Chapter 10 Review Game 2015 AP
advertisement

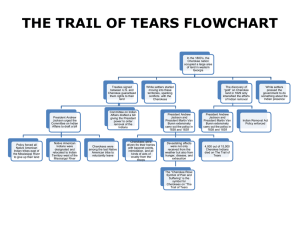
Chapter 10 Review Game 2015 AP 1. How did nominating conventions contribute to the expansion of democracy in the 1820s? a. They drew media attention to the election. b. They allowed people to become more active in politics. c. They led to a voting system based on majority rule. d. They increased the presidential candidate’s popularity. b. They allowed people to become more active in politics. 2. All of the following is an example of how voting rights were expanded in the early 1800s EXCEPT a. Maryland passed a state constitutional amendment that removed religious qualifications for voters. b. New western states allowed white men to vote regardless of property, religion, or other standards. c. Voters, rather than state legislators, began to nominate their own electors to the electoral college. d. Massachusetts granted one-half of a vote to each literate, free-born, Christian, African-American man. d. Massachusetts granted one-half of a vote to each literate, free-born, Christian, AfricanAmerican man. 3. What caused an onlooker to observe, “The reign of King Mob seemed triumphant”? a. the rush of Democratic party members to receive jobs in Andrew Jackson’s government through the spoils system b. the celebration of Andrew Jackson’s presidential victory on the White House lawn with 20,000 raucous partygoers c. the rage people expressed about Martin Van Buren during the Panic of 1837, a severe economic depression d. the 1836 resistance of the Creek Indians to federal troops, who captured 14,500 and led them to the Indian Territory b. the celebration of Andrew Jackson’s presidential victory on the White House lawn with 20,000 raucous partygoers 4. How did Andrew Jackson reward some of his supporters? a. with Indian lands b. with government jobs c. with a grand party d. with gold and silver coins b. with government jobs 5. In the early 1800s, Northerners supported tariffs because they helped them compete with a. Western hunters and ranchers b. Southern agriculturalists c. British manufacturers d. French-Canadian fur-trappers c. British manufacturers 6. All of the following were important reasons why Southerners opposed tariffs in the early 1800s EXCEPT a. Tariffs increased the price of the goods they needed. b. Tariffs angered their European trading partners. c. They didn’t want tariffs to benefit their Northern rivals. d. They didn’t want Europe to raise tariffs on American goods. c. They didn’t want tariffs to benefit their Northern rivals. 7. What effect did the Tariff of Abominations have on Andrew Jackson’s America? a. Southerners, who had industries to protect, were angered by the tariff. b. Ill feelings between Northerners and Southerners grew because of the tariff. c. Northerners were angry with government for setting the tariff too high. d. Westerners, who manufactured goods for American buyers, were pleased. b. Ill feelings between Northerners and Southerners grew because of the tariff. 8. Arguments over which issue sparked the nullification crisis? a. a national tariff b. economic depression c. bank operations d. the states’ rights doctrine a. a national tariff 9. How did President Andrew Jackson react to Vice President John C. Calhoun’s views on nullification? a. Jackson commended him because he and Calhoun whole-heartedly agreed. b. Jackson stood back and let Calhoun be judged by the voting public. c. Jackson openly disagreed with Calhoun and watched as Calhoun resigned. d. Jackson fired Calhoun over the issue and forced duty collection on the South. c. Jackson openly disagreed with Calhoun and watched as Calhoun resigned. 10. What ruling did the Supreme Court make in the case of McCulloch v. Maryland? a. that states like Maryland, have more power than the federal government b. that the national bank was constitutional and could not be taxed by Maryland c. that the federal government could forcibly collect taxes from Maryland and McCulloch d. that the national bank’s charter could be renewed in Maryland b. that the national bank was constitutional and could not be taxed by Maryland 11. How did Andrew Jackson’s presidency set the stage for later economic trouble? a. He built the national bank out of statebased “pet banks.” b. He caused inflation by giving credit to settlers in the West. c. He created conflict with Britain by insisting on foreign tariffs. d. He raised the national debt by overspending on expansion. b. He caused inflation by giving credit to settlers in the West. 12. What did the Virginia and Kentucky Resolutions of 1798-1799, the Hartford Convention, and John C. Calhoun’s South Carolina Exposition and Protest have in common? a. They were all written or organized by supporters of the states’ rights doctrine. b. They were all used to argue for the Tariff of Abominations. c. They were all written or organized by members of the Democratic Party. d. They were all used to resolve the nullification crisis. a. They were all written or organized by supporters of the states’ rights doctrine. 13. What did Vice President John C. Calhoun argue regarding the Tariff of Abominations? a. The federal government should have less power than the states. b. State governments should have no right to dispute federal laws. c. The federal government should favor his region over others. d. International trade should be a matter of federal law alone. a. The federal government should have less power than the states. 14. What was the Bureau of Indian Affairs? a. A congressionally-approved office established to protect the ways of American Indians. b. A federal government office established to oversee policy toward American Indians. c. A federal government agency designed to negotiate with Creek and Chickasaw Indians. d. A group established by the Mississippi legislature to track American Indian deaths. b. A federal government office established to oversee policy toward American Indians. 15. What was MOST significant about the Choctaw Indians after 1830? a. They were the first American Indians removed to Indian Territory. b. Their government was the first to be abolished by an American state. c. Their example inspired other American Indians to settle in Indian Territory. d. They were the first American Indians to be raided by settlers. a. They were the first American Indians removed to Indian Territory. 16. Where was the Indian Territory? a. east of the Mississippi River b. most of present-day Oklahoma c. south of the Blue Ridge Mountains d. most of present-day Arkansas b. most of present-day Oklahoma 17. Who benefited MOST from Andrew Jackson’s plan to remove American Indians to the West? a. American Indians, who gained protection by the U.S. government b. Andrew Jackson, who gained public approval as a result of his policy c. American farmers, who gained millions of acres of land for settlement d. Cherokee Indians, who gained a new model of constitutional government c. American farmers, who gained millions of acres of land for settlement 18. What did the Supreme Court rule in Worcester v. Georgia? a. The Cherokee Indians had to move from their land in Georgia. b. The state of Georgia had no legal power over the Cherokee. c. Only state governments had authority over American Indians. d. U.S. troops in any state had the right to move American Indians. b. The state of Georgia had no legal power over the Cherokee. 19. Which statement describes “The Trail of Tears”? a. the streams of blood that flowed from the Sauk Indians at the end of the Black Hawk War b. the involuntary 800-mile march Cherokee Indians made in their removal from Georgia c. the line connecting Seminole Indian settlements up and down Florida’s east coast d. the traces of salt reportedly seen on Osceola’s face when he was found dead in prison b. the involuntary 800-mile march Cherokee Indians made in their removal from Georgia 20. Which word BEST describes Andrew Jackson’s treatment of American Indians? a. sympathetic b. strange c. legal d. brutal d. brutal 21. Based on the U.S. government policy toward the Cherokee, why was the United States’ political leadership in such a hurry to uproot the American Indian population? a. The promise of resources like gold on tribal grounds outweighed any commitments to American Indian land rights. b. The removal of American Indians was politically popular at a time when fearful citizens were migrating west. c. Property for farming grew expensive as it became scarce and Americans wanted an opportunity to buy cheap land. d. Urban centers struggled with a growing population and city dwellers longed for the freedom of open spaces. a. The promise of resources like gold on tribal grounds outweighed any commitments to American Indian land rights. 22. What did the Seminole Indians do after signing a treaty in 1832 in which they agreed to leave Florida within three years? a. They brought a case against the state of Florida. b. They respected the treaty and took a deadly journey west. c. They ignored the treaty and resisted removal with force. d. They stayed in Florida and adopted white people’s culture. c. They ignored the treaty and resisted removal with force. 23. Which group did Osceola lead against U.S. troops? a. Sauk b. Cherokee c. Fox d. Seminole d. Seminole 24. Who was Chief Black Hawk? a. The leader of the Fox and Sauk Indians who decided to fight U.S. officials rather than leave Illinois. b. The Seminole leader who called upon his tribe to resist removal and wound up dying in prison. c. The Cherokee leader who persuaded his tribe to appeal to the U.S. Courts instead of using violence. d. The leader of the Chickasaw Indians who negotiated a treaty to get more supplies for the trip to Indian Territory. a. The leader of the Fox and Sauk Indians who decided to fight U.S. officials rather than leave Illinois. 25. What do supporters of the states rights’ doctrine believe? a. State power should be greater than federal power. b. The Constitution grants Congress authority over interstate commerce. c. Northern interests should be considered before the interests of other regions. d. The Constitution treats Congress as less valuable than state legislatures. a. State power should be greater than federal power. 26. During 1827, northern manufacturers began to demand a tariff on foreign-made woolen goods so that their products would sell better in American markets. What is the term for the kind of tariff they were demanding? a. a protective tariff b. a competitive tariff c. an revenue tax d. a homeland tax a. a protective tariff 27. What kind of policies did Westerners support during Andrew Jackson’s presidency? a. policies that boosted the farming economy and encouraged further settlement b. policies that lowered tariffs on manufactured goods from overseas c. policies that expanded the military presence in regional settlements d. policies that maintained the slavery system throughout the country a. policies that boosted the farming economy and encouraged further settlement 28. What would a Democrat have nicknamed Andrew Jackson? a. the Mob King b. the People’s President c. the Spoiler d. the Indian Chief b. the People’s President 29. What is the practice of giving jobs to political backers called? a. The Favor System b. The Spoils System c. The Nullification System d. The Impressment System b. The Spoils System 30. What was Jackson’s informal group of trusted advisors he met with to discuss issues known as? a. Kitchen Cabinet b. The Parlor Group c. The White Stripes d. The Backyard Brigade a. Kitchen Cabinet 31. What was the economy of the North based upon? a. Emerging Economy b. Fur trade and trapping c. Agriculture or farming d. Manufacturing and trade d. Manufacturing and trade 32. What was the economy of the South based upon? a. Agriculture or farming b. Manufacturing and trade c. Emerging Economy d. Fur trade and trapping a. Agriculture or farming 33. What was the Tariff of 1828 called by Southerners? a. Tariff of Repugnance b. Tariff of Improbability c. Tariff of Superiority d. Tariff of Abominations d. Tariff of Abominations 34. What was stated in the States’ Rights Doctrine? a. Since the National Government formed the states, the National Government was supreme. b. Since the states had formed the National Government then state power should be greater than National power c. Since the states were each separate, they behaved like individuals and should be given all of the rights outlined in the Bill of Rights d. Since the states each had their own state governments, each state legislature could select the governor b. Since the states had formed the National Government then state power should be greater than National power 35. Who was a vocal supporter of states rights and eventually resigned as vice-president to support his home state of South Carolina? a. Jack White b. John Tyler c. Henry Clay d. John C. Calhoun d. John C. Calhoun 36. In the opinion of John C. Calhoun, who had the power to determine whether federal was constitutional? a. The States b. The Senate c. The Supreme Court d. The President a. The States 37. Daniel Webster debated intensely on the Senate floor in 1830. Which of the following supports his position? a. That nullification gives a state a way to lawfully protest against federal legislation b. That the United States is one nation, not a pact of independent states and that the welfare of the nation should override that of individual states c. That nullification was really a state issue and that the states should be able to decide the constitutionality of each federal law d. That the United States should let nullification be decided by Congress and not the Supreme Court b. That the United States is one nation, not a pact of independent states and that the welfare of the nation should override that of individual states 38. Robert Y. Hayne debated intensely on the Senate floor in 1830. Which of the following best supports his position? a. That nullification was actually unconstitutional and should never be allowed to be used by the states b. That the United States is one nation, not a pact of independent states and that the welfare of the nation should override that of individual states c. That nullification was really a state issue and that the states should be able to decide the constitutionality of each federal law d. That the United States should let nullification be decided by Congress and not the Supreme Court c. That nullification was really a state issue and that the states should be able to decide the constitutionality of each federal law 39. How did President Jackson try to help the Southern states economic problems in 1832? a. He helped southern farmers reduce the price of seeds for planting b. He urged Congress to lower their earlier tariffs c. He helped triple the amount of slaves imported from Africa and the Caribbean area d. He asked the Supreme Court to make the Tariffs of 1828 and 1832 unconstitutional b. He urged Congress to lower their earlier tariffs 40. What did President Jackson do in response to South Carolina’s threat to secede from the Union? a. He backed down and signed the Olive Branch Petition b. He increased the taxes on slaves and goods produced by their state c. He urged Congress to pass the Force Bill to allow him to send in the army d. He kicked South Carolina out and told them to see what it would be like to be their own independent country c. He urged Congress to pass the Force Bill to allow him to send in the army 41. What does Inflation mean? a. An increase in prices and a decrease in the value of money b. A decrease in prices and increase in the value of money c. An increase in prices and an increase in the value of money d. A decrease in prices and a decrease in the value of money a. An increase in prices and a decrease in the value of money 42. What was the Indian Removal Act of 1830? a. It was a law that allowed Native American Indians would come back and forth across the Florida Georgia Line b. It was a law that authorized the removal of Native American Indians who lived east of the Mississippi River to be relocated to lands west of the Mississippi River c. It was a law that allowed Native American Indians to remove white settlers from their lands and reservations d. It was a law that authorized Native American Indians to be allowed to settle from the Northeast to parts of the Southeastern United States b. It was a law that authorized the removal of Native American Indians who lived east of the Mississippi River to be relocated to lands west of the Mississippi River 43. What rationale did President Jackson and VicePresident Calhoun use that Indian Removal was a good thing for the Native American Indians that it affected? a. The land was much more fertile in the new Indian Territories than where they originally lived b. All Native American Indians would be closer together allowing them to trade more easily with each other c. It would protect them from being harassed by settlers and allow them to keep their own way of life d. The weather in the area they currently lived was dangerous, but the Southwest would have a much better climate c. It would protect them from being harassed by settlers and allow them to keep their own way of life 44. What is a severe economic slump in the economy known as? a. Inflation b. Recession c. Depression d. Compression c. Depression 45. Who came up with the writing system for the Cherokee? a. Samoset b. Sequoya c. Squanto d. Pearl Jam b. Sequoya 46. Which case did the Cherokee file with the help of a missionary and take to the Supreme Court saying that the Cherokee Nation was not subject to Federal Indian Removal? a. McCulloch v. Maryland b. Plessy v. Ferguson c. Roe v. Wade d. Worcester v. Georgia d. Worcester v. Georgia 47. What were the wars fought by the Fox and Sauk Indians known as? a. The Seminole Wars b. The Black Hawk Wars c. The Great Sioux Wars d. The Cold War b. The Black Hawk Wars 48. Which two rulings did John Marshall give in the case of the Cherokee Indians? a. He ruled that the Cherokee did not have the right to the land they lived on and consequently they needed to move b. He ruled that the Cherokee nation was a distinct community in which the laws of Georgia had not force and only the federal government had authority over them c. He ruled that the Cherokee did have a claim to the land, but that each individual state could override the federal government d. He ruled that the Cherokee could remain, but only if they allowed burial grounds to be torn up and used by developers b. He ruled that the Cherokee nation was a distinct community in which the laws of Georgia had not force and only the federal government had authority over them 49. All of the following were views in which the North and South differed distinctly on, EXCEPT a. Conflicting views on the issue of slavery b. Different economic interests c. Disagreement over the Indian policy d. Disagreement over protective tariffs c. Disagreement over the Indian policy 50. Who came up with a compromise over the tariffs in 1833 to help put off bloodshed for a few more years? a. Daniel Webster b. John Lennon c. Patrick Henry d. Henry Clay d. Henry Clay 51. What new party came about for the 1828 from supporters of Andrew Jackson? a. Whig Party b. Democratic Party c. Block Party d. Republican Party b. Democratic Party 52. What state was the first to threaten to secede or withdraw from the United States if the army was used to collect the tariffs of 1828 and 1832? a. Kentucky b. Georgia c. Virginia d. South Carolina d. South Carolina 53. What might a typical Southern small farmer have said about the National Bank? a. “That institution is good for wealthy folks, not for me.” b. “I don’t want to mix my money with some Northerner’s.” c. “It can’t be safe to keep all that money in one place.” d. “I would question its legality under the Constitution.” a. “That institution is good for wealthy folks, not for me.” 54. Andrew Jackson’s stance on federal power was not consistent, as evidenced by what? a. He felt that the president should try to control inflation but believed state-based pet-banks were unconstitutional. b. He argued to use U.S. troops to enforce tariff collection but argued against establishing a national bank. c. He used presidential power to remove American Indians but did not respect American Indians’ capacity to govern themselves. d. He felt that the president should try to control inflation but believed state-based pet-banks were unconstitutional. b. He argued to use U.S. troops to enforce tariff collection but argued against establishing a national bank. 55. Who was the director of the Second Bank of the United States? a. Nicholas Biddle b. Alexander Hamilton c. Henry Clay d. Tom Petty a. Nicholas Biddle 56. What was the name of the new party that developed for the election of 1836 and favored the idea of a weak president and a strong Congress to go against the policies of President Jackson? a. Democratic b. Republican c. Whig d. Bull Moose Party c. Whig 57. What was the depression that resulted from President Jackson’s failed economic policies called? a. The Incredible Inflation of 1835 b. The Rising Recession of 1838 c. The Great Depression of 1836 d. The Panic of 1837 d. The Panic of 1837 58. Which president took the blame for the economic problems the nation suffered even though they came about from President Jackson’s failed economic policies? a. John Tyler b. Martin Van Buren c. William Henry Harrison d. Eric Clapton b. Martin Van Buren 59. What was discovered on Cherokee land in Georgia that helped lead to their forced removal? a. Gold b. Platinum c. Oil d. Diamonds a. Gold 60. Which of the following would best describe the Nullification Crisis? a. A period when state governments could place laws on the federal government and the federal government would then have to go to the Supreme Court in order to not have to follow the new laws b. A conflict between the federal government and state governments over whether a state could rule that a law passed by the federal government unconstitutional and refuse to follow c. An arguments between the states about what laws each one could place against the other was challenged in court d. A time when the federal government was able to place any law it wanted on state governments and they had no say so b. A conflict between the federal government and state governments over whether a state could rule that a law passed by the federal government unconstitutional and refuse to follow 61. How did the Cherokee people finally resist removal to Indian Territory? a. They published a newspaper directed toward federal officials. b. They traded tribal goods for knives, guns, and other weapon c. They filed a law suit against Georgia in a federal court. d. They prepared their tribe for war with months of training to be ready for war c. They filed a law suit against Georgia in a federal court. BEST OF LUCK ON YOUR TEST