Law 12 Foundations Codes and Codifications
advertisement

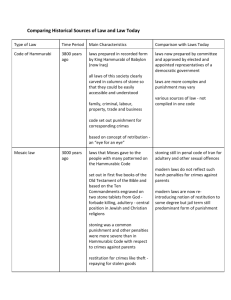
Early History of Codified Law • Code of Hammurabi • Mosaic Law • Justinian Code • Greek Early History of Codified Law • Code of Hammurabi • Earliest • Literally carved in stone • Categorisation: family, criminal, labour, property, trade, business. • Retribution • Established system of judges Early History of Codified Law • Mosaic Law • First give books of Old Testament, Ten Commandments • Literally carved in stone • Corporal/capital punishment • Retribution Early History of Codified Law • Justinian Code • Became basis for Western law traditions • Established profession of experts • Equity • Lives on in Napoleonic (French Civil) Code Early History of Codified Law • Greek • responsible for 4 main types of law: 1. Tort Law 2. Public Law 3. Procedural 4. Family •creating the legal process trials, convictions, and sentencing Foundations of Canadian Law • Two of three founding nations of Canada • France- Napoleonic/French Civil Code • England- Common Law Foundations of Canadian Law • French Civil Code •Private Law, based on Roman Law of Emperor Justinian •1 book •Associated with “Civil Code” & “Justinian Code” •Contains almost all private law •Major influence Quebec Law- permitted in Proclamation 1770/Quebec Act 1774 Foundations of Canadian Law • English Common Law •“Judge-made law” “Stare Decisis” – to stand by previous decision •Founded in feudal England •Established impartial & standard law •Judges rulings recorded – creating Law, which was •Judges traveled fromCase town to town applied in future similar legal cases the law similarly in similar cases *King always maintained veto •Known as: “Rule of Precedent” & applied Foundations of Canadian Law • English Common Law Evolution (I) King Lords Barons (Sole Judges of law) Judges English Common Law (Judges met (assizes) to increase consistency) Foundations of Canadian Law • English Common Law Evolution (II) • Rule of Law • Equality • No restrictions without reason • Legal rights could not be changed without consent (of the people, where true power lay) • Habeas corpus