Plant & Animals Adaptations to their Environment

Plant & Animals
Adaptations to their
Environment
ecosystem
all the living and nonliving things that interact with one another in a given area (includes soil, water, light, inorganic nutrients, and weather)
Example
Sandy beaches are the perfect ecosystem for the ghost crab.
community
the group of living things of
different species found in an ecosystem
Example
The Tropical Rainforest is one of the most active communities on Earth.
population
all the member of the same type of
organism living in an ecosystem
Example
Approximately 10,000 pairs of bald eagles live in the Continental United
States.
biome
a large group of similar ecosystems
Example
Earth has six major land biomes including tundra, taigas, temperate forests, tropical rain forests, grasslands, and deserts.
climate
the normal pattern of weather in an area over many years
Example
Johnson County has 167 frost free days. The hottest month of the year is July with an average temperature of 70.2 degrees
Fahrenheit. December is the coldest month with an average temperature of 35.2 degrees Fahrenheit. Johnson County receives
55 inches of precipitation annually. Seventeen inches of this is in the form of snow.
habitat
the natural environment where an organism lives
(vary greatly in size - Florida Everglades, rotting log, patch of soil, forest, prairie)
Examples -
Wild Bactrian Camels live in the Gobi Desert of China and Mongolia.
In a small pond frogs and fish live together.
niche
The role of an organism in its habitat.
(includes living space, diet, and seasonal habitats)
Examples
The Oregon Brown Bat lives in the temperate coniferous forests where it sleeps in rock crevices, caves, and dense trees near water. It actively feeds at night and prefers insects with aquatic life stages. It hibernates during the winter months.
Producers are a major niche in all ecosystems.
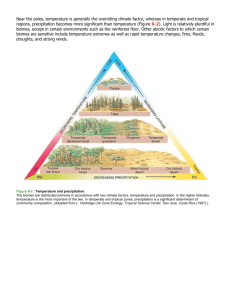
Biomes
Tropical Rain Forest
Temperate Forest
Grasslands
Deserts
Taiga
Tundra
Marine
Freshwater
Tropical Rain Forest
hot, moist biome found near Earth's equator
60 to 160 inches of precipitation yearly over 15 million species of plants and animals - a greater number and variety of animals than any other biome
Rainforest
toucan
Tropical Rain Forest
Animals chimpanzee
Anaconda piranha
Anaconda
Bengal Tiger poison dart frog sloth
Tropical Rain Forest
Plants
Temperate Forests
most of the trees lose their leaves in the winter growing season of 140-200 days
Soil is fertile
Temperate Forests
Temperate Forests
Animals eagle skunk opossum squirrel deer rabbit bear
Temperate Forests
Plants
Grasslands
2 Kinds
Savanna
Temperate Grassland
Savanna
grassland with scattered individual trees warm or hot climates rainfall is from about 20-50 inches per year
Savanna
Savanna
Animals giraffe zebra wildebeest elephant lion rhino ostrich
Savanna
Plants
Temperate Grassland
grasses as the dominant vegetation with a few trees hot summers and cold winters amount of rainfall is less in temperate grasslands than in savannas
Temperate Grassland
bison fox
Temperate Grassland
Animals coyote antelope badger prairie dog
Temperate Grassland
Plants
Desert
get their water from the food they eat including succulent plants, seeds nocturnal
Scorpions and wolf spiders have a thick outer covering which reduces moisture loss.
Desert
Desert
Animals camel rattlesnake scorpion
Desert
Plants
Taiga & Tundra
coldest environment The treeless land is covered with snow and ice most of the year.
Much of the land has ground that is
permafrost
, permanently frozen.
short summers
Taiga & Tundra taiga
walrus
Taiga & Tundra
Animals snowshoe hare
Polar bear reindeer
Artic fox
Taiga & Tundra
Plants cotton grass
Red leaves can absorb more heat.
lichen
Marine Biomes
Marine Biomes
stingray
Marine Biomes
Animals fish whale sea horse shark
Marine Biomes
Plants
Freshwater Ecosystems
ponds, lakes, streams, rivers
Freshwater Ecosystems
fish
Freshwater Ecosystems
Animals beaver frog turtle duck
Freshwater Ecosystems