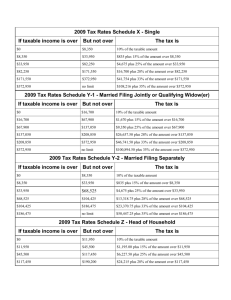
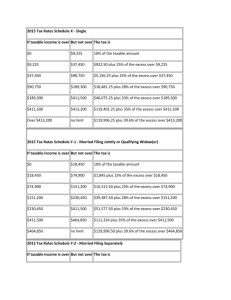
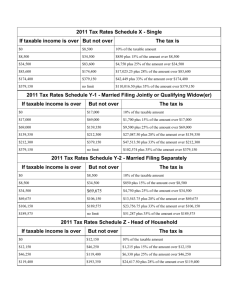
If you cannot use Form 1040EZ, you may be able to use Form 1040A if
advertisement

Chapter 4: Managing Taxes Objectives • Describe the two ways of paying taxes: payroll withholding and estimated taxes. • Identify the three steps involved in calculating federal income taxes. • Understand planning strategies to legally avoid overpayment of income taxes. • Explain the basics of IRS audits. Taxes on Purchases • State and local taxes are added to the purchase price of goods. • Excise tax is imposed on specific goods and services • • • • • • Gasoline Cigarettes Alcohol Tires Air travel Telephone service Taxes on Property • Real estate property tax is based on the value of land and buildings. • Personal property taxes on the value of automobiles, boats, furniture, and farm equipment are imposed in some areas. Administration/Classification of Income Taxes • Federal tax laws • Marginal tax rate • Progressive nature of income tax • Effective marginal tax rate • Regressive • Average tax rate New Math Taxes on Wealth • Estate tax-federal tax imposed on the value of an individual’s property at the time of death. • Inheritance tax-state tax levied on the value of property bequeathed by a deceased individual. 3 Steps in Determining Taxes 1. Determining Adjusted Gross Income 2. Computing Taxable Income 3. Calculating Taxes Owed What is Tax Management? ATTENTION! A PLANNING PROCESS FOR TAX: • Reduction • Deferment • Elimination Total Income Tax Bracket Federal Income Tax Bracket + State Income Tax Bracket (Federal Income Tax Bracket x State Income Tax Bracket) Example: Mike’s federal income tax bracket is 28% and his state income tax bracket is 7%. What is Mike’s total income tax bracket? 28% + 7% - (28%x7%) = .28+.07 - (.28 x .07) = .35 - .0196 = .33 or 33% Step 1: Determining Adjusted Gross Income (AGI) Earned Income-money received by personal effort. Investment Income-money received in the form of dividends, interest, or rent Passive Income-activities in which you do not actively participate. Other Income-Alimony, awards, lottery winning, prizes Other Items That Impact Income Exclusion-amount not included in gross income. Tax Exempt Income-another name for exclusions-Qualified scholarships and fellowships where money is used for tuition, fees, supplies, and equipment, VA payments Tax Deferred Income-income that will be taxed at a later date Adjusted Gross Income (AGI)-gross income after certain reductions have been made Tax Shelters-immediate tax benefits and a reasonable expectation of a future financial return (IRA’s Keogh’s) Taxes on Earnings • Social Security • Income Tax • Federal tax • State tax in all but 7 states • • • • • • • Alaska Florida Nevada South Dakota Texas Washington Wyoming 2014 Federal Tax Rate Schedules Single If taxable income is over— but not over— the tax is: $0 $9,075 10% of the amount over $0 $9,075 $36,900 $907.50 plus 15% of the amount over $9,075 $36,900 $89,350 $5,081.25 plus 25% of the amount over $36,900 $89,350 $186,350 $18,193.75 plus 28% of the amount over $89,350 $186,350 $405,100 $45,353.75 plus 33% of the amount over $186,350 $405,100 $406,750 $117,541.25 plus 35% of the amount over $405,100 $406,750 no limit $118,118.75 plus 39.6% of the amount over $406,750 The Marginal Tax Rate Affects Your Final Decision $3,950 personal exemption is not taxed $6,200 standard deduction is not taxed Next $9,075 of income is taxed at 10% Remaining $42,950 of income is taxed at 25% Next $27,825 of income is taxed at 15% 0 + 0 + $835.00 + $3,840.00 + $4,175 Gross Income = $90,000 Taxable Income = $79,850 Taxes = $15,819 Marginal Tax Rate = 25% Average Tax Rate = 19.8% (Taxes Paid / Taxable Income) How We Pay Taxes Eight Steps in Calculating Your Income Taxes Step 1 Total Income Step 2 Gross Income Step 3 Adjusted Gross Income Step 4 Subtotal Step 5 Taxable Income Subtract exclusions Subtract adjustments to income. Subtract standard deduction or total itemized deductions. Subtract value of exemptions Step 6 Apply tax table or tax-rate schedule to determine liability. Step 7 Final tax liability Step 8 Calculate balance owed or refund. Subtract tax credits Step 2: Computing Taxable Income Deduction-an amount subtracted from AGI to arrive at taxable income. • Standard deduction ($6,200/single in 2014) • Itemized deduction Exemption-a deduction from AGI for yourself, your spouse, and qualified dependents ($3,950 in 2014) Step 3: Calculating Taxes Owed • Use your taxable income in conjunction with the appropriate tax table or tax schedule. • Marginal tax rate-the tax on the last dollar of income. • Average tax rate-total tax due divided ty your taxable income. • Tax credit-amounts subtracted from the amount of tax owed. Who Should File a Tax Return? STUDENTS WITH: • Earned income • Unearned income • Transfer payments Which Tax Form Should I Use? Form 1040EZ is the simplest form to fill out. You may use Form 1040EZ if you meet all the following conditions: 1.Your filing status is single or married filing jointly 2.You claim no dependents 3.You, and your spouse if filing a joint return, were under age 65 on January 1, 2015, and not blind at the end of 2014 4.You have only wages, salaries, tips, taxable scholarship and fellowship grants, unemployment compensation, or Alaska Permanent Fund dividends, and your taxable interest was not over $1,500 5.Your taxable income is less than $100,000 6.Your earned tips, if any, are included in boxes 5 and 7 of your Form W-2 7.You do not owe any household employment taxes on wages you paid to a household employee 8.You are not a debtor in a Chapter 11 bankruptcy case filed after October 16, 2005 9.You do not claim any adjustments to income 10.You do not claim any credits other than the earned income credit 11.Advance payments of the premium tax credit were not made for you, your spouse, or any individual you enrolled in coverage for whom no one else is claiming the personal exemption If you file Form 1040EZ, you cannot itemize deductions or claim any adjustments to income or tax credits (other than the earned income credit). Which Tax Form Should I Use? If you cannot use Form 1040EZ, you may be able to use Form 1040A if: Your income is only from wages, salaries, tips, taxable scholarships and fellowship grants, interest, ordinary dividends, capital gain distributions, pensions, annuities, IRAs, unemployment compensation, taxable Social Security or railroad retirement benefits, and Alaska Permanent Fund dividends Your taxable income is less than $100,000 You do not itemize deductions You did not have an alternative minimum tax adjustment on stock you acquired from the exercise of an incentive stock option Your only adjustments to income are the IRA deduction, the student loan interest deduction, the educator expenses deduction, the tuition and fees deduction, and The only credits you are claiming are the credit for child and dependent care expenses, the earned income credit, the credit for the elderly or the disabled, education credits, the child tax credit, the additional child tax credit, or the retirement savings contribution credit If line 43 (taxable Income) is And you are -- At least But less than Single Married Filing Jointly Married Filing Separately 26,000 26,050 3,450 2,996 3,450 Head of A HouseHold 3,256 26,050 26,100 3,458 3,004 3,458 3,264 26,100 26,150 3,465 3,011 3,465 3,271 26,150 26,200 3,473 3,019 3,473 3,279 26,200 26,250 3,480 3,026 3,480 3,286 26,250 26,300 3,488 3,034 3,488 3,294 26,300 26,350 3,495 3,041 3,495 3,301 26,350 26,400 3,503 3,049 3,503 3,309 Tax Credit Versus Tax Deduction • $100 tax credit reduces your taxes by $100 • $100 tax deduction reduces taxes by your tax bracket. For instance, if a person is in the 25% tax bracket it would reduce your taxes by 25% Is it Taxable Income? Is it Deductible? Is it Taxable Income? Yes No Is it Deductible? Lottery Winnings Life Insurance Premiums Child Support Received Cosmetic Surgery for Improved Looks Worker’s Compensation Benefits Fees for Traffic Violations Life Insurance Death Benefits Mileage for Driving to Volunteer Work Municipal Bond Interest Earnings An Attorney’s Fee for Preparing Will Bartering Income Income Tax Preparation Yes No Is it Taxable Income? Is it Deductible? Is it Taxable Income? Lottery Winnings Yes No Is it Deductible? x x Cosmetic Surgery for Improved Looks x Fees for Traffic Violations x x Worker’s Compensation Benefits X Life Insurance Death Benefits x Mileage for Driving to Volunteer Work Municipal Bond Interest Earnings x An Attorney’s Fee for Preparing Will x No Life Insurance Premiums Child Support Received Bartering Income Yes Income Tax Preparation x x x