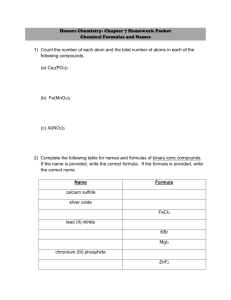
empirical formula - Madison Public Schools
advertisement

Section 6.3 Formulas of Compounds Objectives 1. Recognize and explain the differences between empirical and molecular formulas 2. Calculate the empirical formula of a compound from experimental data or percentage composition data. Section 6.3 Formulas of Compounds Empirical Formula: Examples Compound Hydrogen peroxide Water Ethane Tetrachloroethylene Molecular Formula Empirical Formula Section 6.3 Formulas of Compounds A. Empirical Formulas • The empirical formula of a compound is the simplest whole number ratio of the atoms present in the compound. • It may or may not be the exact molecular formula of a compound • The empirical formula can be found from the percent composition of the compound. Section 6.3 Formulas of Compounds B. Calculation of Empirical Formulas Section 6.3 Formulas of Compounds B. Calculation of Empirical Formulas Finding the empirical formula from experimental data Question: Determine the empirical formula of a compound containing 5.75 g Na, 3.5 g, N, and 12.0 g O. 1. Convert masses of each element into moles. Section 6.3 Formulas of Compounds B. Calculation of Empirical Formulas 2. Find mole ratios by dividing the # moles of each element by the smallest # of moles. 3. Write the empirical formula. Section 6.3 Formulas of Compounds B. Calculation of Empirical Formulas Finding the empirical formula from percent composition Question: Find the empirical formula for a compound that has the following mass percentages: C – 23.54 %, H – 1.98%, and F-74.48 %. 1. Convert percentages to maass (assume 100g sample) Section 6.3 Formulas of Compounds B. Calculation of Empirical Formulas 2. Follow the same procedure from the previous problem. Section 6.3 Formulas of Compounds C. Calculation of Molecular Formulas Objective: Determine the molecular formula for an unknown compound from its empirical formula and molar mass. Remember: An empirical formula is the simplest whole number ratio of atoms of each element that make up a compound. Section 6.3 Formulas of Compounds C. Calculation of Molecular Formulas A molecular formula gives the actual number of atoms of each element in a compound. • A molecular formula is always a whole number multiple of an empirical formula For example: Ethane (C2H6) is 2 X its empirical formula (CH3) • Therefore, the molar mass of a compound is a whole number multiple of the molar mass of the empirical formula Section 6.3 Formulas of Compounds Sample Problem: The empirical formula of a compound is C3H4NO3. The compound has a molar mass of 408 g/mol. What is the molecular formula of the compound? 1. Find the molar mass of the compound. 2. Divide the molar mass of the compound by the molar mass of the empirical formula. 3. Multiply the empirical formula by the result from #2 and write molecular formula. Section 6.3 Formulas of Compounds Formula Summary For the sugar glucose