File
advertisement

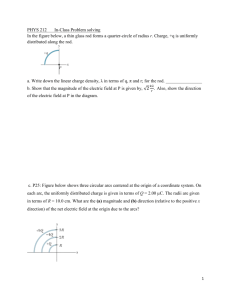
Name ________________________________________________________ Date _________ Per ______ Electrostatics Worksheet Fill In The Blank 1. Each electron and each proton bears a net charge of __________________________C. 2. The proton has a ____________________ charge, while the electron has a _______________ charge. 3. Under ordinary circumstances, an atom or molecule is electrically _________________. 4. Most electric phenomena are due to the movements of ____________________. 5. A neutral object becomes ___________________ charged if electrons leave. 6. Unlike charges ___________________ one another. 7. Because they are poor _____________________________, rubber and plastic rods are used for electrostatic experiments. 8. The process of charging a neutral body by touching it with a charged body is called charging by __________________________. 9. Charges added to a(n) ______________________ will immediately spread throughout it. 10. Charges added to a(n) _____________________ will not move away from it. 11. A charged body of either sign will __________________ a neutral body in which charge separation is induced. 12. The quantity of charge on an object is measured in the unit called the ____________________________. 13. When a rubber rod is rubbed against fur, ______________are stripped from the ______, giving the rod a net __________________ charge. 14. When a plastic rod is rubbed against cloth, ______________are stripped from the ______, giving the rod a net __________________ charge. Problems 15. Two metal balls carry charges of 3x10-6C and -6x10-6C. Their centers are 1 meter apart. a. What is the electrical force between them? b. Is this force attractive or repulsive? 16. A rubber rod with -4x10-6C is 0.1m east of a pith ball with a charge of 5x10-6C. A plastic rod with 2x10-6C is .05m north of the pith ball. a. Use Coulomb’s Law to find the magnitude of the electric force between the rubber rod and the pith ball. b. What is the compass direction of the rubber rod’s push/pull on the pith ball? c. Use Coulomb’s Law to find the magnitude of the electric force between the plastic rod and the pith ball. d. What is the compass direction of the plastic rod’s push/pull on the pith ball? 17. A thundercloud has an electric charge of 30C near the top of the cloud and -30C near the bottom of the cloud. The electric force between the set of charges is 3.6x106N. What is the distance between the charges? Matching 18. _____ A positively charged rod is brought near, but not touching the left side of a neutral sphere. 19. _____ A plastic rod is charged positively by rubbing it with felt. The felt is then touched to a neutral sphere and later removed. 20. _____ A positively charged rod is brought near a neutral sphere, the sphere is charged by induction, and the rod is taken away. 21. _____ A sphere is charged by conduction with a positive rod. 22. _____ A negatively charged rod is brought near but not touching the right side of a neutral sphere. 23. _____ A positively charged rod is brought near the right side of a sphere that was already positively charged.\ 24. _____ A person holding a metal rod touched it to a positively charged sphere. Multiple Choice 25. Which atom below is electrically neutral? 26. In which direction will the positively charged ball move (diagram to right)? 27. A negatively charged rod is brought near the right hand side of two neutral metal spheres that are touching one another while insulated from the ground. The spheres are then separated and the rod is taken away. Which pair of spheres shows the correct signs of each sphere’s net charge? 28. Two objects exert an electric force of size F on each other. If the charge on each object is doubled, the electric force will now be, A. 1/4 F B. F C. 2F D. 4F 29. Two objects exert an electric force of size F on each other. If the objects are moved three times closer together, the electric force will now be, A. 1/3 F B. 3F C. 1/9F D. 9F Use Information for Questions 29-31 Electric charges can be collected in a glass jar, which is referred to as a capacitor. The diagram shows a Leyden that is made by covering the inner and outer surfaces of a glass jar with pieces of metal foil. A metal rod protrudes through the top of the jar and a metal chain connected to the rod touches the metal foil inside the jar. A rubber rod is rubbed with fur and touched to the metal knob on the top of the jar. 30. What is the charge on the metal foil on the inside of the jar? a. Positive b. Negative c. Neutral 31. What is the charge on the metal foil on the outside of the jar? a. Positive b. Negative c. Neutral 32. If a person (who is insulated from the ground) touched one finger to the metal knob, and another finger to the metal foil on the outside of the jar, __________ would flow through them from the _________ to the ______. a. Electrons, knob, outer foil b. Electrons, outer foil, knob c. Protons, knob, outer foil d. Protons, outer foil, knob Answers: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 1.6x10-19 Positive, negative Neutral Electrons Positively Attract Conductors Conduction Conductor Insulator Attract Coulomb Electrons, fur, negative Electrons, rod, positive A. -0.162 N B. attractive A. 18 N B. east C. 36 N D. south 1499.17 m B D B C B C E B D C D D B A A