Chapter 16: Transformations in Europe
advertisement

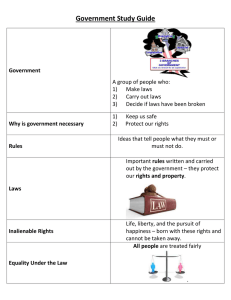
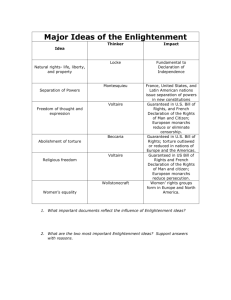
Chapter 16 Transformations In Europe 1500-1750 How were Culture & Ideas Changing? • Sale of Indulgences • Martin Luther • John Calvin • Protestant Reformation • Religious Wars • Counter Reformation Religious Changes Traditional Culture & Witch Hunts • Conflict between formal religion & preChristian local beliefs & practices • Witch hunts What was the “Scientific Revolution”? • Challenged prevailing conceptions of physical world • Sought natural causes to explain universe The Early Enlightenment • Scientific method could analyze economics, politics, social organization to create policies Who Am I? • Leviathan • Religion should be separate from politics • Emphasized reason • People are fearful and predatory • State should have “absolute power” Who Am I? • People are born “good” • God given “Natural Rights” • Life, Liberty, Property • Power of state should be limited • Social contract • Freedom of Religion Who Am I? • The accused should have rights • Death penalty and torture are wrong • Education essential • Right to fair and speedy trial • Punishment should fit the crime Who Am I? • Limit power of King • Three Branches of Government • Separation of Powers • Checks and Balances Who Am I? • Individuals have rights • Majority rule • Reason and individual rights essential • Individuals should be allowed to experience and explore life. Who Am I? • Single legislature with advisory board • Advisory board would work for the government and not receive paid • Slavery wrong and should be abolished • Simple lifestyle was best • Inventor • Diplomat Who Am I? • Trusted the people to make best decisions • Limited government • Education crucial to success of democracy • All should have the opportunity for education Who Am I? • All things should be explained logically and reasonably • Fought against intolerance, tyranny, superstition • Freedom of thought and respect for all • Religion too powerful • Literature useful for understanding problems of the day • “Candide” Who Am I? • Fought for the rights of women • Fought against inequalities in education • Equal opportunity for all • People should be judged on individual merit and moral virtue, not on gender Who Am I? • “Wealth of Nations” • Self-interest guides the efficient use of resources • “free enterprise” • People who earned money benefited themselves and society • Charity virtuous but society should not depend upon it Social & Economic Changes • Wealthy urban bourgeoisie thrived • Built relationships w/ monarchs • Bought land & titles • “Married up” • Facilitated trade • Joint-stock companies • Stock exchanges • Transportation infrastructure How did life change for Peasants & Laborers? West Europe=Serfdom declined East Europe=gained prominence African slaves working in Americas contributed to Europe’s economy How were women & families changing? • Women’s status same as husband & family • Love, affection led to slight increase in status • Late marriage led to increased independence from parents • Low birth rate • Emphasis on education led to more schools • Women barred Political Changes • Monarchs power increased • Strong armies • Elaborate bureaucracies • High taxes Monarchies in England & France English Bill of Rights Bourbon Kings Develop “absolutist” style government Versailles Warfare & Diplomacy New military technologies (cannon, muskets), & large standing armies or navies Paying the Piper High cost of war led rulers to form alliances with commercial elites. Spain’s economy declined with expulsion of Jews, Protestants, and Muslims. Summary • The religious reformations combined with the Scientific Revolution led the way for the Enlightenment, an age of reason, and the movement to apply newly discovered natural laws to social behavior. • Foreign and domestic trade spawned rapid growth in European cities and the rise of a wealthy commercial class, with Amsterdam in the Netherlands the most vivid example. Agricultural improvements increased production but the Little Ice Age and increased mining of forests caused more difficulties for the poor. • The Holy Roman Empire declined in strength from religious fragmentation while Spain and France increased centralized power. The English increased naval power and established direct taxation and a central bank, making the nation stronger financially than other European powers.