atomic mass
advertisement

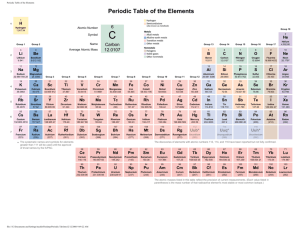
What is the periodic table? • A compact way of organizing the elements that contains a lot of information and allows us to make predictions about the behavior and properties of the elements. • Elements History of the Periodic Table • End of the 1700’s – less than 30 elements known. • Many elements were discovered during the 1800’s. Many experiments were done to determine atomic masses. John Newlands - Octaves • 1864: Newlands noticed that when the known elements were arranged by atomic masses, their properties repeated every 8th element. • Law of Octaves did not work for all known elements. • Key idea was correct: Properties of elements do repeat in a periodic way. Mendeleev & Meyer • 1869: Mendeleev produced 1st accepted periodic table. • Elements ordered by increasing atomic mass into columns with similar properties. • Predicted the existence & properties of undiscovered elements. • Not totally correct. As more accurate determinations of atomic mass were made, several elements weren’t in the right place. Remember • 1860’s: No subatomic particles had been discovered yet. • People were going by Dalton’s billiard ball model of the atom. 1913 – Henry Moseley • By 1913, protons & electrons discovered. Neutrons predicted. • When cathode rays hit stuff, they produce X-rays. • Mosely used 30 different elements as “stoppers” • Found that the greater the atomic weight of the “stopper,” the shorter the wavelength of the x-rays. • What does any good scientist do? PLOTS THE DATA! •Tried correlating the wavelength of the x-ray with the atomic mass of the stopper. Not so nice. Change in much more regular than change in atomic weight. •Then tried correlating the wavelenth of the x-ray with an integer, n. Got a very pretty graph. Atomic Number - 1913 • Mosley interpreted the integer, n, to be the positive charge on the nucleus. • Mosley suggested that the size of the nuclear charge increased by 1 with each step up the periodic table. (Before, it was organized by atomic weight.) • Moseley determined that atoms of each element contain a unique number of protons – atomic number. • Moseley rearranged Mendeleev’s periodic table by atomic number instead of mass. • Problems disappeared. Periodic Law • There is a periodic repetition of chemical and physical properties of the elements when they are arranged by increasing atomic number. Vocabulary of the P.T. • Columns are called groups or families. 2 different notations. – 1 thru 18, Arabic numerals. – Split into A & B groups. Use Roman numerals. • A-Group = Columns 1,2,13-18 = representative elements • B-Group = Transition metals • Rows are called series or periods. Numbered 1 thru 7. Classifying the Elements • 2/3 of the elements are metals. • Remaining elements are non-metals and metalloids (semi-metals). • Metalloids have some properties of metals and some properties of nonmetals. • Know the “staircase” dividing line on the P.T. between metals & nonmetals. Everything to left, except H, is a metal. Metalloids • • • • • • • Boron, B Silicon, Si Arsenic, As Tellurium, Te Astatine, At Germanium, Ge Antimony, Sb Names of Families • • • • Group 1 = Alkali Metals (IA) Group 2 = Alkaline Earth Metals (IIA) Group 17 = Halogens (XVIIA) Group 18 = Noble Gases (XVIIIA or O) – The noble gases are extremely unreactive. Weren’t discovered until 1890’s. Transition Metals • Elements in Columns 3 through 12 • Also called the group B elements – Transition elements form brightly colored salts and brightly colored solutions. – Have multiple, positive oxidation states • Actinide and Lanthanide series = inner transition elements Calcium Metal