Notes
advertisement

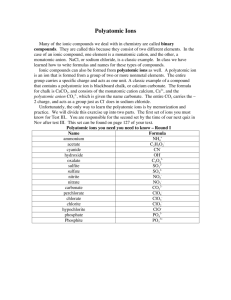
Ionic Compounds Atoms vs. Ions Ion: an atom that has lost or gained electrons Ions have a charge because the # of protons does NOT equal the # of electrons Ions How do you know if an atom will lose or gain electrons? Less than 4 valence electrons = lose More than 4 valence electrons = gain Ions cation: positive ion anion: negative ion Lewis Dot Diagram Se Ionic Bonding Electrons are transferred from one atom to another so that each has 8 valence electrons - called the octet rule + Cation Anion Ionic Compound Ionic bond: bond formed by attraction between + and - ions Ionic Bonding Ionic bonds occur between metals and non-metals H He Li Be B C N O F Ne Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar K Ca Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Br Kr Rb Sr Y Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd In Sn Sb Te I Xe Cs Ba Lu Hf Ta W Re Os Ir Pt Au Hg Tl Pb Bi Po At Rn Fr Ra Lr Rf Db Sg Bh Hs Mt Uun Uuu Uub Uut + Cation Metals Metalloids Non-metals Anion Binary Ionic Compounds Formula to Name Binary Ionic Compounds Formula to Name • Formula will have… – only 2 elements – a metal and a non-metal • To name: Metal name + nonmetal name ending in –ide The subscripts in the formula do not matter when naming this type Examples CaBr2 K2O Write the name for the following compounds Practice 1. CaF2 calcium fluoride 2. Na3P sodium phosphide 3. NaI sodium iodide 4. SrBr2 strontium bromide Binary Ionic Compounds Name to Formula Example The “magic number” is 8! Binary Ionic Compounds Name to Formula • Names will… – end in “-ide” (except “hydroxide and cyanide”) – NOT contain covalent prefixes • To write the formula: 1. Draw Lewis dot diagrams of each element and transfer electrons to complete the octet. 2. Use subscripts to show how many of each type of ion you have. Example Rubidium sulfide Write the formula for the following compounds Practice 1. cesium chloride CsCl 2. potassium oxide K2O 3. calcium sulfide CaS 4. lithium nitride Li3N Multivalent Ionic Compounds Name to Formula Multivalent (Transition) Metals Multivalent Metal: a metal that can form more than one ion (has more than one + charge) Examples: Cobalt Copper Iron Lead Manganese Mercury Tin Co+2 Cu+1 Fe+2 Pb+2 Mn+2 Hg2+2 Sn+2 Co+3 Cu+2 Fe+3 Pb+4 Mn+3 Hg+2 Sn+4 Multivalent Ionic Compounds Name to Formula • Names will… – have roman numerals (I, II, III, IV, etc.) • To write the formula: – Same as binary, except Roman numerals tell the charge of the metal cation Examples Iron (III) oxide Copper (I) nitride Write the formula for the following compounds Practice 1. Iron (II) nitride Fe3N2 2. Copper (I) chloride CuCl 3. Lead (IV) sulfide PbS2 4. Tin (II) oxide SnO Multivalent Ionic Compounds Formula to Name Multivalent Ionic Compounds Formula to Name • Formula will have… – a transition metal • To name: Metal name + (charge in Roman numerals) + nonmetal name ending in -ide • To determine the metal charge, make a list! 1. List each nonmetal ion with the charge 2. Total negative charge = total positive charge 3. Divide the total positive charge between the metal atoms 4. Write the charge of one atom in roman numerals in parenthesis after the metal’s name Examples CuCl2 Fe2O3 Write the name for the following compounds Practice 1. PbCl2 Lead (II) chloride 2. SnBr4 Tin (IV) bromide 3. MnO Manganese (II) oxide Polyatomic Ionic Compounds Polyatomic Ionic Compounds Polyatomic Ion: a group of atoms that has lost or gained electrons – so it has a charge! Polyatomic Ionic Compound: compound containing at least one polyatomic ion + Cation Polyatomic Anion Polyatomic Ionic Compound Identifying Polyatomic Ions • Only one cation: NH4+ • All others are anions (second part of formula) • Subscripts must match exactly as it appears on the list on your periodic table Practice Identifying Polyatomic Ions Identify and name the polyatomic ion in each compound 1. NaNO3 2. NH4Cl 3. Ca(OH)2 4. (NH4)3PO4 5. K2CO3 Practice Identifying Polyatomic Ions Identify and name the polyatomic ion in each compound NaNO3 Nitrate NH4Cl Ammonium Ca(OH)2 Hydroxide (NH4)3PO4 Ammonium & phosphate K2CO3 Carbonate Polyatomic Ionic Compounds Formula to Name Polyatomic Ionic Compounds Formula to Name • Formula will have… – MORE than 2 capital letters – at least one metal and one non-metal • To name: Metal name + nonmetal polyatomic ion name • write the polyatomic ion’s name exactly as it appears on your periodic table Examples NaNO3 Fe(OH) 2 Write the name for the following compounds Practice 1. Ca(NO3)2 2. Na3PO4 3. NH4ClO 4. K2CO3 Polyatomic Ionic Compounds Name to Formula Polyatomic Ionic Compounds Name to Formula • • Names will… – end in –ite or –ate (except for hydroxide) – Do not use covalent prefixes To write the formula: • Make a list! 1. Write the symbol and charge of the cation and anion 2. Add additional cations or anions until the charges cancel out to zero 3. Use subscripts to show the number of each ion When using subscripts with a polyatomic ion, you must put the polyatomic ion in parenthesis. Examples Sodium carbonate Magnesium nitrate Write the formula for the following compounds Practice 1. Sodium nitrate NaNO3 2. Calcium chlorate Ca(ClO3)2 3. Potassium sulfite K2SO3 4. Calcium hydroxide Ca(OH)2 Example Anion Fe2O3 Total Total negative positive charge in charge in compound compound Cation Name