LESSON 3.2 The Brain
advertisement

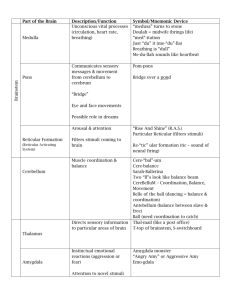
+ SUN DEVILS BEAT STANFORD 2610! ASU is 5-1! Next up- @ Washington How was your weekend??? Continuing the brain this week + Learning Goals: Students will be able to: Identify the structure and functions of the human brain Today- using your book to READ and identify key features of the brain Reinforcing activity May do with partners Must finish in class + Learning Goals: Students Identify will be able to: the structure and functions of the human brain. Discuss the ways the brain helps humans in their daily life. Quick activity: DRAW out the learning goal Stick figures please Show me that you understand what the learning goal is trying to get you to do. Slide 4 + The Brain + Pinkie and the Brain http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=snO68aJTOpM&list=PL02 DaVPqFP-P5SNpVHyjLrdrxn7cTxL0M + Who has the larger brain? + Facts about the Brain Weighs approximately 3 pounds Mostly water - 78% Fat - 10% Protein - 8% Soft enough to cut with a butter knife Grapefruit-sized organ + Three Major Areas of the Brain Hind brain Mid Brain Fore Brain + Hindbrain + Hindbrain The hindbrain is the part of the brain found at the rear base of the skull that controls the most basic biological needs for life. Sli de 10 + Medulla, Pons, Cerebellum • Pons: above the medulla ▫ • Medulla: middle of spinal cord ▫ • Sleep and arousal Controls breathing, heart rate, swallowing and digestion, upright posture Cerebellum ▫ Regulation and coordination of movement ▫ learning Sli de 11 + Damage DAMAGE TO THE CEREBELLUM Results in deficits in balance, coordination, skilled movement. Shake my hand… DAMAGE TO THE BRAIN STEM Results in the disruption of vital involuntary actions such as heart rate, breathing death + Midbrain + Midbrain The midbrain is the part of the brain above the hindbrain that plays a role in attention, stimulation, and consciousness. + Reticular formation: Regulation and maintenance of sleep and consciousness Startled by loud noiseheightened arousal Sleep through familiar sounds Damaged: may have permanent coma + Limbic System Limbic System: inter-related doughnut shaped neural structures. Two main structures: Amygdala: controls fear and aggression Hippocampus: memory formation Removed for H.M. Sli de 16 + 50 First Dates… http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ErjP5xMTc8I + The Vow- Hippocampus http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IGjUAHS8pHY + Forebrain + Forebrain The forebrain is the part of the brain above the midbrain + Thalamus Thalamus: the brains sensory relay station. Sorts and sends messages from the eyes, ears, tongue, and skin to other parts of the brain. Kind of like sorting the mail… Sli de 21 + Hypothalamus Hypothalamus: located under the thalamus ▫ ▫ ▫ Provide homeostasis, constant internal body state Regulates eating and drinking Eating, shivering, hunger, anger and emotion + Are you hungry? If yes, your blood sugar and body temperature are probably low. The hypothalamus uses these cues, along with others, to tell us we’re hungry. AS we eat our blood sugar level and temperature level rise, and our hypothalamus tells us that we are full. This explains why we sometimes sweat when we eat. It also explains why we eat less when we’re warm. Sli de 24 + Activity: TED Talk http://www.ted.com/talks/allan_jones_a_map_of_the_brain + Block Day: WOO HOO!!! Looking at the lobes of the brain Lobotomies Drawing out your brain TWO WEEKS: project is due… Will be in Seattle Friday- so will see you Monday Hiking the Grand Cayon with Mrs. Gould November 14-15want to join??? + Slide 27 Brain Part II: The Lobes + Retrograde Amnesia- Hippocampus http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qRzjur-rBvY + Four Lobes of the Brain Frontal Parietal Occipital Temporal + Lobes of the Brain - Frontal Where: The Frontal Lobe of the brain is located deep to the Frontal Bone of the skull; they are the largest Higher mental processes: •Decision making •Emotional control •Planning •Social skills •Abstract thinking •Moods- positive and negative + Damage to Frontal Lobe Changes in awareness Lack of understanding of or concern for past or future events Decreased Lack range of emotions of goal-directed behavior Inappropriate behaviors or reactions, especially to social situations + Possible Scenario Someone with frontal lobe damage walks into the bedroom to make the bed, becomes distracted by the wallpaper, which he decides to be changed and rips it down! My uncle…. Sli de 32 + Lobotomies… + The Lobotomist http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_0aNILW6ILk + Lobes of the Brain - Parietal Lobe • Where: The Parietal Lobe of the brain is located deep in front of the occipital lobes, behind the frontal lobe. Higher Mental Processes: -Spatial awareness and perception -Touch sensation -Perception + Damage to Parietal Lobe astereognosis touching them). (objects can not be recognized by + Hemi spatial neglect If an entire hemisphere of the parietal is damaged, the result is hemi spatial neglect: where an individual is oblivious to one half of their visual field. + http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ymKvS0XsM4w + Prosopagnosia Damage to the back of the parietal on both sides may result in prosopagnosia, the inability to recognize faces. You can still recognize objects, and features of faces, but you can not put the features together to recognize a face. + http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vwCrxomPbtY + Occipital Lobe How do you paint or create art? Do you visualize the art before you begin? Does your mental image change as the process progresses? It is the occipital lobe that helps us visualize something even before it exists! Sli de 45 Lobes of the Brain – Occipital Lobe Where: The Occipital Lobe of the Brain is located behind the parietal lobe. Primary function: •Processing of shapes, colors and motion • integration •interpretation of VISION and visual stimuli. Damage: •Can cause blindness even if the eyes are healthy. Temporal Lobes Where: Located on the sides of the brain, on the underneath of ‘everything else’, near the temples. Primary Function: - Information Retrieval (Memory and Memory Formation) -Hearing and language Damage: - To the left, can have trouble with differentiating what words and sentences mean. + Broca’s Area + Damage to Broca’s Area Damage to Broca’s Area results in Aphasia (the inability to use spoken language properly). They often omit small words such as "is," "and," and "the." For example, a person with Broca's aphasia may say, "Walk dog," meaning, "I will take the dog for a walk," or "book book two table," for "There are two books on the table." People with Broca's aphasia typically understand the speech of others fairly well. Because of this, they are often aware of their difficulties and can become easily frustrated. + http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=f2IiMEbMnPM + Wernicke’s Area + Damage results in problems in receptive language (you can not understand what you hear.) may speak in long sentences that have no meaning, add unnecessary words, and even create made-up words. For example, someone with Wernicke's aphasia may say, "You know that smoodle pinkered and that I want to get him round and take care of him like you want before.“ As a result, it is often difficult to follow what the person is trying to say. + http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dKTdMV6cOZw + Activity: Draw your own brain Trace your partners head on TWO sheets of paper. On one side, label the parts of the hind brain, mid brain, and fore brain, including the medulla, pons, cerebellum, reticular formation, hippocampus, amygdala, thalamus and hypothalamus. On the other side: Lake the occipital, parietal, frontal and occipital lobe. Draw images that represent the function of that part of the brain. Sli de 54 + Monday, October 27th Welcome Back! ASU Won 24-10 Against Washington in Seattle VERY tired today Great JOB Chandler Football- I’ll be at the dinner Thursday M-looking at the Split Brains/ Brain Review T- L/R side of brain W/TR- Endocrine System F- Halloween Psych Special BRAIN DAY: NEXT WEEK + Collect your brain diagrams now + Slide 57 Brain Part III: Split Brain Patients and Hemispheres + The Corpus Callosum •The corpus callosum is a thick band of nerve fibers that divides the cerebrum into left and right hemispheres. •connects the left and right sides of the brain allowing for communication between both hemispheres. Sli de 58 + Split-Brain Patients Split brain patients: had the nerves of their corpus collosum surgically cut to help with epileptic seizures. Helped the seizures; kept personality intact Right and left hemispheres had no longer a direct connection Sli de 59 + Take out two pencils or pens With your right hand draw a circle on a piece of paper WHILE you are drawing a square on a piece of paper. Your corpus collosum is intact! If it wasn’t, the right and left hemisphere could work independently like split brain patients. Sli de 60 + Severed Corpus Collasum http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lfGwsAdS9Dc + Tuesday, October 28th Welcome Notes Back!! and an activity today REMINDER: BRAIN DAY NEXT THURSDAY Get out your notes please! + The Cerebral Cortex The cerebral cortex is the thinking center of the brain that coordinates and integrates all areas of the brain into a fully functioning unit. Sli de 63 Cerebrum -The largest division of the brain. It is divided into two hemispheres, each of which is divided into four lobes. Cerebrum Cerebru m Cerebellum http://williamcalvin.com/BrainForAllSeasons/img/bonoboLH-humanLH-viaTWD.gif + Cerebral Features: • Gyri – Elevated ridges “winding” around the brain. • Sulci – Small grooves dividing the gyri – Central Sulcus – Divides the Frontal Lobe from the Parietal Lobe • Fissures – Deep grooves, generally dividing large regions/lobes of the brain Gyri (ridge) Sulci (groove) Fissure (deep groove) http://williamcalvin.com/BrainForAllSeasons/img/bonoboLH-humanLH-viaTWD.gif + Hemisphere Removal http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2MKNsI5CWoU + Split Brain patients + + Phineas Cage Phineas Cage Phineas Gage: Phineas Gage was a railroad worker in the 19th century living in Cavendish, Vermont. One of his jobs was to set off explosive charges in large rock in order to break them into smaller pieces. On one of these instances, the detonation occurred prior to his expectations, resulting in a 42 inch long, 1.2 inch wide, metal rod to be blown right up through his skull and out the top. The rod entered his skull below his left cheek bone and exited after passing through the anterior frontal lobe of his brain. Frontal Remarkably, Gage never lost consciousness, or quickly regained it (there is still some debate), suffered little to no pain, and was awake and alert when he reached a doctor approximately 45 minutes later. He had a normal pulse and normal vision, and following a short period of rest, returned to work several days later. However, he was not unaffected by this accident. + Contemporary Phineus Cage http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jK1sj4JEJ2o + Right Brain/ Left Brain? + Are you left brained or right brained? In general, the left and right hemispheres of your brain process information in different ways. We tend to process information using our dominant side. However, the learning and thinking process is enhanced when both side of the brain participate in a balanced manner. This means strengthening your less dominate hemisphere of the brain. + Dominance Activity Write LEFT, RIGHT, or NO PREFERENCE to these questions: Which hand do you write with? Which hand holds scissors? Which hand holds a hammer? Which arm goes first into a jacket? Which arm goes first into a loop of a book bag? Which hand is on top when you clap? Which hand deals out cards? Which foot kicks a ball? Sli de 76 + Tests https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zYZ1INWueKM https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9CEr2GfGilw + Right Brain/Left Brain Cross eyes Look at Center Watch the cross on the third circle. Every few seconds, it will change from a horizontal line to a vertical line and back. This is because the hemispheres of your brain are alternating in dominance for this activity. When the right hemisphere is dominant you see the blue circle and vertical line on top; when the left hemisphere is dominant, the red circle and horizontal line are on top. + + Known For: Left Processes things more in parts and sequentially Musicians process music in left hemisphere Language and Logic Right • Recognizing faces, analyzing visual-spatial information. • Geometry, chess. • Higher-level mathematicians, problem solvers, and chess players actually have more right-brained activity, but beginners use more left brain. + Rub your stomachs with one hand and pat your heads with another. Can you do this??? This illustrates that we really have two hemispheres that control opposite sides of the body. It also shows how well the two hemispheres work together. It’s rare for your hands to get confused, as in this activity. It’s also interesting to note that the brain will quickly adapt to dual tasks like this. Any musicians in the class? What was your coordination like when you first started? Those who type? Text? How was your coordination at first? Another example: write your name and rotate your leg at the same time- see if you can do it! Sli de 82 + Learning Style Left Right Learning Style If you are left brain dominant, then you probably like to work through learning step by step. You will prefer to start work on a broad goal or project, and fill in the detail, the specific skills you need as you go. Verbal Vs. Nonverbal Left Brain Right Brain Little trouble expressing Know what they mean themselves in words but often have trouble finding “right” words. + Reality-Based Vs. FantasyOriented Left Deals with the way things are—reality Adjust Want to things to know rules and follow them. If none, want to make up rules to follow. Right Try to change environment Not aware anything wrong Need constant feedback and reality checks + + + Learn best by… Left Left brains learn by hearing. They find the lecture system just fine. Right Right brains need to see something done-show me, to feel, and to actually experience the process--then, they remember. Lecture style is a challenge for a right brain. + Planning Left Lefts plan days in advance and are prepared for weekends, parties, and going to the movies. Right Rights decide things on the spur of the moment. +Neatness Lefts usually have a tidy personal space and know where things are. + Neatness Rights have a "piling" system that they use quite often. They sometimes say, "Don't touch my piles. I know where everything is." + Punctuality Lefts Lefts will be on time and even early for everything. They are the ones in the theatre before anyone else gets there. Rights Rights, on the other hand, are usually only on time for the most important things. Rights are likely to be on time for church if in the choir. If not in the choir, it is probably optional to be on time. + Gestures Lefts Lefts speak with few gestures and are not very animated. Their voice does not fluctuate much. Rights Rights can not talk without using the hands. Their facial expression and voice may both be quite animated and entertaining. + Activity: Split Brain You have a split brain in front of you On each of the sides, draw 8 different characteristics of the right and left side of the brain, for a total of 16 pictures. Make sure to label these pictures as to what each side does. When you are done, color each side of the brain. + Left/ Right Review What does your L & R side control? What is the L side more like? R side?