Coniferous Forest Biome
advertisement

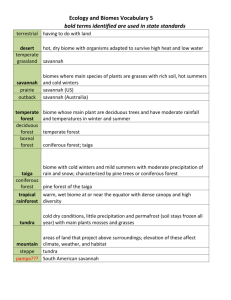
Coniferous Forest Biome Cassie Conkwright And Raven Tuck Key Points Coniferous forest is a terrestrial biome found in temperate regions of the world with warm summers and cool winters and adequate rainfall to sustain a forest. Short summers and long winters. Location • The northern coniferous forest biome occupies a vast area below the tundra, extending completely across Canada and into interior Alaska. The biome is also referred to as the boreal forest or taiga. Abiotic Factors • Average Annual Rainfall- 14-29.5 in. • Average Temperatures in the Summer57.2°F • Average Temperatures in the Winter14°F • The weather in this biome is very cold. • It is stormy in the winter and hot. • There are usually many lightning storms in the summer Abiotic Factors •The length of daylight is 12 hours and varies little. •Clear-cut logging is the biggest threat to the Coniferous forest •Land is being cleared for ski slopes, landfills, housing, new roads, etc. Biotic Factors Animals: White tailed deer, Reeve's muntjac, fox, mice, owls, and squirrels. Biotic Factors There are many plants in this biome, but three dominate more than others. • These are: • pine, • fir, • Cedar • and spruce trees. • Mosses are also found almost anywhere here. Biotic Factors ☼Major Biotic Factors: – Disease • Needle Cast Tree Disease • Needle Blight Tree Disease – Predation – Parasitism Competition • Coniferous forests cover huge areas but have fewer kinds of plants and animals than any other forests. – Therefore, many of the animals in the Coniferous Forest have to compete for food and shelter. • Because the plants grow so slowly, animals need to roam over large areas to find enough food. – This sometimes causes problems because many forest animals are very territorial. Plant Adaptations • Because the plants grow so slowly, animals need to roam over large areas to find enough food. • Some coniferous trees depend on fire as a catalyst for seedrelease – The heat from naturally occurring fires force the Lodgepole Pine tree's serotinous cones to burst open, thus releasing the tree's seeds. • Trees in the Coniferous forest primarily possess pine needles instead of broad leaves. Needles are an important adaptation to the extreme conditions present in the climate. • Pine needles contain very little sap, so freezing is not much of a problem. Animal Adaptations Thick fur to keep warm. • = Flat tails to warn other beavers. Thick fur to help keep warm. Webbed feet to swim faster Large teeth the help hunt. Long legs to run faster. Human Influence/Impact • Clearcut logging is the biggest threat to the Coniferous forest! – Replanting after logging leads to single-species conifer monocultures not conducive to species biodiversity. • In Canada, one acre of forest is cut every 12.9 seconds! • Since the mid-1800s, about 320 billion tons of carbon have been pumped into the atmosphere from the burning of fossil fuels and the destruction of the world's forests. • Over the years, the rain in many areas of the world has become more acidic. Land cleared for ski resort Affects of acid rain Interesting Facts The largest Coniferous forest exists in a ring in Alaska, Canada, northern Europe, and northern Asia, in a ring in the Northern Hemisphere. This forest is called the "Taiga". Most of the world's commercial softwood timber, used for paper, comes from the Coniferous Forest. Coniferous Forests are the largest land Biome of the World. Works Cited • http://www.inchinapinch.com/hab_pgs/t erres/coniferous/c_forest.htm • http://lsb.syr.edu/projects/cyberzoo/con iferous.html • http://www.fw.vt.edu/dendro/Forsite/ncf biome.htm http://www.dnr.state.mn.us/snas/conifer ous.html