MATH 1410/6.3 and 6.4pp
advertisement

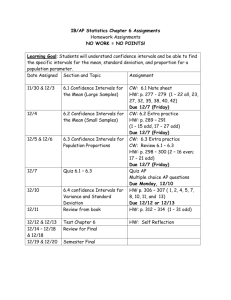
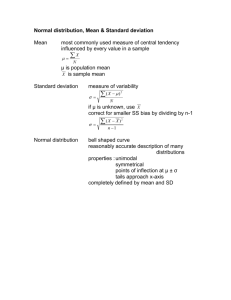
Section 6.3 Confidence Intervals for Population Proportions Point Estimate for Proportions The Population Proportion is called p The Point Estimate is the sample proportion is called “p hat” To find the Margin of Error, E Confidence Intervals for the Population Proportion Construct a C.I. for the Proportion 1. Find n and x to find p-hat 2. Make sure the normal approximation is allowed 3. Find the critical value zc that corresponds with the given level of confidence. 4. Find the margin of error, E. 5. Find the left and right endpoints and form the confidence interval. EX from p 325-326 14. In a survey of 4013 US adults, 722 say they have seen a ghost. Construct a 99% C.I. for the population proportion of US adults who have seen a ghost. 16. In a survey of 2303 US adults, 734 believe in UFOs. Construct a 90% C.I. for the population proportion of US adults who believe in UFOs. To find minimum sample size 20. You wish to estimate, with 95% confidence, the population proportion of US adults who say chocolate is their favorite ice cream flavor. Your estimate must be accurate within 5% of the population proportion. A) No preliminary estimate is available. Find the minimum sample size needed. B) Find the minimum sample size needed, using a prior study that found that 28% of US adults say that chocolate is their favorite ice cream flavor. C) Compare results from parts (A) and (B) Which Table do I use??? Confidence Interval for MEAN: If σ is known, use the Z table. If σ is unknown, consider the sample size n. If n > 30, use the Z table. If n < 30, use the T table. Confidence Interval for PROPORTION: Use the Z table. C.I. for VARIANCE or STANDARD DEVIATION: use CHI-Squared Table. Section 6.4 Confidence Intervals for Variance & Standard Deviation Point Estimates Population variance is σ2 The point estimate for variance is s2 Population standard deviation is σ The point estimate for standard deviation is s. The Chi-Square Distribution 2 (table #6) Chi-Square = X Use for sample sizes n > 1 All X2 > 0 Uses Degrees of Freedom: d.f. = n – 1 Area under the curve = 1 Chi-Square distributions are positively (or right) skewed. NOTE: The shaded area is to the RIGHT! Finding Critical Values for X2 X2R is the RIGHT hand critical value. To find this, use ½ of c as α on the table. X2L is the LEFT hand critical value. To find this, use the COMPLEMENT of ½ of c as α on the table. Keep in mind that X2L < X2R Find the critical values X2L & X2R 7. c = 0.95 n = 20 8. c = 0.80 n = 51 Confidence Interval for Variance Remember… intervals are always left to right, smaller to larger! To find Confidence Intervals 1. Verify the population has a normal distribution. 2. Find degrees of freedom: d.f. = n – 1 3. Find point estimate s2, use StatCrunch if needed. 4. Find critical values using chi-square table. 5. Find the left and right endpoints for the C.I. for the population VARIANCE. 6. Square root to find the left and right endpoints for the C.I. for the population STANDARD DEVIATION. Examples from p 334-5 10. The volumes (in fluid ounces) of the contents of 15 randomly selected bottles of cough syrup are listed. Construct a 90% C.I. for the population variance and the standard deviation. (Assume the population is normally distributed.) 4.211 4.264 4.269 4.241 4.260 4.293 4.189 4.248 4.220 4.239 4.253 4.209 4.300 4.256 4.290 18. A magazine includes a report on the prices of subcompact digital cameras. The article states that 11 randomly selected subcompact digital cameras have a sample standard deviation of $109. Assume the population is normally distributed. Construct a CI for the population variance and standard deviation using an 80% level of confidence.