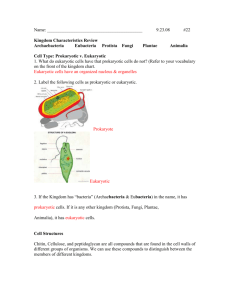
MLA Heading: Classification Review 2014 Fill in the Venn diagram
advertisement

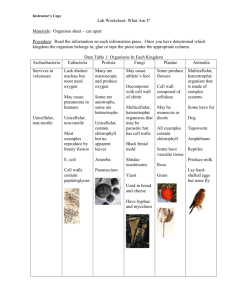
MLA Heading: Classification Review 2014 1. Fill in the Venn diagram for prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic Eukaryotic No nucleus DNA DNA is loose in the cytoplasm Have a cell membrane Has a nucleus Have cytoplasm Multicellular Simple cell Unicellular DNA is in the nucleus Complex cell 2. What is the difference between unicellular and multicellular organisms? Unicellular organisms are made of only one cell. Multicellular organisms are made of more than one cell. 3. What is the difference between autotrophic and heterotrophic organisms? Autotrophic organisms can produce their own food. Heterotrophic organisms consume other organisms for food. 4. What is the difference between asexual and sexual reproduction? Asexual reproduction involves one parent cell making exact copies of itself through cell division. Budding is also a form of asexual reproduction in which plants and animals (very rare) can break off pieces of the parent cell to then grow into a new organism. A disadvantage to asexual reproduction is the lack of genetic diversity- genetic material from only 1 parent. Sexual reproduction involves two different types of cells (a male cell and a female cell) that combine to form a unique organism. Usually involves 2 parents that each contribute genetic material. 5. What is the broadest category for classification? domain Define the following. 6. Phylogenic Tree- a diagram that shows the levels of classification 7. Taxonomy- the science of describing, classifying, and naming living things 8. List the 3 Domains and the Kingdoms that go with each domain. Domains (3 total) Kingdoms (6 total) 1. archaea archaebacteria 2. bacteria eubacteria 3. eukarya protista, fungi, plantae, animalia For the following questions, list ALL of the Kingdoms that fit the listed characteristics. 9. Which kingdom is ONLY autotrophic? 10. Which kingdoms are ONLY heterotrophic? plantae fungi and animalia 11. Which kingdoms are ONLY unicellular? archaebacteria and eubacteria 12. Which kingdoms are ONLY multicellular? plantae and animalia 13. Which kingdom ONLY reproduces asexually? archaebacteria 14. Which Kingdom(s) include(s) prokaryotes? archaebacteria and eubacteria 15. Which Kingdom(s) include(s) unicellular heterotrophs? archaebacteria, eubacteria, protista, fungi 16. Which Kingdom(s) include(s) multicellular heterotrophs? protista, fungi, animalia 17. Which Kingdom(s) include(s) unicellular autotrophs? archaebacteria, eubacteria, protista 18. Which Kingdom(s) include(s) Eukaryotes that are multicellular and reproduce mostly sexually. plantae and animalia 19. Which Kingdom is a “catch all” kingdom or “junk drawer” kingdom? (If something doesn’t fit in another kingdom it goes here). protista Give at least 2 examples of organisms for each kingdom: ANSWERS WILL VARY Kingdom: Archaeabacteria Example: blue green algae Example: methanogens Eubacteria salmonella streptococcus Protista paramecium amoeba Fungi mushrooms yeast Plantae grass trees Animalia centipede sea anemone Give a unique characteristic for each of the 6 kingdoms below. Archaeabacteria Eubacteria Protista Fungi live in extreme environments Common- can live almost everywhere “catch all” or “junk drawer” kingdom both uni/multicellular, auto/heterotrophic, asexual/sexual reproduction decomposers Plantae only autotrophic Animalia Very complex