Speeches Focused on Persons
advertisement

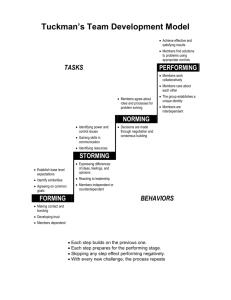
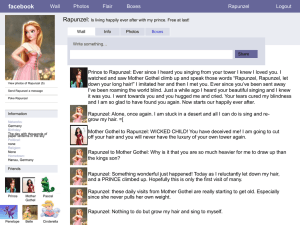
SEMESTER/FINAL EXAM Review Answers Life Cycle of a Group • • • • Forming Storming Norming Performing Performing Norming Storming Forming Forming • The infancy stage of a • Martha, Tim, Evonne, group in which and Sarah meet to members become start a book club. acquainted with one They have never met another and before, so they take leadership roles are the first meeting to established get to know each other better. Storming • The adolescent stage • Sariah and Jeff are of a group in which both members of a members challenge large volunteer group. goals and approaches They are each afraid in an effort to express that they will become individuality. just a random group member so they are always pushing their opinions on the group. They want to stand out. Norming • The cohesive stage in the formation of a group when members learn to function effectively as a group. • Jim has started to compromise on doing things his way, so that other members of his group feel welcome and appreciated. Performing • The final stage in the formation of a group when members bond and work together effectively and harmoniously. • Teresa’s research group has been working together for over 6 months. They now know what to expect from each other and how to compromise and accommodate their differences while still completing their goals. Factors that affect group discussion • • • • • • Size Cliques Personal Goals Physical Environment Seating Arrangement Time • These are influences over how successful/unsuccess ful a group is. Size • How big or small the group is. • This can alter success because of having too few or too many people. If the amount of group members is not appropriate to reach the goal, the group will be impacted. • Marcus is leading a research team that must work over the next year to collect rain samples in 12 locations. There are only 4 group members, which means they each have to go to multiple locations. If he had more people the task would be easier. Cliques • A small group of people within a group that isolate others. • When there is a small group of people working together within a group, they might interfere with the whole group goals and only focus on their own. If the clique sticks together it can create a power struggle. • Shawn, Mark, and Tom are best friends and part of a group of 10 people that meet to discuss music. They work toward controlling what types of music the group talks about because they all like the same thing and are such good friends. Personal Goals • An individual within a group is concerned with their own goals not the group’s goals. • This creates conflict when one person is using the group to further a personal goal or is not focusing on the group. • Jeremy wants to be asked to lead the next committee at work. Currently he is a committee member for the party committee. He wants to prove his leadership skills to the company, so often times takes over the group and ignores the current leader. Physical Environment • The actual place to meet and materials needed to reach the goals. • Without the proper setting or resources a group cannot function effectively. • Martin needs his group to be able to do internet research in order to complete the task on time. However, they only have access to 1 computer and have 12 group members. Seating Arrangement • Where everyone sits and who they sit by. • This impacts the idea of who is in control and may cause problems if people have personality conflicts. • Amber and Cheri talk a lot when they are together. It is almost impossible to get them to focus and be quiet. If they aren’t seated by each other, this is not a problem. Time • The actual meeting time(s) and the length of time given to complete a goal. • If the times are inconvenient for group members or there is not a reasonable amount of time to do the work, the group may not work out. • The Amazing Theater Group has been asked to write and perform a play for the city of Roanoke. They have only 2 weeks to write, design, rehearse, and perform a 14 person play. Outcomes of Discussion • Consensus- everyone • All 5 group members agrees vote the same • Compromise- some • Mark decides to give changes are made to in on one issue in reach an agreement order to get his way on another issue. • Majority vote- the majority of the group • 51% of the group vote have to vote the same for pepperoni pizza, 49% for cheese. Pepperoni wins. Types of Leadership • Appointed – a leader that is assigned the position to lead • Margaret is told by her boss to assemble a group of coworkers and be in charge of a finance committee. • Emergent – A leader that arises out of how the group works together • Super Book Club works very well together. They all noticed that Anne is really good at coordinating the dates and locations of their meetings. Anne’s skill has made her the leader of the book club. Speeches Focused on Persons Speech of Introduction • Speech used to build enthusiasm and interest for a guest speaker • Albert Einstein is going to speak to a group of 7th graders. Before he goes on stage, the counselor speaks a little bit about who Albert is and what he does. Speech of Presentation • Speech honoring the recipient of a gift or award. • The class president gives a speech to the school about Ms. Yaya in order to present the Teacher of the Year award. Speech of Acceptance • Speech of thanks given by a recipient of a gift or award. • Taylor Swift wins an award and gives a short speech about how grateful she is to her fans and the people that gave her the award. …then Kanye interrupts her… Commemorative Speech • An inspiring address designed to recall heroic events or people • Alexander presents a speech to his classmates in honor of all the people have served in the U.S. military. Testimonial Speech • An address of praise or celebration honoring living persons at occasions such as weddings, retirement dinners, or roasts. • Jamie gives a toast to the bride and groom at their wedding. It is a short speech about how awesome the couple is. Eulogy • A commemorative speech honoring an individual who has died. • Megan presented a speech about her grandmother at the funeral. Debate • To engage in argument by presenting opposing points. • Formal debate has 2 sides: Affirmative and Negative. • Arthur believes PS3 is better than XBOX 360. Marcus believes the opposite of that. They argue back and forth to show their side. Cross Examination • Used to clarify points and attempt to discredit your opponent. You should ask questions that are about the topic being debated. • Angela asks questions about her opponents’ points in order to better understand them. Time Requirements for Comm Apps Debates • • • • • • • 2 minutes for AFF 1 minute for CX 3 minutes for NEG 1 minute for CX 3 minutes for AFF 1 minute for CX 2 minutes for NEG Comm App Debate Case Requirements • 1 case has 5 arguments or points • Marty and Sam are affirmative for popcorn is better than candy. Their case: – Healthier – Get more for your money – More to share – No sugar, so makes a good school snack – Can make at home Oral Interpretation • The process by which a speaker performs literature aloud for an audience • Jack memorizes part of a book and performs it in front of his class. Minstrel/Bard • Professional storyteller from ancient times that traveled from village to village bringing news and entertainment. • Edward goes from town to town to tell stories and spread news. He is paid by the townspeople. Prose • The ordinary form of written or spoken language, without rhyme or meter. • “A long time ago, a husband and wife lived happily in a cottage at the edge of a wood. But one day the wife fell ill. She could eat nothing and grew thinner and thinner. The only thing that could cure her, she believed, was a strange herb that grew in the beautiful garden next to their cottage. She begged her husband to find a way into the garden and steal some of this herb, which was called rapunzel.” Types of Prose Fiction • Material created in the imagination. The prince saw the witch climb up the hair and disappear through the window, and he made up his mind he would wait until she had gone and see if he could do the same. So after the witch had gone, he stood where the witch had been and called, "Rapunzel, Rapunzel, let down your long hair." Nonfiction • Material based entirely on truth as the author understands it. • The Raymond Firehouse School is located in Raymond, Maine, a sleepy little town in a scenic part of the state of Maine. Hardly anything big ever happens in Raymond, Maine, except for the big herd of moose that once walked down Main Street on a Tuesday afternoon without any prior warning last November. Poetry • The communication of thought and feeling through the careful arrangement of words for their sound, rhythm, and meaning. Messy Room by Shel Silverstein Whosever room this is should be ashamed! His underwear is hanging on the lamp. His raincoat is there in the overstuffed chair, And the chair is becoming quite mucky and damp. His workbook is wedged in the window, His sweater's been thrown on the floor. … Types of Poetry Narrative Poetry • Poems that tell stories. On Turning Ten by Billy Collins The whole idea of it makes me feel like I'm coming down with something, something worse than any stomach ache or the headaches I get from reading in bad light-a kind of measles of the spirit, a mumps of the psyche, a disfiguring chicken pox of the soul. Lyric Poetry • “song-like” poetry expressing emotions. “A word is dead when it is said. Some say. I say it just begins to live that day.” ~Emily Dickinson Drama • Public communication that uses both language and actions to tell a story of human conflict. • 10 kids get together and memorize a script and act out a story in front of an audience. Rehearsals Blocking • Arranging the movements on stage of actors in a play • All 10 cast members get together and go through all the actions they will make during the play on stage. Off Book • Without a script, having memorized dialogue, cues, and blocking. • All the actors know their parts and go through the actions. The director may interrupt to make changes. Run-through • A rehearsal straight through from beginning to end. • The 10 actors go through the entire play in order to practice. Dialogue • A conversation; passages of talk in a play. • Mary’s character talks with another character in the play. Characterization • The movements and the voice that the character has. • Jackson decides to make the ant character have a squeaky voice and jump up and down when excited. Choreography • Dance patterns; the arrangement of the movements of a dance. • Thomas designs the way all the characters will move on the stage for the play. Parts of Storytelling • The teller • Who says it and how? • The tale • What is the story? • The tradition • Why do we tell stories? Delivery for Storytelling • Speak your story like a conversation. • Keep your eyes moving over your audience, but speak to one person at a time. • Stand or sit close to your audience. • Visualize all your work. Costuming • Dress appropriately – Eliminate anything that interferes with performing • Make it practical • Want the audience to focus on the story not your appearance • Don’t wear something that makes noise and covers up your voice. • Don’t wear something that prevents you from moving or talking. • Don’t wear something that is so weird your audience is distracted. Educational Value • Storytelling uses oral language. Our language comes alive when heard. • Storytelling develops memory. • Storytelling increases knowledge of literature. • We become better speakers. • We build our ability to memorize. • We hear and read more literature.