Chapter 5 Global Selling Process, II
advertisement

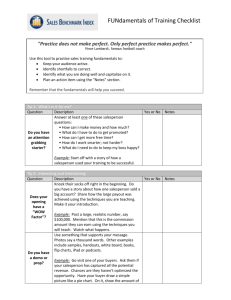
Chapter 5 Global Selling Process, II Sales Management: A Global Perspective Earl D. Honeycutt John B. Ford Antonis Simintiras Introduction • This chapter builds upon Chapter 4: – Interpersonal communication process – Sales negotiation process – Initial steps of the global selling process • Interpersonal communication and sales negotiation processes interwoven into the global selling process Sales Process • • • • • • • Finding customers Preparing Relationship building Product offering Offer clarification Securing the purchase Maintaining the relationship Relationship Building • Making a favorable impression and gaining trust of potential customer – Time required varies by culture • Number of ways to meet client: – – – – Guaranteed introduction Referral introduction Personal introduction Benefit introduction Relationship Building • Should know appropriate greeting and phrases in customer’s language – Business cards in English and customer’s language – Business cards have taken the place of personal introductions in Japan What is a Buying Center? • One or more people in the B2B customer firm that play different, but important, roles in the buying process. They include: – – – – – – Initiators Users Influencers Buyer Gatekeeper Salesperson must identify and interact correctly with each group of clients playing specific roles Product Offering • Salesperson must select an appropriate method to offer the product to the client • This step normally includes one or more of the following styles: – – – – – Stimulus response Mental States Need satisfaction Problem solving Consultative selling Stimulus Response • Salesperson provides appropriate stimulus through words and actions that will derive desired response – – – – – Utilized with canned sales presentations Seen with low involvement products Purchaser involvement limited Often not flexible Used for one-time interactions Mental States • Salesperson attempts to move customer through the purchase stages (attention, interest, desire, action) – – – – – Presentation must be well-planned Limited purchaser involvement Hard to know what stage customer is in Difficult when used across cultures Not well received by professional purchasers Selling Approaches • Need satisfaction – meets and asks questions in an effort to identify and satisfy a customer need – Focuses on customer’s need(s) • Problem solving – extension of Need Satisfaction that includes study or team of experts • Consultative selling – salesperson functions as a consultant and may even recommend a competitor’s product that best satisfies customer need(s) Buyer-Seller Meeting • Meet with customer at appointed time – Punctuality more important in some cultures – Make favorable impression • Sharing information through small talk • Presenting gifts • Begin meeting by restating last communication as understood – Insure customer’s goals understood – No slick presentations – Explain how the solution solves goals and needs Offer Clarification • Once presentation finished, expect questions – Clarify offer or ask for price concessions – Remember that negotiations take place during the entire process – May request test data or testimonials from satisfied customer – View this step as normal negotiations Securing the Purchase • Simply asking the customer to purchase – Difficult to manipulate buyer into purchase – This is especially true in B2B interactions • Best approach is the direct one – Since our product addresses your need(s), shall we agree to the purchase? – Some countries, like China, seller may await the buyer to raise issue of purchase Maintaining the Relationship • Final, but very important step in sales process – Satisfied customers purchase again and again – Customer wants supplier they can trust and who will be there when problems arise – Customer satisfaction very important in Japan – B2B firms track customer satisfaction levels – Salesperson must have authority to keep customer satisfied Ethical Considerations • Personal selling generates buyer complaints – Salespersons believed to have low ethical standards – Some firms operate from a selling orientation – Most complaints attributable to management • Setting unrealistic sales goals/quotas • Rewarding for sale even when questionable behavior is involved Role of Salesperson • That of a boundary spanner – Must bring buyer and seller together – Initial positions often far apart • Seller wants: highest price, standard product, longest delivery, and no service • Buyer wants: lowest price, custom product, shortest delivery, and service contract • Salesperson must mediate Role Conflict • Salesperson experiences role conflict when two or more parties want her to comply with their expectations – Each party can reward or punish salesperson • Sales manager can give or withhold raise • Customer can order or withhold purchase • Family can give or withhold love, approval • Salesperson must attempt to satisfy concerns of all parties – not an easy task! Chapter 5 Summary • The sales process is completed – Approach must be modified based upon culture of buyer – No “tricks” to selling; just hard work! • Salesperson may be viewed as being less than ethical because of role played • Role conflict can occur in B2B sales • Ethical behavior always the best approach Discussion Questions • What is the benefit of the global salesperson making informal sales presentations? • What kinds of questions might the prospective buyer have for the global salesperson after the presentation? • What is role conflict and how might it affect the global selling process?