Earthquake Strength vs. Intensity
advertisement

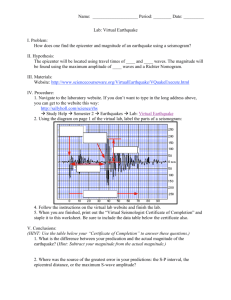
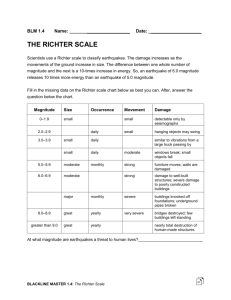
Seismologists use two scales when classifying earthquakes. 1) Richter Scale 2) Modified Mercalli Scale Measures the Magnitude of an earthquake on a ten (10) point scale. In 1935, Charles Richter introduced the concept of earthquake magnitude. Richter magnitude is determined by measuring the largest amplitude (wave height) recorded on the seismogram. Largest recorded earthquake had a Richter magnitude equal to 8.6 Magnitude: measure of the strength of an earthquake Wave amplitude increases tenfold (10X) with each increase in Richter magnitude. Each increase in 1 in Richter Magnitude represents a 10 fold increase in the wave amplitude (height). A magnitude 7 earthquake measures 10 times more amplitude than a magnitude 6 earthquake. A magnitude 8 earthquake measures 10 x 10 (or 100 times) more amplitude than a magnitude 6 earthquake. And so on. measures the strength of the ground Richter scale motion • 10 for each level. Based on a factor of _____ • 10 times as strong as a A magnitude 3 is ____ magnitude 2. • A magnitude 4 is _____ 100 times as strong as a magnitude 2. • How much stronger is a magnitude 7 than a magnitude 4? 4 5 6 7 x10 x10 x10 = 1,000 times stronger • Lag Time: • The difference in arrival time between the P-wave and the S-wave. • How is it calculated? • ∆T (S-P) • What is amplitude? • The maximum vibration (height) from equilibrium. • measured from zero 1. Label the beginning of the P-wave on the seismogram. 2. Label the beginning of the S-wave on the seismogram. 3. What is the lag time? _______ 4. What is the amplitude? ______ 5. What was the estimated magnitude? _______ Haiti earthquake List of greatest magnitude earthquakes Measures the Intensity of an earthquake on a twelve (XII) point scale. In 1902 G. Mercalli developed a fairly reliable intensity scale which assesses the damage to various types of structures at a specific location. Note that earthquake intensity is determined by several factors including: 1) Strength of earthquake 2) Distance from epicenter 3) Nature of surface materials 4) Building design • Intensity: measure of the degree to which an earthquake is felt by people and the amount of damage caused by the earthquake • Modified Mercalli Scale • I to XII (eyewitness accounts) The Mercalli scale does not give a true indication of the actual strength of an earthquake because the amount of damage done to different places will largely depend on, the type of materials used and the degree of construction of buildings and structures. EARTHQUAKE DOMINOES 3 minutes End Use the information on the worksheet to determine the Mercalli Intensity Scale for each zip code Place a on the map where you think the epicenter is located. Answer all worksheet questions II-III VIIVIII V VI VI IX IX VI IX IV V VIIVIII V II-III IV Identify the Richter Scale Magnitude of the earthquake? Las Vegas Seismic Station 1. What is the S-P lag time? 2. What is the distance to the earthquake epicenter? 3. What is the S-wave amplitude? 4. What is the magnitude using the nonogram? 6.7