Invest. securities
advertisement

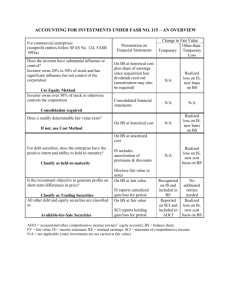
Investments in Debt and Equity Securities TEMPORARY INVESTMENTS Use of idle cash Low risk investments Quickly and easily converted to cash Securities of federal, state, and local government agencies LONG-TERM INVESTMENTS Develops beneficial intercompany relationships. May indirectly improve profitability of investing company. May represent ownership interest. ACCOUNTING ISSUES Classification issues – Management’s intended holding period for the security Valuation and investment income measurement – Cost vs. fair value – Treatment of holding gains & losses Disclosure issues Invest. secur - 5 ACCOUNTING FOR VARIOUS INVESTMENTS Classification Investment in Debt Securities Investment in Equity Securities Control-greater than 50% ownership of voting stock Not applicable Consolidation Significant influence - 20% to 50% ownership of voting stock Not applicable Equity method Debt securities classified as held to maturity, and equity securities for which fair value is not readily determinable Amortized cost method Cost method Debt and equity securities classified as trading securities Fair value method, with unrealized holding gain or loss included in earnings Debt and equity securities classified as available for sale Fair value method, with unrealized holding gain or loss included as a component of comprehensive income/ stockholders’ equity CLASSIFYING INVESTMENTS Debt or equity security? Fair value readily determinable? Management’s intended holding period? Influence or control over investee? Only for equity securities with voting rights DEBT SECURITIES n Represent creditor relationship with an entity – US Treasury securities, municipal securities, corporate bonds, convertible debt, commercial paper, and redeemable preferred stock EQUITY SECURITIES n Represent ownership interest in an entity or the right to acquire or to dispose of an ownership right at a fixed price – Capital stock (common and preferred), warrants, rights, and options EQUITY SECURITIES CONTROLLING INTEREST Investor (parent) owns more than 50% of voting stock in investee (subsidiary). = Consolidated financial statements EQUITY SECURITIES SIGNIFICANT INFLUENCE Investor holds 20% to 50% of voting stock = Equity method EQUITY METHOD The investment account is increased by: – Original investment cost – Proportionate share of investee's earnings The investment account is decreased by: – Dividends received EQUITY SECURITIES NO SIGNIFICANT INFLUENCE Investor holds less than 20% of voting stock Measure carrying value of securities at fair value, if readily determinable. = If fair value is not readily determinable, use cost method. DEBT SECURITIES CLASSIFICATION Held to maturity (HTM) – Only for debt securities – Investor intends and has the ability to hold security to maturity date. – Carry at amortized cost on balance sheet. DEBT & EQUITY SECURITIES CLASSIFICATION Trading securities (TS) – Debt or equity securities – Bought and held primarily to be sold in the near term – Current assets – Unrealized holding gains and losses included in earnings (net income) DEBT & EQUITY SECURITIES CLASSIFICATION Securities available for sale (SAS) – Debt or equity securities – Investments expected to be held for an unspecified period of time – Typically noncurrent assets – Unrealized holding gains and losses reported as a separate component of stockholders’ equity TS AND SAS ACQUISITIONS Recorded at cost when acquired. – Purchase price and incidental costs Basket purchase requires allocation of the total cost to each class of security purchased. – Based on relative market values TS AND SAS RECORDING AT FAIR VALUE TS and SAS are reported at fair value on the balance sheet. The difference between the fair value and the carrying value from the previous balance sheet date (cost if acquisition occurred in the current period) is an unrealized holding gain or loss. TS AND SAS RECORDING AT FAIR VALUE The unrealized holding gain or loss must be determined for individual securities. Each security has a valuation allowance account. TS AND SAS RECORDING AT FAIR VALUE The individual unrealized holding gains and losses are added together to arrive at the net portfolio unrealized holding gain or loss. Net unrealized holding gains and losses are calculated separately for the TS portfolio and the SAS portfolio. NET UNREALIZED HOLDING GAINS AND LOSSES Trading securities: The net unrealized holding gain or loss is treated as a component of investment income and is included on the income statement for the period. NET UNREALIZED HOLDING GAINS AND LOSSES Securities available for sale: The net unrealized holding gain or loss is not included in earnings for the period but rather is closed to a separately reported component of stockholders’ equity. TS AND SAS TRANSFERS Transfers are accounted for at fair value on the transfer date. Fair value at the reclassification date is regarded as cost of the security for accounting purposes. TS AND SAS TRANSFERS The entry will: – Remove the investments at cost. – Record the investments with a carrying value equal to fair value. – Remove the valuation accounts. – Recognize the portion of unrealized holding gains or losses not previously included in income. TS AND SAS SALES Sales are accounted for in a manner similar to transfers. The only difference is that Cash is debited instead of the fair value of the securities. EQUITY INVESTMENTS SPECIAL ISSUES Stock dividends and stock splits – Not included in investment revenue. – Increase in number of shares reduces carrying value per share. EQUITY INVESTMENTS SPECIAL ISSUES Stock rights (Warrants) – Allocate investment cost between stock and stock rights based on market value of stock and stock rights. – Reported at fair market value.