TOPIC: Waves AIM: What are the properties of waves?
advertisement

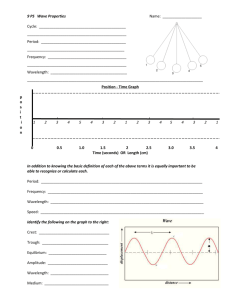
Topic: Waves Aim: Describe the parts of a wave. Do Now: Take out your HW ditto http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Z3O2Ju3ULvo HW: Bottom of Kinetic and Potential Energy ditto/ Identify the type of wave described below. 1. Does not require a medium. 2. Compressional waves 3. Particles of the medium move PARALLEL to the direction of the wave. 4. Requires a medium. 5. Can travel through a vacuum. 6. Particles of the medium move at RIGHT ANGLES to the direction of the wave. 7. Sound waves Parts of a Transverse wave y- axis x- axis Normal resting position Crest Trough •Crest – high points •Trough – lowest points Crest Trough Amplitude •Amplitude – height –Related to energy –High amp = a lot of energy •Wavelength – distance bw 2 crests or 2 troughs Wavelength Wavelength • compression = Parts of a Compressional where particles are close together (longitudinal) • rarefaction = wave where particles are far apart rarefaction compression • Wavelength = Distance bw 2 compressions or 2 rarefactions wavelength • High amplitude: – compression = particles are very close together – rarefaction = particles are very far apart • # of waves passing a Frequency point in a given time • 1 wave = 1 crest + 1 trough • As frequency increases, wavelength decreases 1 second Hertz •Unit for frequency •Hz •1 Hz = 1 wave per second The human ear is capable of detecting sound waves with a wide range of frequencies, ranging between approximately 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz. Period • Time it takes 1 wavelength to pass a point • Units = seconds • As frequency increases, period decreases Low period High period Let’s summarize… 1. Describe the parts of a transverse wave. 2. Describe the parts of a longitudinal wave. 3. Describe the frequency of a wave. 4. Describe the relationship between frequency and wavelength. 5. Identify the units for frequency. 6. Describe the period of a wave. 7. Describe the relationship between frequency and period. http://www.brainpop.com/science/energy/waves/ A B C D Identify each part of a wave labeled in the diagram above. Which change in wave properties increases wave amplitude? 1. Increased wavelength 2. Increased height 3. Decreased frequency 4. Shortened wavelength Which is the lowest part of a transverse wave? 1.Amplitude 2.Crest 3.Period 4.Trough The height of a transverse wave is known as its 1.amplitude 2.crest 3.period 4.trough The part of a longitudinal waves where particles are farther apart is known as the 1.crest 2.compression 3.trough 4.rarefaction Which of the following changes in wave properties is a result of an increase in wavelength? 1. Higher crests 2. Reduced height 3. Lower frequency 4. Faster movement The number of waves passing a point at a given time is known as 1. wavelength 2. frequency 3. period 4. amplitide The time it takes one wavelength to pass a certain point is known as 1. wavelength 2. frequency 3. period 4. amplitude Which of the following best describes the relationship between frequency and wavelength? 1. If the frequency remains constant, wavelength increases. 2. The wavelength decreases and frequency decreases. 3. The frequency increases as wavelength decreases. 4. If the wavelength remains constant, frequency increases. 1. Which wave has the greatest amplitude? 2. Which wave has the greater wavelength? 3. Which wave has the greater frequency?