wavelength
advertisement

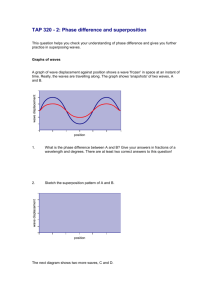
Review: Separating Mixtures and States of Matter KIPP INSPIRE ACADEMY 5th Grade Science Separating Mixtures- Main Idea! Pure substances are made of 1 kind of material; cannot be separated into other parts Mixtures are made of 2 or more materials; CAN be separated back into individual components Tools Used To Separate sifter/sieve filter magnet hot plate What Tool Should We Use? 1. Gravel (tiny rocks) + sand: 2. Big rocks + tiny rocks: 3. Sand + iron: Hand Magnet 4. Gravel (tiny rocks) + salt: 5. Sugar + water: Sifter/sieve Hot plate Sifter/sieve States of Matter- Main Idea! We can decide what state of matter an object is in by looking at its volume and shape. Volume = the amount of space something takes up What is matter? •Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. •Solids, liquids, and gases are the 3 main types of matter. Solids • A solid has definite (fixed) shape and a definite volume. • Solid molecules are packed closely together. Examples of Solids How can you describe a solid item? Liquids • A liquid has a definite (fixed) volume but no shape of its own. • Liquids take the shape of their containers • Liquid molecules move loosely. Liquids can flow or be poured easily. Liquids change their shape depending on the container they are in. Examples of Liquids Gases • Gases don’t have definite volume or shape. • Gas molecules can move around freely. • Gases spread out and change their shape to fill up whatever container they are in. Examples of Gases Do You Get It? Which of these would be an example of a liquid? The type of matter that is inside this balloon is a… 1. Solid 2. Liquid 3. Gas The pyramid is an example of a… a. solid b. liquid c. gas What am I? I’m an object with definite volume and shape. I’m an object with no definite shape but definite volume. I’m a object with neither definite volume nor shape. Now, some new stuff before the quiz… QUIZ Name: Harry Potter Subject: ME Quiz 2 Period: “D” for Dayton Bubble in your ID number! Properties of Waves February 4th, 2011 5th Grade Science KIPP: Inspire Academy The 5 Properties of Waves…? Why do we care about WAVES in our Matter and Energy unit? Light and sound energy travel in waves. 5 Properties of Waves • Crest • Trough • Wavelength • Frequency • Energy Crest . . Trough Wavelength Wavelength is the distance between any two crests or any two troughs (the length of a wave). Wavelength Crest . . Wavelength Trough • A shorter wavelength has less distance in between the two points. • A longer wavelength has more distance in between the two points. Class Check: Which one has a longer wavelength? a. b. Frequency Frequency is the speed of a wave. • measured by the number of wavelengths that pass through a point in one second. • A higher frequency means the wave occurs (happens) faster • A lower frequency means the wave occurs slower Class Check: Which one has a higher frequency? 1 second a. 6 1/2 wavelengths per second b. About 3 wavelengths per second Wavelength & Frequency Together • The higher the frequency, the shorter the wavelength ; • The lower the frequency, the longer the wavelength. Energy • High frequency waves have high energy • Low frequency waves have low energy. Class Check: Which one is the higher energy wave? a. b. High frequency waves have high energy! Low frequency waves have low energy! Video Clip • BrainPop – Waves Exit Question Draw a diagram of a wave and label the crest, trough, and wavelength.