Global Climates and Biomes
advertisement
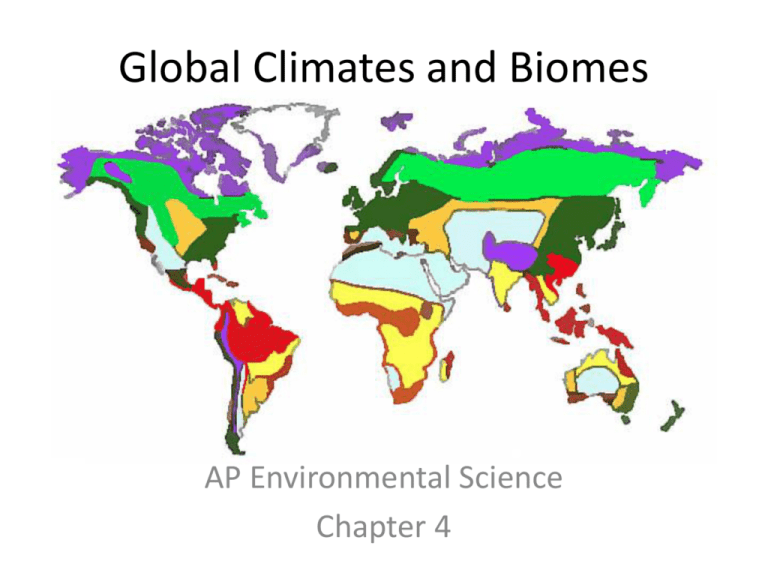
Global Climates and Biomes AP Environmental Science Chapter 4 Get your brains working: At the beginning of chapter 4, there is a story about climatic changes occurring in Kenya during 2003. For credit, take a couple minutes and write down 1) what these shifts were and 2) why they mattered to the Kenyan people. Global processes determine weather and climate Weather: Short-term atmospheric conditions (minutes to days) Climate: Long-term. Climate is the average weather that occurs in a given region over a long period (typically several decades) Earth’s Atmosphere Earth’s atmosphere consists of five layers of gasses. Gravity keeps those layers in place, but because gravity weakens as you move away from the plant, the layers near the top are less dense than those nearer the surface. Ozone is primarily located between the troposphere and stratosphere Unequal Heating of Earth The unequal heating of Earth has three primary causes: 1) Variation in the angle at which the Sun’s rays strike Earth 2) Variation in the amount of surface area over which the Sun’s rays are distributed 3) Some areas of Earth reflect more solar energy than others Reason #1: Variation in the angle at which the Sun’s rays strike Earth Reason #2: Variation in the amount of surface area over which the Sun’s rays are distributed Reason #3: Some areas of Earth reflect more solar energy than others Atmospheric Convection Currents Convection: Transfer of heat of heat via gas/liquid currents Air has four properties that determine how it circulates in the atmosphere: density, water vapor capacity, adiabatic heating/cooling, and latent heat release Density of air determines its movement: less dense air rises, more dense air sinks Water vapor capacity: maximum amount of vapor air can hold is called the saturation point. As temperature falls, saturation point falls. This is how clouds form and bring about precipitation. As temperature increases, saturation point increases. Atmospheric Convection Currents Adiabatic cooling: As air rises in the atmosphere, it expands due to decreased pressure and it and cools Adiabatic heating: As air sinks toward the surface pressure increase and air warms Latent heat: When water vapor condenses into liquid water, heat is released. This means when water condenses, air will become warmer and begin to rise. ____________________________________________________ _ Convection currents: These are global patterns of air movement that are initiated by this unequal heating of Earth Hadley cells, polar zones, and Coriolis Effect - Forms on convection currents - Earth’s tilt and seasons Ocean Currents Rain Shadows