Reconstruction
advertisement

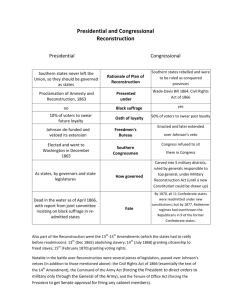
Reconstruction 1865-1877 Lincoln’s Reconstruction • Was very Lenient • All Confederates would receive pardon who swore allegiance – Exception for high-ranking officials & crimes against POW • Become a state once 10% of population take oath Wade-Davis Bill • Congress opposed Lincoln’s Plan and created their own • Too lenient and didn’t protect former slaves • Congress Wanted: – Majority of population must take loyalty oath – State must formally abolish slavery – No Confederate officials can participate in Gov’t • Pocket Vetoed by Lincoln Johnson’s Reconstruction • Sworn in after Lincoln’s assassination • Announced in May 1865 • Largely followed Lincoln’s Plan except: – Excluded high ranking officials AND wealthy plantation owners from taking oath – Personally pardoned more than 13,000 Confederates • Felt that “white men alone must manage the South” • States must abolish slavery to be readmitted • States must repeal secession Radical Reconstruction • 1866 – voted to create the Freedman’s Bureau • 1866 – passed Civil Rights Act of 1866 – Granted citizenship to blacks and banned discriminatory laws • Johnson vetoed both bills Radical Reconstruction cont. • Congress overrode both vetoes • Drafted 14th Amendment – Prevented states from denying rights and privileges to any US citizen • Designed to overturn and Nullify Dred Scott decision of 1857 • Impeached President Johnson for violating Tenure of Office Act when he removed Sec. of War Edwin Stanton. Senate vote fell short of removing him from office • Introduced 15th Amendment after US Grant elected President in 1868 – Ratified in 1870 it prevented states from denying vote based on “race, color, or previous conditions of servitude” Reconstruction Act of 1867 • Divided Confederacy into 5 military districts – Authorized use of military to enforce • States required to give blacks the right to vote • Required ratification of 14th Amendment Johnson vetoed but Congress was able to override the veto Impact of Reconstruction • • • • • Scalawags – Southerners who joined Republican Party Carpetbaggers – Northerners who moved South after the war Black voting rights – 90% supported Republican party (voted for Grant) Freeman’s Bureau – helped create and run schools for ex-slaves 16 blacks elected to Congress from South – Hiram Revals the first • Sharecropping – former slaves provided a few acres, seeds and tools to work land owned by others. Paid with portion of their crops • Rise of the KKK lead to Enforcement Acts of 1870 and 1871 – Provided Federal supervision of elections and Use of troops in Klan controlled areas • 1872 – Amnesty Act returns right to vote and hold public office to 150k former Confederates – Freedman’s Bureau allowed to expire – Leads to growth in power of Southern Democrats Election of 1876 • Democrat – Samuel Tilden • Republican – Rutherford B Hayes • Tilden wins Popular Vote but doesn’t earn enough Electoral Votes • Southern Democrats agree to support Hayes in return for removal of Federal troops • Hayes becomes President and reconstruction officially ends