Work from 9.11.15
advertisement

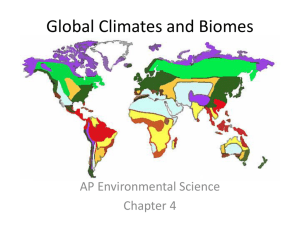
APES Module 10—Air Currents Name __________________________ Why does warm air have a lower density than cold air? The unequal heating of Earth affects climates because it determines regional _____________________ and it drives the _____________________ of air around the planet. Atmospheric Convection Currents Air has four properties that determines its movement: • (1) Density—the density of air determines its _____________________ • -less dense air _____________________, denser air ____________________ • Why does warm air rise? • (2) Water vapor capacity- warm air has a _____________________capacity for water vapor than cold air. The maximum amount of water vapor in the air is __________________________________________ When the temperature of air falls, its saturation point _____________________, water vapor _____________________ and _____________________ happens • • (3) response to changes in _____________________ Adiabatic heating or cooling- as air rises in the atmosphere its pressure _____________________and the air _____________________. Conversely, as air sinks, the pressure _____________________and the air _____________________in volume. (4) Latent heat release- when water vapor in the atmosphere condenses into liquid water and energy is _____________________. • Formation of Convection Currents • Atmospheric convection currents are global patterns of air movement that are initiated by the _____________________heating of Earth. Air warmspressure ______________________ air _____________________ _____________________ atmospheric pressure _____________________ cooling condensation and _____________________ _____________________ release air _____________________ air _____________________ more _____________________ atmospheric pressure _____________________ cooling _____________________ displacement and sinking _____________________ atmospheric pressure _____________________ warming Hadley cells- the convection currents that cycle between the equator and _____________________ north and south. Why are regions at 30oN and 30oS hot, dry deserts? Intertropical convergence- the area of Earth that receives the _____________________sunlight and where the _____________________branches of the two Hadley cells converge. Polar cells- the convection currents that are formed by air that rises at 60˚ north and south and sinks at the _____________________ (90˚ north and south) Ferrell cell—a convection current in the atmosphere that lies between _____________________ and _____________________ Describe each process: • Earth's Rotation and the Coriolis Effect • As Earth rotates, its surface moves much faster at the equator than in mid-latitude and polar regions. • The faster rotation speeds closer to the equator cause a deflection of objects that are moving directly north or south. • Earth's Rotation and the Coriolis Effect • Coriolis Effect- the deflection of an object's path due to Earth's rotation. • The prevailing winds of the world are produced by a combination of atmospheric convection currents and the Coriolis effect. • Earth's Tilt and the Seasons • The Earth's axis of rotation is tilted 23.5 ˚. • When the Northern Hemisphere is tilted toward the Sun, the Southern Hemisphere is tilted away from the Sun, and vice versa.