File
advertisement

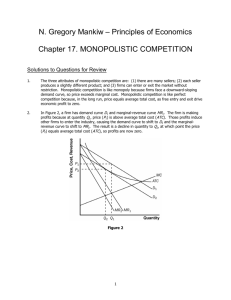
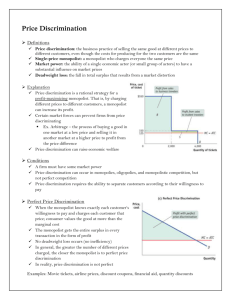
AP Micro Unit 3 Name _________________________________________- Chapter 13 – Costs of Production Profit = ___________+ ___________ Explicit Costs Implicit Costs Accounting Profit = ________ - ________ Economic Profit = ________ - ________ Production Function Marginal Product (include equation & graph) Diminishing Marginal Product A. Definition B. Reason why it occurs Marginal Cost (include equation & graph) Total Costs = ________ +_________ Variable Costs Fixed Costs ATC = AFC = AVC = Efficient Scale Relationship between Marginal Costs and Marginal Product Costs in the Short Run vs Long Run Long Run Average Cost Curve (LRATC) Economies of Scale Constant Returns to Scale Diseconomies of Scale Minimum Efficient Scale for LRATC Economies of Scope (look up) Why is the ATC curve U-Shaped? MRP Definition & Formula – Chapter 14 – Perfect Competition Market Structure Characteristics (4) Characteristics of Pure/Perfect Competition Price Taker Marginal Revenue/MR (include equation) Total Revenue (TR) / Average Revenue (AR) Equations Why does MR = D = AR = P for competitive markets? Profit Maximizing Quantity is where _____=_______ Shutdown (and when do you choose this option) Exit (and when do you choose this option) Competitive Firm’s Short Run Supply Curve Sunk Costs Firm’s Long Run Supply Curve When do new firms enter a competitive market? Long run economic profit for competitive markets is _____ Productive Efficiency Allocative Efficiency Long Run Market Supply Curve for a Competitive Market Demand curve for Competitive Market Perfectly Competitive Labor Market Increasing Cost Industry Decreasing Cost Industry Chapter 15 – Monopolies Monopoly Barriers to Entry Natural Monopoly Fair Price Social Optimum Price Demand Curve for a Monopoly Price ___MR __MC for a Monopoly Why do monopolies produce deadweight loss? Price Discrimination 1st Degree (Perfect) Price Discrimination 2nd Degree Price Discrimination 3rd Degree Price Discrimination Why & how do governments regulate natural monopolies? Monopsony Bilateral Monopoly Chapter 16 – Monopolistic Competition Demand curve for firms in monopolistic competition? Long run economic profits for firms in monopolistic comp? Market Niche Why is differentiation important for firms in monopolistic comp? Real Product Differentiation Perceived Product Differentiation Why is long run economic profits = zero from firms in monopolistic comp? Excess Capacity Markup over Marginal Costs Chapter 17 - Oligopolies Concentration Ratio Oligopoly Cartels Why do legal cartels seek out government regulation? Horizontal Mergers / Vertical Mergers Collusion Collusive vs non-collusive Oligopolies Price Leadership Game Theory Nash Equilibrium Payoff Matrix Prisoner’s Dilemma Be Able to Graph MP MC Total Cost Curves (TC, FC, VC) Average Cost Curves Perfect Comp 1. 2. 3. 4. SR Profit SR loss (stay in biz) SR loss (shutdown) Long Run adjustment for all a. Inc. Cost b. Dec Cost c. Constant Cost Perfectly Competitive Labor Market Monopoly Natural Monopoly Perfect Price discrimination Monopsony Monopsony w/ min. wage Monopolistic SR & LR 1. Profit 2. Loss