American literary periods - Effingham County Schools
advertisement

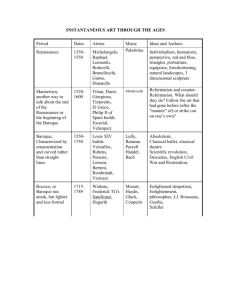
American Literary Timeline Colonial Period Age of Reason Romanticism Transcendentalism Anti-Transcendentalism Realism Naturalism Regionalism Modernism Contemporary Colonial Period Early America-1776 This period was at the very beginnings of America and it made way for the rest of the countries literature. In the first stages of America there were writers, such as Thomas Hariot, who wrote A Brief and True Report of the New-Found Land of Virginia in 1588; in which he described “The Americas” in words and picture. The book was quickly translated into Latin, French, and German; it was a window for the Old World to see an embellished version of the New World. Others that dominated this era were the Puritans whose definition of good writing was writing that brought home a full awareness of the importance of worshipping God and of the spiritual dangers that the soul faced on Earth, and the literature that was produced by the Puritans reflected this. Authors of the Colonial Period Edward Taylor John Woolman Anne Bradstreet William Bradford Age of Reason Late 1770s to Early 1800s This period was a time when authors were focused more on their own reasoning rather than simply taking what the church taught as fact. During this period there was also cultivation of patriotism. The main medium during that period were political pamphlets, essays, travel writings, speeches, and documents. Also during this period many reforms were either made or requested, for instance during this time the Declaration of Independence was written. Authors of the Age of Reason Abigail Adams Benjamin Franklin Thomas Jefferson Thomas Paine Romanticism 1800-1850 After the “Age of Reason” came to an end, the people of America were tired of reality; they wanted to see life as more than it was. This was the Era of Romantics. The main medium that presented itself at that time were short stories, poems, and novels. During this era, as opposed to the “Age of Reason,” the imagination dominated; intuition ruled over fact, and there was a large emphasis on the individual/common man and on nature or the natural world. Gothic literature was also introduced at this time, which is a sub-genre of Romanticism. This genre includes stories about characters that had both good and evil traits. Gothic literature also incorporated the use of supernatural elements. Authors of the Romanticism Washington Irving Nathaniel Hawthorne Edgar Allen Poe Herman Melville Transcendentalism 1840-1855 This movement pushed America from the elaborate and fantasy writings displayed in the period of Romanticism into a period of literature that stressed individualism, nature, and self-reliance. Often Transcendentalists used nature to gain knowledge or to return to a life of self-reliance and individualism. It also stressed the fundamental idea of a unity between God and the world and that each person was a microcosm of the world. Unlike many European groups, the Transcendentalists never issued a manifesto. They insisted on the differences in each individual. Authors of the Transcendentalism Ralph Waldo Emerson Henry David Thoreau Walt Whitman [Sarah] Margaret Fuller Anti-Transcendentalism 1840-1855 During the same time period when Transcendentalism was taking place, its opposite, Anti-Transcendentalism, was also happening. As opposed to Transcendentalism, which focused on the natural world and its relationship to humanity and the quest for understanding of the human spirit, Anti-Transcendentalism focused on the limitations of mankind and its potential destructiveness of the human spirit. For instance, water brings life, but its excess, i.e. a flood, can bring death and destruction. (Notice how they sometimes use nature in their writings to reflect what goes on with humans. Example: Scarlet Letter and the forest – reflects Pearl’s wild nature, the only place Hester and Dimmesdale can be free, etc.) Authors of the AntiTranscendentalism Herman Melville Nathaniel Hawthorne Realism 1865-1915 This literary movement took place during the Civil War. At a time when a war was taking place, people were tired of Transcendentalism and AntiTranscendentalism. For one thing, they were both extremes of the same spectrum; one was nice, happy, and “frilly;” the other was dark and destructive. People wanted to see things how they were, so Realism came about. Realism also came about as a reaction to Romanticism, in which there were heroic characters and adventures with strange and unfamiliar settings. In response, Realism’s authors tried to write truthfully and objectively about ordinary characters in ordinary situations. Authors of the Realism Mark Twain [Samuel Clemens] Bret Harte Sarah Orne Jewett James Henry Naturalism 1865-1915 The Naturalism literary movement that took place in the late nineteenth and early twentieth century tended to view people as hapless victims of immutable natural laws. Naturalism is closely related to Realism, only it usually views the world in a darker perspective. In Naturalism, it is widely shown that free will is an illusion that things that happen in the universe happen and could not happen any other way. Also a defining characteristic of Naturalism is that its characters’ lives are shaped by forces they cannot control. Authors of the Naturalism Stephen Crane Jack London Theodore Dreiser Frank Norris Regionalism 1865-1915 Regionalism was a literary movement in which authors would write a story about specific geographical areas. By writing about regions, the authors explore the culture of that area, including its languages, customs, beliefs, and history. Not only did writers in this time try to show the region they wrote about to their readers, but they also made an attempt at a sophisticated sociological or anthropological treatment of the culture of the region. Authors of the Regionalism Willa Cather William Faulkner Kate Chopin Frank Norris Modernism 1915-1946 This type of writing is one of the most experimental types. Modernist authors used fragments, stream of consciousness, and interior dialogue. The main thing that authors were trying to achieve with Modernism was a unique style, one that they could stand out and be known for its uniqueness. During this period, technology was taking incredible leaps. There were also two world wars and destruction on a global scale. The younger generation began to take over the main stage. Authors of the Modernism Ernest Hemingway F. Scott Fitzgerald John Steinbeck Robert Frost Contemporary 1946-present In the years since the Modern period, American authors have begun to write from a plethora of genres. Many Americans simply write in the style that suits them individually rather than mimicking specific styles. There are more different types of writing being done at one time than at any other period in history: fantasy, fiction, science fiction, horror, political writings, romantics, plays, and poems, anything and everything. Authors of the Contemporary J. D. Salinger Stephen King Joyce Carol Oates Robert Jordan End of Power Point • The following slides are accessible from the slides above Edward Taylor (c. 1644-1729) • Taylor was a Minister who studied at Harvard College, and whose works were never published by Taylor, himself, until they were discovered in 1930s. He wrote such pieces as Metrical History of Christianity, which mainly a history of Christian martyrs. Colonial Period John Woolman (1720-1772) • The best known work by a Quaker was written by this man, simply named Journal in 1774, this journal was a complete and full account of his life in a pure, heartfelt style of great sweetness that have attracted many American and English writers for many years after Woolman had past away. Colonial Period Anne Bradstreet (c. 1612-1672) • The first publication of a book of poems in America, was also the first publication by a woman in America. She also wrote The Tenth Muse Lately Sprung Up in America in 1650. Colonial Period William Bradford (1590-1657) • He was elected governor of Plymouth shortly after the pilgrims landed in on Plymouth Rock. He was essentially the first historian of the new colonies. His participation in the voyage of the Mayflower and being governor made him the ideal person for this job. He wrote Of Plymouth Plantation in 1651. Colonial Period Abigail Adams (1744-1818) • She wrote letters that campaigned for women’s rights. Her grandson, Charles Francis Adams, published The Familiar Letters of John Adams and His Wife Abigail During the Revolution, which were just what they said they were, letters written by Abigail and her husband. Age of Reason Benjamin Franklin (1706-1790) • Franklin is well known worldwide for his discoveries in the world of science and also for works that he contributed to, such as the Declaration of Independence, and his theories on electricity. His works were all new ideas things people never thought of before because they always took what they got as fact. Age of Reason Thomas Jefferson (1743-1826) • Jefferson is bets know for writing the Declaration of Independence, the document came about as a response to these times, people were thinking for themselves, and one of the major thing the Americans discovered was that they didn’t need England. So Jefferson wrote the D of I to formally state that. Age of Reason Thomas Paine (1737-1809) • Paine wrote mostly pamphlets that would spur ideas and immediate action. In the document "The American Crisis," Paine wrote about the oppression that America suffered from Britain, and propelled America into a war with Britain. Paine, to this day, is well known for his propaganda. Age of Reason Washington Irving (1789-1851) • Irving was the first “famous” American author; he’s also known as the “Father of American Literature.” He wrote travel books, short stories, and satires. Some of his works include; Legend of Sleepy Hollow, Rip Van Winkle, and Devil and Tom Walker. Romanticism Edgar Allen Poe (1809-1849) • Poe had a bad childhood that made him despise the world, and his works reflected his work. He is credited for creating the modern short story, and the detective story. He also challenged two long-standing theories, one, a poem had to be long, and two, a poem had to teach you something. Some of his works include, "The Raven", "Bells", "Annabel Lee", and "Dream." Romanticism Herman Melville (1819-1891) • In his time Melville was not entirely recognized, however, in the more recent years he has been considered one of the most top rated novelist of all time. He is most well known for his epic novel Moby Dick. Romanticism Anti-Transcendentalism Ralph Waldo Emerson (1803-1882) • Emerson had a strong sense of a religious mission though he was accused of subverting Christianity. He left the church saying, “to be a good minister, it was necessary to leave the church.” Some of his mayor works include Nature, published in 1836. Transcendentalism Henry David Thoreau (1817-1862) • Thoreau Lived his life, to do just that, live his life. He was never rich and for the most part lived with little money all his life. His work he is most well known for is Walden, published in 1854. Transcendentalism Walt Whitman (1819-1892) • Whiteman was born on Long Island, and was, for most of his job life, a carpenter; he was a man of the people. Most of his learning career was done on his own, after he left school the age of eleven. His major work was entitled His Leaves of Grass, published in 1855; over the years he made many rewrites for this book. Some of his famous poems are, "Crossing Brooklyn Ferry," "Out of the Cradle Endlessly Rocking," and "When Lilacs Last in the Dooryard Bloom'd." Transcendentalism [Sarah] Margaret Fuller (1810-1850) • Fuller was born in Cambridgeport, Massachusetts. She learned Greek and Latin at a very young age, and later learned German and Italian. After her father, a congressman, died she became a schoolteacher. She worked with Ralph Emerson as editors of The Dial, a literary and philosophical journal, for which she wrote many articles including “The Great Lawsuit. Man versus Woman, Woman versus Man;” in which she spoke for the equality of men and women. Some of her other works include Summer on the Lakes, published in 1844, and Women in the Women in the Nineteenth Century, published in 1845. Transcendentalism Nathaniel Hawthorne (1804-1864) • Hawthorne was a Puritan who utilized his writings to express his dark, and gloomy outlook on life. Some of his works include; Twice Told Tales, published in 1837; The Scarlet Letter, published in 1850; and The House of the Seven Gables, published in 1851. Anti-Transcendentalism Romanticism Mark Twain [Samuel Clemens] (1835-1910) • Twain is known by many as the greatest American humorist and one of our greatest novelists. He was known for using vernacular, exaggeration, and deadpan narrator to create humor. Twain wrote many great novels including, the Adventures of Tom Sawyer, published in 1876; and The Prince and the Pauper, published in 1881. Realism Bret Harte (1836-1902) • Harte was born in New York, and later worked in California, on The California writing stories. He worked with other well-known authors as well, while at The California, authors like Mark Twain, Charles Warren Stoddard, and Prentice Mulford. He was later appointed Secretary of the United States Branch Mint at San Francisco; he held this office until 1870. He then became the editor of Overland Monthly, where he published "The Luck of Roaring Camp," which brought him instant fame. Some of his works included; "The Heathen Chinese,” a poem published in 1870, Devil's Ford, "The Twins of Table Mountain," "By Shore and Sedge," and "A Millionaire of Rough and Ready." Realism Sarah Orne Jewett (1849-1909) • Jewett grew up with books all around her, it was only fitting she grow up to be a writer. The early years of her life were much like the story she wrote in A Country Doctor. Some of her works include; Miss Tempy's Watchers, originally published in 1888; The Dulham Ladies, originally published in 1886; A White Heron, originally published in 1886. Realism James Henry (1843-1916 ) • His father was an important theorist and lecturer, and his older brother was a famous American philosopher, William James. He attended Harvard College. His early stories depict the leisurely life of the well-to-do. In his time he wrote many short stories including; “The Short Story of a Year,” published in 1865; “Gabrielle de Bergerac,” published in 1869; and “Guest's Confession.” Realism Stephen Crane (1871-1900) • Crane’s writing was known for attacking patriotism, individualism, and organized religion; it also confronted the meaninglessness of the world. His work was also very well known for its imagery and symbolism. The work he is most famous for Red Badge of Courage, which was set in the Civil War. Some of his other works include; The Open Boat, published in 1894; “An Episode of War,” originally published in 1890. Naturalism Jack London (1876-1916) • London was born in San Francisco, California; he lived a hard life, switching from job to job for whatever money he could get, after his father abandoned him at a young age. He is one of the most highly acclaimed writers of all time; his stories of life and death struggles are vivid and engaging. Some of his works include; The Call of the Wild, published in 1903; White Fang, published in 1906; “Lost Face,” published in 1910; and “The Night Born,” published in 1913. Naturalism Theodore Dreiser (1871-1945) • One of Dreiser's favorite fictional devices was the use of contrast between the rich and the poor, the urbane and the unsophisticated, and the power brokers and the helpless. Some of his works include; Twelve Men, published in 1919; A Book About Myself, published in 1922; The Color of a Great City, published in 1923; An American Tragedy, published in 1925. Naturalism Frank Norris (1870-1902) • Norris studied in Paris, at the Univ. of California, and Harvard. He also spent several years as a war correspondent in South Africa (1895-96) and Cuba (1898). Some of his works include; The Responsibilities of the Novelist, published in 1903; The Octopus, published in 1901; and The Pit published in 1903. Naturalism Willa Cather (1873-1947) • Cather has been called, one of the most interesting female writers in American literary history. She was a teacher, a journalist and a critic as well as a writer. She has a talent for presenting settings, and characters that are rich in language and imagery. She also won a Pulitzer Prize. Some of her works include; April Twilights, published in 1903; and O Pioneers!, published in 1913. Regionalism William Faulkner (1897-1962) • He served in both the Canadian and the British Royal Air Force. He wrote most of his novel on a farm in Oxford, Mississippi. Some of his novels included; The Hamlet, published in 1940; The Town, published in 1957; and The Mansion, published in 1959. Regionalism Kate Chopin (1851-1904) • Chopin loved literature as a child, and secluded herself in it after her grandmothers death. She never achieved much until 1884 when she finally decided to pursue a career in writing. Some of her writing included; "Desiree’s Baby," published in 1893; "The Awakening," published in 1899. Regionalism Ernest Hemingway (1899-1961) • Hemingway won a Pulitzer Prize and Noble Peace Price for Literature. He used concise, direct, spare, objective, precise, rhythmic writing styles to create larger than life heroes, big game hunters, etc. Some of his works include; The Sun Also Rises, published in 1922; A Farewell To Arms published in 1929; For Whom the Bell Tolls, published in 1940. Modernism F. Scott Fitzgerald (1896-1940) • Fitzgerald wrote about the times. In his novel The Great Gatsby, published in 1925, he wrote about the roaring twenties, a time when no one cared about the future and they had fun with what they had then. Some of his other works include; The Side of Paradise, published in 1920; and The Beautiful and the Damned, published in 1922. Modernism John Steinbeck (1902-1968) • Steinbeck wrote about the both the pains and joys of life. The Grapes of Wraith, published in 1939, his most well known work told the story of families ring to survive and stay together during the depression. In other works like Tortilla Flat, published in 1935, Steinbeck wrote about the joys of life. Some of his other works include; East of Eden, published in 1952; Of Mice and Men, published in 1937; and The Pearl, published in 1947. Modernism Robert Frost (1874-1963) • America’s best known and most loved poet, Frost wrote his poems in a traditional verse form. He used the plain speech of rural New Englanders. Some of his works include; “Death of the Hired Man,” published in 1951; “Birches,” published in1920; and “The Road Not Taken,” published in 1920. Modernism J. D. Salinger (b.1919) • Salinger studied at NYU, and Columbia University. After which he decided to devote his life to his writing. His writing career was interrupted by World War I, where he served in the U.S. Army. His most well known work was his novel Catcher in the Rye, published in 1951, a novel about a high school student who tries to run away from his life that he thinks is “phony.” Some of his works are A Perfect Day for Bananafish published in 1948; For Esmé With Love and Squalor, published in 1950. Contemporary Stephen King (b.1947) • King write novels that frighten people. Some of his major works are; Carrie published in 1974; The Shining, publishing in 1998; Salem's Lot, published in 1993; and The Stand, published in 1991. Contemporary Joyce Carol Oates (b.1938) • Oates received a type writer at the age of fourteen and trained herself to write novel after novel through high school and college. She earned an M.A. in English at the University of Wisconsin. Some of her works include; Blonde, published in 2000; Wonderland, published in 1971; and The Tattooed Girl, published in 2003. Contemporary Robert Jordan (b.1948)• He went to the Citadel, the Military College of South Carolina, where he received a degree in physics. Jordan’s main area of expertise is in the genre of fantasy. He is currently in the process of writing a series of novel entitled The Wheel of Time, some of the novels from this series are, The Eye of the World, published in 1990; Crossroads of Twilight, published in 2003; and The Novel: New Spring published in 2004. Contemporary