Revision for Unit 2 Exam
advertisement

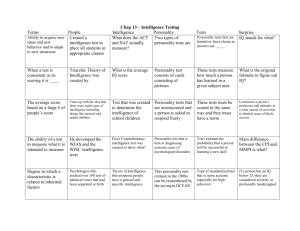
Revision for Unit 2 Exam 1. What are attitudes? Do they stay consistent over time? 2. Define Tri component Theory Affective Behavioural Cognitive 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. Do people’s attitudes and behaviours always match? What are the different self-reports involved in measuring an attitude Define stereotyping. Give an example. Define prejudice. Give an example – can it be positive or negative. Define discrimination. Give an example. What are the different factors that contribute to the development of prejudice? What are the factors reduce the development of prejudice. What was the aim of Zimbardo’s experiment? What research method did Zimbardo use? What type of sampling/allocation was used in Zimbardo’s experiment? When are people more likely to conform? Define social loafing. Give an example. Define the term role. Give an example of when you have used one. What did Milgram’s study demonstrate about obedience? Define de individuation. Give an example. Outline Bandura’s study on the aggression of children. What were the independent and dependent variables? What were the results of Bandura’s study? Understand the different perspectives. Psychodynamic Ethological Biological Define altruism, give an example. Define social norms. Give an example Define aggression, when is this regarded as bullying? How is an attitude acquired through classical conditioning? Give an example. How does this lead to lead to learning an attitude. What is a strength and limitation of the tri-component theory of intelligence? Explain. What are some strengths and limitations of collecting data on attitudes using questionnaires? Define sustained contact in regards to prejudice. Give an example. Define what a group is. What is the difference between a group and a clique? What are some of the different powers involved in Zimbardo’s prison experiments? Define status and social power. Explain how these effect people’s behaviour. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. What were some limitations of Zimbardo’s study? 32. What was Solomon Asch’s experiment on conformity? What were the results of this experiment? What factors affect Erica’s tendency to conform. 33. What is informational influence? Give an example 34. When are people more likely to copy other people’s behaviour? 35. Define the widely accepted view of intelligence. 36. What was Weschler’s theory of intelligence? In his terms what behaviour is needed to be intelligence? 37. Summarise Sternberg’s triarchic theory of intelligence. 38. What is involved in the Cattell-Horn-Carroll model of intelligence? What does it include? 39. Outline the Mayer and Salovey model of emotional intelligence. Define the different factors involved in this intelligence. 40. What is IQ and how is this measured? 41. What is the difference between validity and reliability? 42. Describe the difference between mean, median and mode. 43. What is the Weschler Adult Intelligence Scale? What does this test assess? 44. What are some of the different tasks involved when taking a WAIS? 45. Why do psychologists use this test, instead of some others? 46. What is Garner’s theory of multiple intelligences? What are some of his intelligences? 47. What are the different components involved in Mayer & Salovey’s model of emotional intelligence? 48. What are some strengths and limitations about the emotional intelligence model? 49. What are some intelligence tests, defined as culturally bias. 50. According to Roger’s what is self-actualisation. 51. What is the nature of personality? Do many people have exactly the same personality? 52. According to Freud what are defence mechanisms? 53. Define displacement, sublimation and denial. Give an example of each. 54. What are the three different stages of Freud’s psychodynamic theory of intelligence? Describe what happens at each stage. 55. Describe Gordon Allport’s theory of intelligence. How is it structured? 56. What is Costa and McCrae’s personality made up of? 57. What are some strengths and limitations of trait theories of personality? 58. What is Rodger’s theory of personality? How does someone become a happy and welladjusted person? 59. What is Holland’s Self Directed Search? Why is it used to measure personality? 60. What is the Thematic Apperception Test – what is it used for? 61. Look at the graphs of mean/median and mode. Make sure you understand the differences. 62. What are personality inventories? Why are they used? 63. What are some advantages and limitations of personality inventories? 64. What are the different ethics involved in studying intelligence. 65. What is the difference between qualitative and quantitative data, give an example. 66. What are the strengths and limitations of quantitative and qualitative data.