Study Skills How are you studying?
advertisement

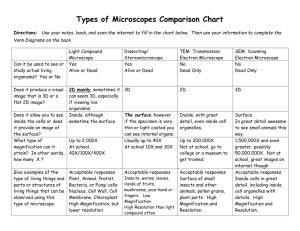
BIOLOGY MIDTERM REVIEW Exam Date: Tuesday, January 22 Exam Time: 8:00 AM Exam Location: Period 9 – W 206 Period 8 – W 205 Period 6 – W 204 Exam Material: Chapters 1, 6, & 7 Chapter 1 Terms biology cells organization grow develop reproduce response stimulus energy homeostasis adaptations evolve science pseudoscience theory peer review metric system ethics observation inference scientific method hypothesis observations controlled experiment experimental group control group variable independent variable dependent variable data qualitative data quantitative data length volume mass temperature time Chapter 1 Concepts Definition of biology and the purpose of biological studies Identify the eight characteristics required for life Understand the difference between: o Growth and development o Response and Adaptation o Adaptation and Evolution Differences between science and pseudoscience Differences between an observation and an inference Understand the difference between a “testable” and an “untestable” hypothesis Four steps that are included in a good scientific method Identification of the independent, dependent, and controlled variables in an experiment conducted by another scientist Difference between qualitative and quantitative data The basic units of mass, volume, length, time, and temperature in the metric system and which unit is appropriate to use when measuring certain quantities Converting metric units The meaning of metric prefixes (i.e. milli-, centi-, deci-, kilo-, etc.) Chapter 6 Terms mass atom protons neutrons electrons elements atomic number mass number isotopes compound ionic bonds covalent bonds chemical reaction reactants products balanced equation activation energy enzymes polar molecules hydrogen bonding universal solvent cohesion adhesion acids bases pH scale buffers carbon organic monomer polymer macromolecule carbohydrates lipids proteins nucleic acids Chapter 6 Concepts Structure of an atom including the charge, location, and mass of all subatomic particles Differences between elements and compounds How to use the periodic table to construct a model of an atom How to interpret an atomic number and mass number when given Differences between ionic, covalent, and hydrogen bonds The structure of a water molecule Describe polarity. Describe how this allows water to form hydrogen bonds and promotes water’s unique properties Explain the pH scale Determine the relative amount of hydrogen ions in different solutions given their pH values Explain the parts of a chemical equation Explain how enzymes work to control the rates of chemical reactions Describe the relationship between monomers and polymers Identify the four groups of organic macromolecules, give their general chemical composition, provide examples, and explain their functions in living things Provide examples of organic macromolecules Chapter 7 Terms cells Robert Hooke Anton van Leeuwenhoek cell theory compound light microscope electron microscope magnification diaphragm course adjustment fine adjustment ocular (eyepiece) objective lenses stage microscope slide high power objective lens low power objective lens total magnification prokaryotic cells eukaryotic cells organelles plasma membrane homeostasis selective permeability phospholipid phospholipid bilayer membrane proteins cholesterol carbohydrates (in membrane) cytoplasm cytoskeleton nucleus ribosomes nucleolus endoplasmic reticulum (ER) smooth ER rough ER Golgi apparatus vacuoles lysosomes centrioles mitochondria chloroplasts cell wall cilia and flagella diffusion concentration dynamic equilibrium facilitated diffusion passive transport active transport osmosis isotonic hypotonic solution hypertonic solution Chapter 7 Concepts List the three parts of the modern cell theory. Explain the significance of the contributions of Leeuwenhoek and Hooke to our understanding of cells. Compare and contrast light microscopes and electron microscopes. Identify the parts of the compound light microscope and explain their function. Calculate the magnification being used when using a compound light microscope Compare and contrast the complexity and organization of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. Explain why a cell is like a tiny factory. List, label, and describe the functions of the parts of a typical eukaryotic animal cell. Compare and contrast animal and plant cells. Explain how the processes of diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and active transport work to move substances into and out of cells. Predict the effect of hypotonic, isotonic, and hypertonic solutions on a cell. Study Skills How are you studying? Strategies: Visual Learners o Color highlighters o Study in a quiet area away from verbal disturbances o Review diagrams in book o Make charts/graphs/tables o Rewrite notes and assignments Auditory Learnes o Talk to yourself/reread notes/note cards o Read out loud o Create musical jingles or rhymes to memorize o Ask someone to quiz you; answer the questions verbally Kinesthetic Learners o Take breaks and vary your activities o Do something physical while studying (chew gum, stand up, walk around the room, hold a tennis ball) o Use bright colors for highlighting o Rewrite your notes o Make charts/tables/graphs of notes TEST TAKING SKILLS DESTRESS D – dump any memorized material E – Enter your name, date, and period S - Survey the test T - Time – plan how you will spend your time R – Read the DIRECTIONS! E - Easy questions first S – See if questions on test provides clues to other items S - Make sure that you review the test to check all items