Document
advertisement

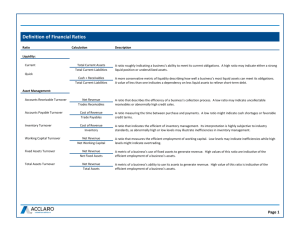
CH.13Cycles (production, collection, accounts payable) Average Collection Cycle/Accounts Receivable= Cash conversion cycle = Production cycle + Accounts receivable cycle – Payment cycle A/R Turnover = Credit Sales/Avg. A/P Turnover = Cost of Goods Sold/Avg. Operation cycle = Collection cycle + Production cycle Collection cycle= 365/A/R Turnover Production cycle = 365/Inv. Turnover Payment cycle = 365/A/P Turnover EAR = (1+HPR)365/n -1 Calculate the APR and EAR implied by the discount being offered using Equations 13.12 and 13.13 as follows: EAR= (Where OC = cost per order; S=annual sales; and Q = order size) The reorder point = daily usage * days of lead time Average inventory = EOQ/2 + safety stock At terms of 1/10, net 30 you will get 1% off and be allowed to pay in 10 days, otherwise the full amount is due in 30 days HPR = .01/.99 = 1.0101% EAR = (1+HPR)365/20 – 1 = (1.0101)18.25 -1 = 20.129% Average Inventory = (Beginning Inventory + Ending Inventory) / 2 Inventory Turnover = COGS / Average Inventory Average Production Cycle = 365 / Inventory Turnover CH.14 (Du-point analysis; return on equity – profitability rates) Equity = total assets - liabilities According to the Du Pont breakdown, we have ROE = Net Profit Margin * Total Asset Turnover * Equity Multiplier ROE = NI/S * S/TA * TA/Equity Note: since we don’t have the accounting information for the average, we have to figure out the industry’s equity multiplier by some algebraic manipulation. Equity Multiplier = Total Assets/Equity Now, debt ratio = Total Debt/Total Assets Total Assets = Total Debt + Equity (Total Debt/Total Assets) +( Equity/Total assets) = 1 Equity/Total Assets = 1 – (Total Debt/Total Assets) TA/E = 1/(1-TD/TA)