Cell Quiz Review
advertisement
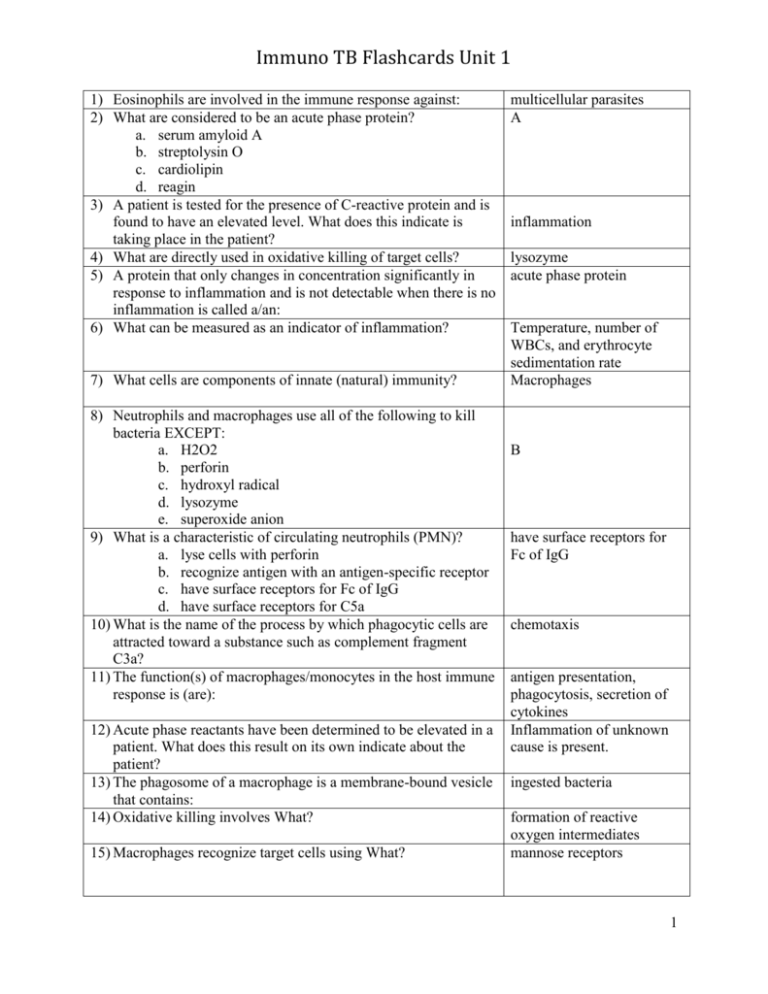
Immuno TB Flashcards Unit 1 1) Eosinophils are involved in the immune response against: 2) What are considered to be an acute phase protein? a. serum amyloid A b. streptolysin O c. cardiolipin d. reagin 3) A patient is tested for the presence of C-reactive protein and is found to have an elevated level. What does this indicate is taking place in the patient? 4) What are directly used in oxidative killing of target cells? 5) A protein that only changes in concentration significantly in response to inflammation and is not detectable when there is no inflammation is called a/an: 6) What can be measured as an indicator of inflammation? 7) What cells are components of innate (natural) immunity? 8) Neutrophils and macrophages use all of the following to kill bacteria EXCEPT: a. H2O2 b. perforin c. hydroxyl radical d. lysozyme e. superoxide anion 9) What is a characteristic of circulating neutrophils (PMN)? a. lyse cells with perforin b. recognize antigen with an antigen-specific receptor c. have surface receptors for Fc of IgG d. have surface receptors for C5a 10) What is the name of the process by which phagocytic cells are attracted toward a substance such as complement fragment C3a? 11) The function(s) of macrophages/monocytes in the host immune response is (are): 12) Acute phase reactants have been determined to be elevated in a patient. What does this result on its own indicate about the patient? 13) The phagosome of a macrophage is a membrane-bound vesicle that contains: 14) Oxidative killing involves What? 15) Macrophages recognize target cells using What? multicellular parasites A inflammation lysozyme acute phase protein Temperature, number of WBCs, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate Macrophages B have surface receptors for Fc of IgG chemotaxis antigen presentation, phagocytosis, secretion of cytokines Inflammation of unknown cause is present. ingested bacteria formation of reactive oxygen intermediates mannose receptors 1 Immuno TB Flashcards Unit 1 16) Diapedesis is: 17) The respiratory burst is: 18) What is part of the external defense system? 19) Which is characteristic of natural immunity? 20) What is the major function of C-reactive protein (CRP)? 21) All of the following are considered part of natural immunity EXCEPT: a. eosinophils b. lymphocytes c. acute phase reactants d. neutrophils 22) Where does the immune response to foreign antigen in the tissue mainly occur? 23) Which white cell in the peripheral blood migrates to the tissue to become a macrophage? 24) What acute phase reactants is an important clotting factor? 25) Which substance best inactivates bacterial proteins? 26) A white blood cell that is 16 to 18 um in diameter, has a horseshoe-shaped nucleus, and is capable of further differentiation in the tissues best describes: 27) Jenner's discovery that cowpox generated immunity against smallpox is based on the principle of: 28) All of the following are characteristic of acute phase reactants EXCEPT: a. increase rapidly in response to infection b. used to diagnose a specific disease c. enhance phagocytosis d. promote inflammation 29) What is the function of the acute phase protein haptoglobin? 30) Measurement of CRP levels could be used for What? 31) Acquired (adaptive) immunity can be characterized by What? 32) Neutrophils are characterized by all of the following EXCEPT: a. found in the marginating pool in blood vessels b. capable of diapedesis c. granules stain bright orange with Wright stain d. segmented nucleus cells squeezing through endothelial cells to leave the circulation an increase in oxygen consumption skin It depends on normally present body functions. acts as an opsonin B lymph nodes monocyte fibrinogen OCl– monocyte cross-immunity B binds hemoglobin to determine risk of a heart attack, to determine flare-up of rheumatoid arthritis, to detect an inflammatory process involves memory C 2 Immuno TB Flashcards Unit 1 33) All of the following occur during the process of inflammation EXCEPT: a. increased capillary permeability b. migration of basophils to tissue c. increase in blood flow d. swelling and pain 34) What best explains the reaction that takes place in the latex agglutination slide test for CRP? 35) What is true of NK cells? 36) What is NOT characteristic of acquired immunity? A. Memory is involved. B. Lymphocytes play a major role. C. It is very specific. D. It depends on normally present body functions. 37) All of the following are characteristic of a lymph node EXCEPT: a. filters drainage from tissues b. colonized with T and B cells c. between 1 and 25 mm in size d. considered a primary or central lymphoid organ 38) What represents the best explanation for the action of natural killer (NK) cells? 39) All of the following are considered part of natural immunity EXCEPT: a. eosinophils b. lymphocytes c. acute phase reactants d. neutrophils 40) Macrophages that migrate to the liver are called: 41) Acquired immunity can be characterized by What? 42) The ability to resist infection through normally present body functions best characterizes: 43) A white blood cell described as between 12 to 22 um with a large horseshoe-shaped nucleus that further differentiates in the tissue to become a macrophage best describes: 44) What is considered part of the internal defense system? a. cilia b. mucous membranes c. neutrophils d. acidity of the skin B Latex particles are coated with anti-CRP. They kill tumor and virally infected cells. D D They kill by releasing perforins B Kupffer cells involves memory natural immunity monocyte C 3 Immuno TB Flashcards Unit 1 45) All of the following are part of the process of phagocytosis EXCEPT: a. formation of a phagosome b. creation of hypochlorite radicals c. formation of fibrin clots d. outflowing of cell cytoplasm 46) All of the following are examples of natural immunity EXCEPT: a. skin as a structural barrier b. acute phase reactants c. phagocytosis d. antibodies 47) If a slide test for CRP is positive, what does this indicate? 48) All of the following are considered acute phase reactants EXCEPT: a. fibrinogen b. complement c. C-reactive protein d. TNF-alpha 49) B cells that respond against self-antigens will undergo: C D It is a nonspecific indicator of inflammation D receptor editing, anergy, apoptosis memory lymphocyte 50) A cell that can recall previous contact with a particular antigen so that subsequent exposure leads to a more rapid and more effective immune response than the first encounter is by definition which type of cell? 51) D-J rearrangements only have occurred in which stage of B cell pro-B cell development? 52) The germinal center of a lymph node is made up primarily of B cells which type of cell? 53) The purpose of negative selection of B cells is to: Identify B cells that are specific for self-antigens. 54) B cells that express low-affinity IgM, respond to bacterial B-1 cells polysaccharides, and express CD5 are known as: 55) When IgM on the surface of an immature B cell binds to a self- apoptosis antigen, What processes can occur? 56) What distinguishes mature B cells from B cells at other stages co-expression of IgM and of development? IgD 57) What would NOT be found on the surface of a mature, naive B cell? 58) Antigen-independent differentiation of B cells occurs in the: 59) What would be found on the surface of a pre-B cell? 60) The primary site of antigen trapping and presentation to immune cells is the: surrogate light chains bone marrow mu and surrogate light chains spleen 4 Immuno TB Flashcards Unit 1 61) Predominant cell types involved in the humoral immune response are: 62) The receptor for antigen on a mature naïve B cell is: 63) The difference in kinetics between a primary and secondary immune response is due to the presence of: 64) The only cells in the body capable of specifically recognizing and distinguishing different antigenic determinants are: 65) Tissues that function by trapping and concentrating antigens for presentation to cells of the immune system are known as: 66) Neutrophils and other cells have receptors on their surface that bind to the Fc region of IgG, which is known as: 67) T lymphocytes undergo antigen-independent maturation in the: 68) T helper cells recognize what? 69) How are cytotoxic T cells and natural killer cells similar? 70) T cells travel from the bone marrow to the thymus for maturation. What is the correct order of the maturation sequence for T cells in the thymus? 71) Immunoglobulin and T-cell receptors are similar in what properties? 72) T cells emerging from the thymus are: 73) Perforin and granzymes are used by which cells to kill target cells? 74) Which T cell surface protein is associated with the T-cell receptor and is involved in signal transduction? 75) Cytotoxic T cells are the primary immune response against which pathogen? 76) The cells that primarily function by secreting large amounts of cytokines are: 77) The purpose or end result of negative selection of the T cell is to ensure: 78) What binds to CD16 on the surface of natural killer cells? 79) What exhibits allelic exclusion in its expression? 80) Helper Tcels function directly in: 81) An immune T cell differs from a mature T cell because an immature T cell: 82) Natural killer cells recognize and kill target cells that are: 83) A T cell that is rarely found in secondary lymphoid organs and recognizes a limited number of native epitopes is known as a(an): 84) What cells that participate in cell-mediated immunity are antigen specific and directly cytotoxic for target cells? B cells IgM memory cells in the secondary response lymphocytes peripheral or secondary lymphoid organs CD16 thymus exogenous peptide bound to class II Both induce apoptosis in the target cell. maturation and selection occur in the cortex, then the medulla; release of mature T cells to secondary lymphoid organs multiple gene segments encoding the variable region MHC restricted, selftolerant, antigen specific natural killer cells and CD8 T cells CD3 viruses T helper cells self-tolerance Fc of IgG T-cell receptor delayed-type hypersensitivity co-expresses CD4 and CD8 lacking expression of HLA-A, B, and C gamma-delta T cell cytotoxic cells 5 Immuno TB Flashcards Unit 1 85) What is a cytotoxic T cell membrane-bound factor that is involved in Fas ligand inducing apoptosis in target cells? 86) T cells differ from B cell in what ways? a. T cells express surface immunoglobulin b. B cells express CD19 but not CD3 c. T cells express CD19, CD3, and CD4 d. B cells express surface immunoglobulin and CD3 87) The T-cell receptor for antigen comprises what molecules? 88) Granzymes activate what in a target cell? 89) In antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity, target cells are recognized by what? 90) All of the following are characteristic of a lymph node EXCEPT: a. filters drainage from tissues b. colonized with T and B cells c. between 1 and 25 mm in size d. considered a primary or central lymphoid organ 91) Which marker would be found on pre-B cells? 92) What represents the best explanation for the action of natural killer (NK) cells? 93) A lymphocyte exhibits the following markers: CD19, IgM, IgD, What is its likely identity? 94) Sheep red blood cells forming rosettes around T cells is due to the presence of What T cells? 95) All lymphocytes arise from stem cells made in the: 96) Which best describes the specific antigen receptor that is part of CD3 found on T cells? 97) Which is a primary lymphoid organ? 98) Which cell is capable of producing antibody? 99) A plasma cell differs from a B cell in which way? 100) 101) The function of T cells with CD4 antigen is what? The stage in B cell development in which TdT and RAG enzymes appear is called: 102) What contain B cells that are actively responding to antigen? 103) What surface markers are found on mature B cells? 104) Lymphocytes that have IgM, IgD, and MHC class II antigens on their surface, and they mature in the bone marrow itself, are: 105) Which cells are responsible for killing virally infected host cells and tumor cells? 106) What surface markers are found on mature T cells? 107) Lymphocytes that mature in the thymus are involved in which immune response? 108) Which marker is found on the group of T cells that assist B cells in making antibody? 109) What would be considered a primary lymphoid organ? B alpha and beta chains apoptosis CD16 on the effector cell binding to Fc of IgG bound to target cell D μ heavy chains They kill by releasing perforins mature B cell CD2 bone marrow Alpha and beta chains bind antigen thymus plasma cell Only plasma cells secrete circulating antibody to help B cells make antibody thymocyte germinal centers IgM and IgD B cells CD8 T cells CD3 cytokine-mediated responses CD4 bone marrow 6 Immuno TB Flashcards Unit 1 110) Where does contact with antigen and activation of B cells normally occur? 111) Another name for antigenic determinant is: 112) The best immunogen would be: 113) A 50 kDa protein from a bacterial cell that has numerous different epitopes would be called: 114) What molecules are the better immunogen? 115) A low-molecular-weight molecule that has one binding site for an antibody would be what? 116) All of the following are characteristics of both MHC class I and class II molecules EXCEPT: 117) Which MHC class of antigens is necessary for antigen recognition by CD4-positive T cells? 118) Class II molecules bind to what kind of peptides? 119) MHC class II molecules have specificity for: 120) Major histocompatibility (MHC) molecules containing beta-2-microglobulin: 121) The purpose of the invariant chain (Ii, CD74) is to block the peptide-binding site of: 122) What is a characteristic of HLA-DR, -DP, and -DQ molecules? 123) Which is characteristic of thymus-dependent antigens? 124) T-independent antigens: 125) Endogenous peptides binding to HLA-A, B, or C molecules on the surface of hepatocytes is critical for the response by: 126) What substance and what molecular weight is likely to be the most immunogenic? 127) Antigens found in different species that trigger a similar antibody response are called: 128) Blood from a suspect is typed to see if it is a match with a sample found at the crime scene. The suspect's blood exhibits the following reactions: no agglutination with anti-A, no agglutination with anti-B. What is the suspect's blood type? 129) The ability to respond to antigen depends on what factors? 130) A macromolecule that is capable of eliciting an immune response in an immunocompetent host is called a(an): 131) When a human responds to a bacterial antigen, the bacterial antigen is classified as a(an): in lymph nodes epitope multivalent with many specificities immunogen and antigen protein hapten expressed constitutively on all nucleated cells class II processed exogenous peptides with a particular motif are determined by HLAA, HLA-B, and HLA-C genes class II molecules expressed co-dominantly (maternal and paternal) They are proteins stimulate primarily an IgM response cytotoxic T cells a protein with a molecular weight of 45,000 d heterophile antigens type O Age, proper nutrition, genetic predisposition antigen heteroantigen 7 Immuno TB Flashcards Unit 1 132) Which best describes a finding of Landsteiner's study of haptens? 133) Naturally occurring anti-A and anti-B antibodies are thought to be due to exposure to what? 134) A substance that is too small to stimulate antibody production by itself unless it is attached to a larger carrier molecule is called a(an): 135) If a determinant site on a molecule that stimulates antibody formation is produced by the folding of the primary chain, this is known as a: 136) If a person has a reaction to poison ivy, this is due to: 137) A substance used to enhance antibody formation is called a(n): 138) The use of an aluminum salt in the hepatitis vaccine is an example of a 139) What is the function of TAP proteins used in antigen processing? 140) MHC class II antigens are recognized by what cells? 141) What best describes HLA class II molecules? a. They interact with CD8+ T cells. b. They have an alpha chain and beta-2 microglobulin. c. They have alpha and beta chains of equal size. d. They combine with antigen made inside the cell. 142) If a mother is HLA A3A14/ B5B15/ Cw3Cw4, and her child is A3A9/B5B27/Cw4Cw7, What men is the most likely candidate for the father? 143) What is true of HLA (MHC) class I antigens? a. They are recognized by helper T cells. b. They are found on all nucleated cells. c. They combine with exogenous antigen. d. They are coded for on chromosome 9. 144) HLA (MHC) class I protein is found on: a. RBCs b. all nucleated cells c. B cells and macrophages d. stem cells only 145) Heterophile antigens are characterized as: 146) If a patient's red cells agglutinate with anti-A reagent antibody and the serum agglutinates B cells, what is the blood type? Spatial configuration is recognized by antibody. heterophile antigens hapten conformational epit an autocoupling hapten adjuvant adjuvant measure and transport digested proteins to MHC Class I CD4+ T cells C A5A9/B5B27/Cw3Cw7 B B found in unrelated plants or animals but cross-reacting with the same antibody type A 8 Immuno TB Flashcards Unit 1 147) All of the following are characteristics of a good antigen EXCEPT: a. large molecule b. foreign to host c. repeating polymer d. protein in nature 148) Which region of the immunoglobulin molecule can bind antigen? 149) Which immunoglobulin appears first in the primary response? 150) What is an accurate statement about monoclonal antibodies? Monoclonal antibodies are: A. A population of antibodies that all recognize a single specific antigen B. a population of antibodies that arise from single B cell C. used to classify and identify specific cellular membrane antigens D. all of the above 151) The primary response is characterized by: A. naive B cells recognizing antigens B. memory B cells recognizing antigens C. the production of large amounts of IgG D. a very short lag period E. a long duration of high titer 152) Which immunoglobulin appears in the highest titer in the secondary response? 153) What pairings of immunoglobulin and a property are true? A. IgA: crosses the placenta B. IgG: most abundant in serum C. IgM: immunoglobulin produced by a T cell D. IgE: major immunoglobulin of secondary response 154) The antigen specificity of a B cell is determined: 155) All of the following are functions of immunoglobulins EXCEPT: A. neutralization of toxic substances B. facilitating phagocytosis through opsonization C. interacting with cytotoxic T cells to lyse viruses D. combining with complement to destroy cellular antigens 156) The idiotype of an antibody is located on which region? 157) Which immunoglobulin activates the classical complement pathway? 158) What immunoglobulins are found in only trace amounts in the serum? C Fab IgM D naive B cells recognizing antigens IgG B by H and L chain variable region sequences C VH + VL IgM IgD 9 Immuno TB Flashcards Unit 1 159) All polymeric but not monomeric immunoglobulins are characterized by: 160) Kappa or lambda light chains: 161) Variations in immunoglobulin structure that occur because of the use of different constant region domains are known as: 162) The ability of an antibody to opsonize is located in which region? 163) When papain is used to cleave antibody molecules, what are the products? 164) The function of IgD is to: 165) What characteristic is true of an anamnestic response compared to a primary response? An anamnestic response has: 166) An immunoglobulin that contains a peptide that is not synthesized by a B cell is: 167) Which immunoglobulins can cross the placenta? 168) The valence of an IgG antibody molecule is: 169) The receptor for antigen on a mature naive B cell is: 170) The region of an antibody molecule that exhibits the greatest variability from antibody to antibody is known as the: 171) Somatic mutation of immunoglobulin genes accounts for: 172) What is the first step in immunoglobulin gene rearrangement? 173) IgA in the secretions has a valence of: 174) Which represents an isotype of a heavy chain 175) IgD is produced b 176) 177) 178) Which antibody is able to cross the placenta? What is true of a secondary response to an antigen All of the following are true of IgM EXCEPT: A. It can cross the placenta. B. It fixes complement. C. It is a primary response antibody. D. It can bind up to ten antigens. 179) The combination of a plasma cell fused to a myeloma cell is called a: 180) What is true of IgE? A. It fixes complement. B. It binds to mast cells. C. It is found on mucosal surfaces. D. It participates in agglutination reactions. a J-chain associate with only one type of heavy chain at a time isotypes Fc 2 Fab and Fc bind antigen as a B-cell surface receptor a shorter lag phase IgA in secretions IgG Two IgM hypervariable region affinity maturation heavy-chain variable region Four epsilon differential splicing of the RNA transcript IgG IgG is increased 100 to 1000 times. A hybridoma B 10 Immuno TB Flashcards Unit 1 181) What is true of coding for antibody molecules? A. Heavy-chains are coded for on chromosome 2. B. V,D, and J code for heavy chain variable regions. C. DNA coding for light chains are rearranged first. D. V and D code for light chain variable regions. 182) Immunoglobulins are grouped into classes on the basis of similarities in what? 183) What is the main function of IgD? 184) Bence-Jones proteins are identical to what? B heavy chains It helps in class switching. light chains 11 Immuno TB Flashcards Unit 1 185) All of the following are true of IgA EXCEPT: A. It is found in secretions. B. It fixes complement. C. It is a dimer in serum. D. It is important in oral immunizations. 186) Which class makes up 70 to 80 percent of total serum immunoglobulins? 187) All of the following are characteristic of secretory IgA EXCEPT: A) It is found on mucosal surfaces. B) It has a secretory component made in epithelial cells. C) It occurs as a monomer in the tissues. D) It defends against pathogens in the respiratory tract. 188) Which best describes monoclonal antibody? 189) Papain cleavage of IgG results in what? 190) Which antibody agglutinates and fixes complement best? 191) Immunoglobulins IgG, IgM, IgA, and IgD represent what? 192) A Fab fragment consists of: 193) What represent light chains of antibody molecules? 194) Which immunoglobulin causes allergic reactions due to release of histamine from mast cells? 195) Which is the main purpose of the secretory component that is part of IgA? 196) What is true of IgE? A) fixes complement B) binds to mast cells C) found on mucosal surfaces D) participates in agglutination reactions 197) In serum electrophoresis conducted at pH 8.6, which protein group migrates the fastest? A) albumin B) alpha-1 globulin C) alpha-2 globulin D) gamma globulin 198) The antibody that appears first in an immune response and is a pentamer with a molecular weight of 900,000 best describes: 199) The antibody found on mucosal surfaces that acts as a first line of defense is called: B IgG C antibody made from a single antibody-producing cell 2Fab and an Fc fragment IgM isotypes one light chain and one-half of a heavy chain Kappa and lambda IgE transports across endothelial cells B A IgM IgA 12 Immuno TB Flashcards Unit 1 200) Which antibody is found in the greatest supply and is the only one capable of crossing the placenta? 201) All of the following are characteristic of IgE EXCEPT: A) found on mast cells and basophils B) fixes complement C) found in low amounts in the blood D) causes allergic reactions 202) The antibody found on B cells that is thought to be involved in B cell maturation is: 203) The theory that lymphocytes are preprogrammed to respond to a particular type of antigen best describes: 204) In serum protein electrophoresis, which band contains the immunoglobulins? 205) What best characterizes IgD? 206) Where on an antibody molecule does combination with antigen take place? 207) All of the following are true of IgG EXCEPT: A) first class of antibody to appear B) able to cross the placental barrier C) the predominant antibody in serum D) provides immunity for the newborn 208) Which antibody is found mainly as a dimer in mucosal secretions? 209) IgG differs from IgM in which way? 210) The primary response differs from the secondary immune response in what way? 211) Cytokines exhibit pleiotropy, which refers to: 212) IL-2 is synthesized by which type of cell and acts on which type of cell? IgG B IgD the clonal selection theory gamma surface receptor for antigen variable region A IgA IgG is the main antibody in serum. Amounts of IgG and IgM are the same. one cytokine affecting multiple cells TH1; CTL 213) A cytokine that is produced by TH2 cells and inhibits TH1 cells is: 214) IL-1, IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha function by: A. increasing vascular permeability B. increasing acute phase proteins C. acting on the hypothalamus D. promoting migration of inflammatory cells E. all of these IL-10 215) hematopoiesis IL-3, IL-7, and GM-CSF are all involved in: 216) IL-2 is produced by one cell and the same IL-2 stimulates that same cell. This type of cytokine activity is called: 217) IL-2 is a cytokine that could be more specifically called what because of the cells that produce it? E autocrine Lymphokine 13 Immuno TB Flashcards Unit 1 218) IL-4 functions by: activating B cells 219) IFN-gamma is produced by: 220) When multiple cytokines act on the same cell, by definition they have: 221) What cytokines is produced by TH1 cells and is suppressive for TH2 lymphocytes? TH1 cells redundancy 222) All of the following are actions of interleukin-1 EXCEPT: 223) A protein released from a virally infected cell that protects other cells from viral invasion best describes: increased production of IgE interferon-alpha 224) When Il-2 acts on T cells, B cells, and NK cells, this is an example of: 225) The actions of IL-1 and IL-10 are an example of: 226) What is the main function of chemokines? pleiotropy 227) 228) What is the main action of interferon-gamma? What is the function of TGF-alpha? 229) The main target of interleukin-3 is: 230) 231) 232) 233) 234) Which cytokine is involved in natural immunity? Which cells produce interleukin-1? Erythropoietin is classified as what? Which acts as the best defense against gram-negative bacteria? What can be attributed to interleukin-6 (IL-6)? 235) Which best describes the nature of interleukin-2? 236) What is one of the main activities of interleukin-4 (IL-4)? 237) Which complement component is found in both the classic and alternative pathways? 238) What is a characteristic of complement? A. It is activated by IgE in the classical pathway. B. It cannot be activated by molecules other than antigen–antibody complexes. C. It plays a role in the lysis of target cells coated with specific antibodies. D. It is enhanced by decay accelerating factor. 239) What can activate the alternative complement pathway? 240) What functions by inserting itself into target membranes and forming channels or holes in the membranes? 241) What act as opsonins? 242) The C5 convertase of the alternative pathway of complement activation is: 243) C5b6789 functions in: IFN-gamma antagonism enhance migration of white blood cells activation of macrophages regulates cell growth and differentiation macrophages interleukin-6 macrophages colony-stimulating factor TNF increases activation of T and B cells activates T helper cells generation of TH2 cells C3 C C3b C5b6789 C3b C3bBb3bP target cell lysis 14 Immuno TB Flashcards Unit 1 244) The functions of C5a are to promote all of the following EXCEPT: A. phagocytosis of target cells B. contraction of smooth muscle C. increased vascular permeability D. leukocyte attraction to the site of inflammation 245) Chemotactic and anaphylactic factors are produced by proteolytic cleavage of: 246) The alternative and classical pathway C3 convertases are destabilized as a means of down-regulating complement function. One molecule that performs this function is: 247) What is cleaved by C3bBb? 248) What is the correct order of activation of complement in the lectin activation pathway? 249) A native bacterial cell surface itself will activate complement via which pathway(s)? 250) What is cleaved first by C1qrs in the classical pathway of complement activation? 251) What complement components has chemotactic activity? 252) The C3 convertase of the alternative pathway of complement activation is: 253) The target recognition molecule of the lectin pathway that initiates complement activation is: 254) Which immunoglobulin(s) help(s) initiate the classic complement pathway? 255) What has perforin-like activity? 256) What is cleaved by C4b2a3b? 257) A patient has an abnormal alternative pathway activation pattern. What complement proteins should be assessed to further elucidate the problem? 258) The C5 convertase of the classical pathway of complement activation is: 259) A deficiency in complement component C2 would result in: 260) What represents C3 convertase? 261) Which factors are only associated with the alternative pathway? 262) The lectin pathway is initiated by the presence of what? 263) The membrane attack unit of complement is represented by what? 264) Which complement factor polymerizes to cause lysis of a foreign cell? 265) The recognition unit in the classical complement pathway consists of: 266) Binding of a lectin to a sugar found in bacteria and fungi occurs in which complement pathway? 267) Which factor is unique to the lectin pathway? A C5, C3 membrane cofactor protein C3 MBL, C4, C2, C3 Classical and alternative pathways C4 C3a C3bBbP mannose-binding lectin IgG and IgM C5b6789 C5 C3 C4b2a3b immune complex disease C4b2a and C3bBbP factor B and factor D Mannose C5b6789 C9 C1qrs MBL pathway Mannose-binding protein 15 Immuno TB Flashcards Unit 1 268) Lack of the complement inhibitor C1INH results in which disease? 269) All of the following can trigger the alternative pathway EXCEPT: A. fungal cell walls B. bacterial cell walls C. yeast D. antibody 270) In the alternative pathway, C3 and C5 convertase are stabilized by what? 271) Which factors are found in all three pathways? 272) What is able to activate complement? 273) Which complement protein is the key intermediate in all pathways? 274) In the alternate pathway, factor B must bind to what to initiate the cascade? 275) Which factor must be associated with factor H to inactivate complement components? 276) Lack of the complement components C5-C8 may result in which disease? 277) Which factor helps to dissociate C3b from red blood cells? 278) Which protein inhibits the classical complement pathway at the very beginning of it? 279) What are important functions of the complement system? 280) Formation of the membrane attack complex (C5b-C9) is stopped by which factor? 281) What is characteristic of complement components? 282) C4BP acts in association with which factor to inactivate C4b? 283) All of the following statements are true of C3 except 284) What is referred to as C5 convertase? 285) What activities are associated only with the alternative pathway of complement fixation? 286) A system of serum proteins that interact to enhance the immune response by producing cytolytic, chemotactic, and other effects best describes: Hereditary angioedema D Properdin C5-C9 IgM C3 C3b Factor I meningitis DAF C1INH Lysis of foreign cells, Increase in vascular permeability, Clearance of antigen-antibody complexes S protein They play a major part in the inflammatory response. Factor I It is known as the recognition unit. C4b2a3b Factor B and C3b combination complement 16