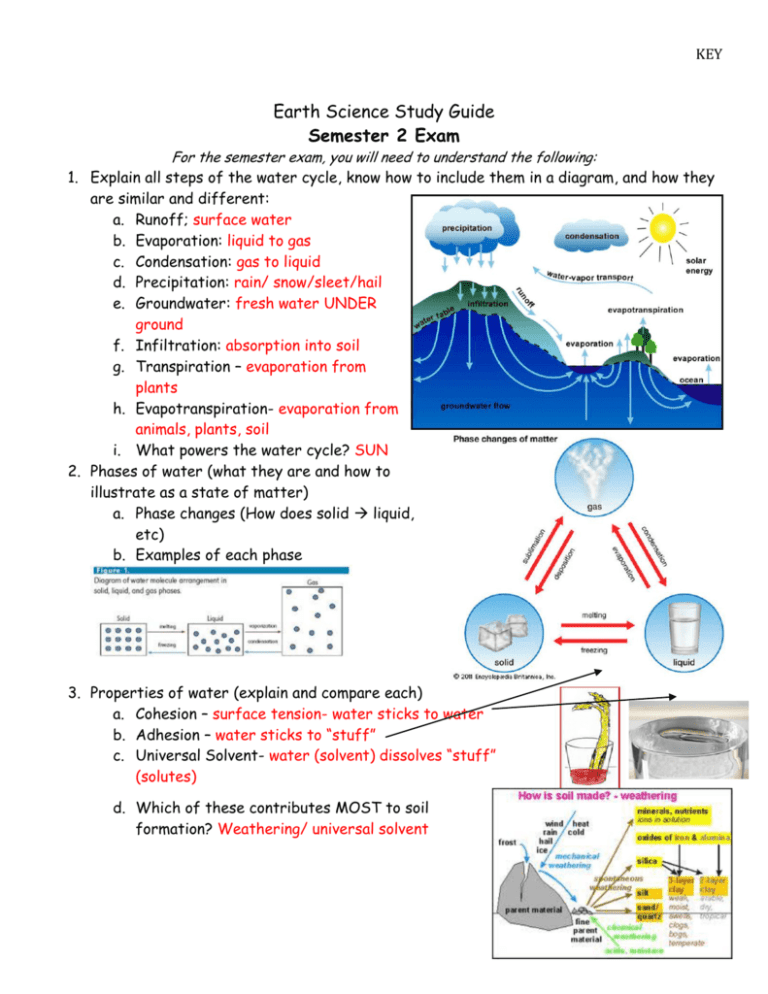
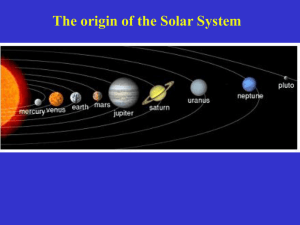
KEY Earth Science Study Guide Semester 2 Exam For the semester exam, you will need to understand the following: 1. Explain all steps of the water cycle, know how to include them in a diagram, and how they are similar and different: a. Runoff; surface water b. Evaporation: liquid to gas c. Condensation: gas to liquid d. Precipitation: rain/ snow/sleet/hail e. Groundwater: fresh water UNDER ground f. Infiltration: absorption into soil g. Transpiration – evaporation from plants h. Evapotranspiration- evaporation from animals, plants, soil i. What powers the water cycle? SUN 2. Phases of water (what they are and how to illustrate as a state of matter) a. Phase changes (How does solid liquid, etc) b. Examples of each phase 3. Properties of water (explain and compare each) a. Cohesion – surface tension- water sticks to water b. Adhesion – water sticks to “stuff” c. Universal Solvent- water (solvent) dissolves “stuff” (solutes) d. Which of these contributes MOST to soil formation? Weathering/ universal solvent 4. Where freshwater/saltwater is found naturally on Earth? Glaciers – frozen, unacessable; Ocean 5. How to conserve H2O? use less water – examples? 6. What is meteorology? study of the atmosphere and weather 7. Types of thermal (HEAT) energy? a. Radiation :Sun b. Convection: circulation (less dense- rise, more dense- sink) Created by UNEQUAL heating c. Conduction: Direct contact (touch) d. How does most thermal energy move in the atmosphere? Illustrate! Moves through convection 8. Layers of the atmosphere? a. How are they divided? Changes in temperature trends: decrease, increase, decrease, increase b. Draw the temperature trends graph from textbook/notes & know how to read it! c. How many main layers? 4 What happens in each layer with temperature and pressure? Temperature varies, pressure decreases d. Most dense layer? Troposphere Least dense layer? Thermosphere e. % and types of gases in the Troposphere? See graph above 9. Greenhouse Gases a. Identify 4 major gases? 1. Water vapor H20 (Naturally occuring on Earth) 2. Carbon dioxide CO23. Methane CH4 4. Nitrous oxide NO2 (#2, 3 & 4 affected by humans) b. Explain what a GG is? Gases that hold on to or absorb energy ;Responsible for regulating the temperatures in the troposphere c. What happens if GG increase? Global temperatures could increase Decrease? Global temperatures could decrease 10. Meteorology a) Explain. – study of weather and the atmosphere b) Difference between weather and climate? Weather is the current conditions of a specific location at a specific time; climate is the average precipitation and temperature over many years. c) What are clouds composed of at low altitudes? Liquid droplets High altitudes? Ice crystals d) What happens to cold air at the poles? Cold air is more dense so - it sinks e) What type of weather does an increase in air pressure lead to? Stormy; low pressure Decrease in air pressure? Fair; high pressure f) What is barometric pressure? Atmosphere (air) pressure g) Mountain v Valley weather—compare/contrast. (Think--Mt Charleston v Las Vegas) Warm Rises Cool Sinks Valley breeze Mountain breeze 11. Weather Tools a. Explain/understand how they work/know what they look like: i. Barometer : ii. Thermometer : measures the average movement of air molecules iii. iv. v. Anemometer: Measures wind speed Wind Sock; Measures wind direction Psychrometer: measures relative humidity and dew point (moisture in the air) vi. Rain Gauge; measure the amount of precipitation b. How to use this chart? 1. Measure the dry bulb (air temp) 2. Measure evaporation, the wet bulb 3. Take the difference between the dry and wet bulb 3. Line up the dry bulb and the difference. Use like you would a multiplication table. Dry bulb = 15°F Wet bulb = 12°F What’s the answer? Air temp . (F) 0 5 10 15 0 1 2 3 67 73 78 82 33 1 46 20 56 34 13 64 46 29 4 6 12. Weather Maps a. Know the symbols for following fronts? i. Cold, Warm, Occluded, Stationary b. Why weather maps are used/compared daily? To predict weather; compared to calculate how fast fronts are moving. c. How to create a station model? 13. NV Topography a. Rain Shadow Effect—How does topography create this? Windward = wet Leeward = Desert/ dry b. Type of NV topography? ___Basin_____and____Range______ 14. Air Masses a. What do c & m stand for? M= wet C= dry b. What do p & t stand for? P = polar t= tropical c. Where are they found on a map? d. Which would affect Vegas the most? mP, Mt, Ct Dry/ Cold Seasonal Rainy/ warm Seasonal 15. Climates a. Latitude Zones (3 types) Tropical, Dry/ Cold Temperate, Polar i. typical weather in those regions? ii. know where to find them on a map with latitude given? b. What does knowing the climate of a region allow a person to do? Plan ahead 16. Seasons a. What are the four seasons? Northern Hemisphere #1 Winter solstice #2 Vernal Equinox (spring) #3 Summer Solstice #4 Autumal Equinox (Fall) b. What causes seasons? Earth’s tilt 23.5o c. Label and describe the objects & seasons for both the Northern & Southern Hemispheres on the diagram below. ( Southern Hemisphere is opposite) Tilt towards Summer N.H. Tilt away Winter S.H. 17. Astronomy a. Planets— i. What are they? Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn , Uranus, Neptune ii. How many? 8 iii. Compare/Contrast each. INNER PLANET = TERRESTRIAL (ROCKY) Small diameter Few moons No rings Less gravity Faster period of revolution iv. v. vi. vii. OUTER PLANETS = JOVIAN, GAS GIANTS Larger diameter Many moons All 4 have rings Strong gravity, More dense Longer period of revolution Tilts? What comes as a result? Earth’s tilt( 23.5º causes Seasons Atmospheres? Venus has very thick CO2 atmosphere = greenhouse effect, that is why it’s so hot. Rings/no rings? See compare contrast Compositions of planets? See compare/ contrast b. Units for measurement in space? Which is for largest distances; which is for smaller? Light Year - Distance light can travel in one year; used in our galaxy and beyond. Astronomical Unit (AU) - Distance between the Sun and Earth; only used in our solar system. a. Solar System i. What objects are included in it? Planets, asteroids, meteoroids, comets How many stars exist? one, SUN ii. Where is OUR solar system located within the Galaxy? On one of the outer arms b. Galaxies i. What galaxy are we in? Milky Way ii. Explain each TYPE of galaxy? (3 types) Spiral – Milky way, Old stars near center bulge, new stars in arms Elliptical –mostly old stars Irregular – when two galaxies collide iii. Components of a galaxy (disc/bulge/arms/halo/etc)? Where are these? Disc/ bulge/ halo contain old stars; arms contain newer stars (sun) iv. How many galaxies are there in the universe? Trillions – limted only by our ability to count them v. How many galaxies are there in our solar system? zero vi. How many stars in a galaxy? trillions c. Moons i. What happens to moons as planets get bigger? WHY? More due to the stronger gravitational pull ii. Phases of the Moon? Waxing = light on right, moon grows bright Wanning = light gets smaller on the left 1. Why do they happen? From Earth we only see one side 2. How do eclipses form during the phases? Be able to illustrate. Solar Eclipse, new moon phase Lunar Eclipse, full moon iii. How the Moon formed? By a possible collision when Earth was forming. iv. Why do we only ALWAYS see one side of the Moon? The rotation and revolution are the same. v. Period of Rotation v Revolution Rotation is spinning on its axis; Revolution is the orbit around something else - for our solar system - the Sun d. Other objects in the solar system i. Comets/Asteroids/ Meteoroids—Know and be able to compare/contrast each! All orbit the Sun, asteroids (large) and meteoroids (small) are rocky. Comets are made of rocky icy material with a tail that points away from the Sun. Very long revolutionary periods e. Rotation v Revolution: Compare/Contrast the terms (see above) All Planets revolve counterclockwise around the Sun. All rotate counterclockwise with the exception of Venus and Uranus. Revolutionary periods increase with further planets. Outer planets have shorter days than inner planets.