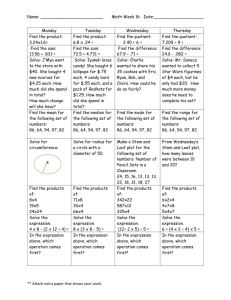
Stem-n-leaf display - University of South Alabama

Stem-n-leaf display
Nutan Mishra
steps
1. Define stem and leaf positions.
2. List all possible values of stem present in the given dataset
3. Record leaf for every observation besides its corresponding stem value
Example 3.7
• Define stem as first two digits (tens of
100s)
• Define leaf as the last digit (unit place)
• Lowest observation in the data set is 43 and the largest one is 152.
• Thus the list of stems ranges from 4 to 15.
Stem Leaf
Example 3.8
• Define stem as first digit (1000th place)
• Define leaf as second digit (100th place)
• Ignore the tenth and unit places.
• Smallest observation is 2227 and largest one is 8260.
• Thus stems range from 2 to 8
Stem leaf
Problem 3.15
• Define stem to be first two digits.
• Define leaf to be the 10 th place (third digit)
• Ignore the unit place.
• Smallest value is 111 and largest is 5508
• Thus the stems range from 01 to 55
Stem Leaf Stem Leaf Stem Leaf
Problem 3.16
• Define stem as 10 th place
• Define leaf as unit place
• Largest value is in 40’s and smallest value is in 10’s
• Thus range of stems ranges from 1 to 4
2
3
Stem
1
4 leaf
Problem 3.17
• Define stems as 1L =10-14, 1H =15-19,
2L= 20-24, 2H=2529……
• Define leaf to be the unit place.
Stem
1L
1H
2L
2H
3L
3H
4L
4H leaf
Problem 3.19
• Define stem to be first digit
• Define leaf to be the last digit.
• Highest value is 93 and lowest is 10
• This stems range from 1 through 9.
Leaf
(very large urban areas)
7
8
9
4
5
2
3
6
Stem Leaf
(large urban areas)
1