Primary motor cortex
advertisement

The “black box” brain
Character
Co-ordination
Non-conscious
control
Thinking
What does
our brain do?
Talking
Sensing
Moving
Remembering
Calculating
Planning
Biological Psychology
Biological psychology
Behaviour
Ethology
Animal learning
theory
Brain and behaviour
Psychopharmacology
Brain structure
and function
Organisation of the mammalian
nervous system
Voluntary NS
Peripheral NS
Sympathetic NS
Autonomic NS
Parasympathetic NS
Nervous
system
Spinal cord
Central NS
Brain
Telencephalon
Cortex
&&
Cortex
Diencephalon
Forebrain
Forebrain
Mesencephalon - Midbrain
- Midbrain
Metencephalon
- Pons,
cerebellum
Rhombencephalon
– Hindbrain
Myelencephalon - Medulla
} {} {
The divisions of the brain
Telencephalon
Diencephalon
Cortex
Basal ganglia
Hippocampus
Amygdala
Thalamus
Hypothalamus
Mesencephalon Metencephalon Myelencephalon
Tectum
Tegmentum
Pons
Cerebellum
Medulla
Subcortical organisation
Cerebral Cortex
Hippocampus
Learning & memory
Corpus Callosum
Connection the two
cortical hemispheres
Cerebellum
Movement, balance,
posture
Basal ganglia
Control of
behavioural patterns
Thalamus
Interface between the
cortex and the rest of
the nervous system
Brainstem
Control of autonomic
function
Hypothalamus
Homeostasis, emotion
Control of endocrine
(hormone) system
Spinal cord
Nerves going to and from
the rest of the body
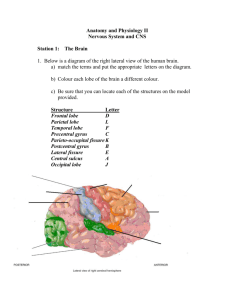
The lobes of the cerebral cortex
Precentral
gyrus
Central
Sulcus
(or fissure)
Postcentral
gyrus
Parietal
lobe
Frontal lobe
Occipital
lobe
Cerebellum
Lateral (Sylvian)
fissure
Temporal lobe
Comparative Brain Structure
(cortical)
Adult
brain
weight
Cortex
as %
Brain wt.
Surface
Area
(cm2)
Rat
2
31
6
Cat
30
60
83
Chimpanzee
420
65
1,000
Human
1,400
80
2,500
Sulci (fissures) – infoldings of the surface
Gyri – the bumps on the cortical surface
Understanding cortical function
• Brain damaged patients
• Assess cognitive deficit
• Locate area of brain damage (post-mortem, neuroimaging)
• Functional neuroimaging
• Functional MRI measurements during task performance
• Measure areas activated by different aspects of the task
Sensory areas of the cortex
Primary somatosensory cortex
Somatosensory association cortex
Primary auditory cortex
Auditory association cortex
Multimodal association cortex
Primary visual cortex
Visual association cortex
Primary olfactory cortex
Olfactory association cortex
We will explore the
visual system in more
detail in lecture 4
Motor control
Primary motor cortex
Motor output to skeletal muscles
Supplementary motor cortex
Motor planning
Basal Ganglia
Motor patterns
Cerebellum
Motor coordination
We will explore motor
control in more detail in
lecture 5
Higher cognitive function
(reasoning, personality, emotion, learning and memory)
Frontal Cortex
Calculation, Reasoning, Inference
Rule learning
Prefrontal cortex
Personality, emotion
Temporal Cortex
Learning, Memory, Spatial recognition
The story of Phineas Gage
• Gage was a young railway construction supervisor in Vermont
• He was well liked, reliable, energetic and good at his job
• In September 1848, while preparing a powder charge for blasting a rock, he tamped a steel rod
into charge-filled hole, without putting in wadding.
• The charge exploded and blew the rod out of the hole straight at Gage
• It entered his head through his left cheek, destroyed his eye, traversed the frontal part of the brain,
and left the top of the skull at the other side.
• After the accident he became extravagant
anti-social, foulmouthed, bad mannered and
a liar: he could no longer hold a job or plan
his future.
• He died in 1861, thirteen years after the a
ccident, penniless and epileptic: no autopsy
was performed on his brain.
Tamping Iron dimensions : 1 meter in length, 2.5 cm diameter
Cortical areas controlling language
We will explore
language in more
detail in lecture 6
Arcuate fasciculus
Wernike’s area
Primary
motor cortex
Primary visual cortex
Broca’s area
Primary auditory cortex
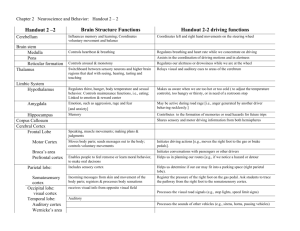
Summary of cortical function
Frontal lobe
- Planning
- Thinking
- Motor planning
- Motor output
Temporal lobe
- Hearing
- Smell
- Memory
- Feelings
Parietal lobe
- Spatial processing
- Spatial orientation
- Somatosensory
function
Occipital lobe
- Vision
- Visual processing
Inter hemispheric communication
the corpus callosum
Corpus callosum : a large bundle of fibres connecting the left and right cortices
Information Transfer in a
Normal Person
Left
Eye
Crossover
outside
brain
Information Transfer in a
"Split Brain" Patient
Right
Left
Eye
Eye
Crossover
outside
brain
Right
Eye
Visual Cortex
Visual Cortex
Visual Cortex
Visual Cortex
Language Cortex
Motor Cortex
Language Cortex
Motor Cortex
BRAIN
SPEECH
BRAIN
Crossover
outside
brain
Left hand
SPEECH
Crossover
outside
brain
Left hand
Studies on ‘split brain’ patients
Based on early work by Roger Sperry, for which he received a Nobel Prize in 1981
The word “ball” is presented in the left visual field only
The subject is asked to say what it is …..
….. and to select it from the objects behind the screen
Unable to say what the object is
• because of the organisation of the
visual pathway, only the right visual
cortex receives information from
the left visual field
Can pick out the ball with his left
hand, but not his right
• right somatosensory cortex (left
hand) ‘knows what it is looking for’,
but the left (right hand) does not
We will explore
laterality in more
detail in lecture 7
The cranial nerves
12 pairs of nerves on the base of the brain, which pass
through holes in the skull (cranium): analogous to spinal
nerves leaving the spinal cord
I
II
III
IV
V
VI
VII
VIII
IX
X
XI
XII
- Olfactory
- Optic
- Occulomotor
- Trochlear
- Trigeminal
- Abducens
- Facial
- Vestibulocochlear
- Glossopharangeal
- Vagus
- Spinal accessory
- Hypoglossal
Functions of the cranial nerves
I
II
III
IV
V
VI
VII
VIII
IX
X
XI
XII
Olfactory : Smell
Optic : Vision
Occulomotor : Eye movement; Pupil dilation
Trochlear :Eye movement
Trigeminal : SS information from the face and head; chewing muscles.
Abducens : Eye Movement
SS = somatosensory
Facial :Taste (anterior 2/3 of tongue); SS from ear;
muscles for facial expression.
Vestibulocochlear : Hearing; Balance
Glossopharangeal : Taste (posterior 1/3 of tongue); SS from tongue,
tonsil, pharynx; muscles for swallowing.
Vagus : Sensory, motor and autonomic functions of viscera
(glands, digestion, heart rate)
Spinal accessory : Controls muscles used in head movement.
Hypoglossal : Controls muscles of tongue