Lab 14 Heart 5
advertisement

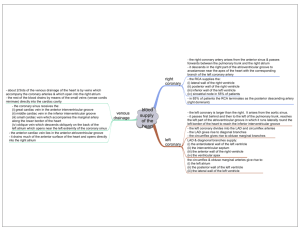
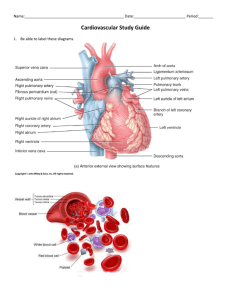
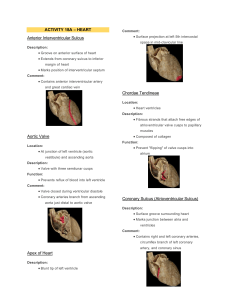
Lab 5-3 Heart Pericardiacophrenic Vessels • Off what vessels do they branch from? • Veins: Drain into R/L Brachiocephalic vv • Arteries: Branch from R/L Internal thoracic aa Fibrous Pericardium Parietal Layer Visceral Layer Clinical Correlates • Accumulation of fluid within the pericardial sac is… • Pericardial effusion • The excess fluid compresses the heart and causes biventricular failure aka… • Cardiac tamponade Transverse pericardial sinus Oblique Pericardial Sinus Apex Base • What makes up the base? – L atrium – Sm. Portion of R atrium – Proximal parts of the great viens Right Atrium Right Ventricle Left Atrium Left Ventricle Orientation of Heart • Which chamber has the largest diaphragmatic contact? • Right Ventricle Crista Terminalis Sinus Venarum • What empties blood into this space? • Superior and Inferior Venae cavae Pectinate Muscles Fossa Ovalis • What was this depression during embryonic development? • Foramen ovale • It’s function? • Oxygenated blood from R atrium to L atrium so it can bypass the lungs Opening of the Coronary Sinus • Any guesses what veins will empty into here? • Great, Middle, and Small Cardiac Veins Tricuspid Valve Pulmonary Valve Mitral Valve Chordae Tendineae Trabeculae Carnae • What are the trabeculae Carnae that have one end attached to the ventricular surface and the other end attached to the chordae tendinae called? • Papillary Muscles Papillary Muscles Papillary Muscles • How many in right ventricle vs left? • Right Ventricle: Anterior, Posterior, and Septal (sometimes small or even absent) • Left Ventricle: Only Anterior and Posterior Conus Arteriosis Membrane Interventricular Septum Muscular Interventricular Septum Septomarginal Trabeculum • What is it and what’s its function? • A band of myocardium that connects the interventricular septum and the anterior papillary muscle • Carries a portion of the cardiac conduction system-the right bundle branch-to the anterior wall of the right ventricle Conduction System: Right Bundle Branch Conduction System: Left Bundle Branch Right Coronary a. Right Marginal a. • What does it supply? • Right Ventricle Right Atrial aa. • Which one is the SA nodal artery? • The artery which passes posteriorly between the aorta and superior vena cava Right Posterior ventricular a AV Nodal a Left Coronary Anterior interventricular a Anterior Interventricular a (posterior view) • What does it supply? • R and L ventricles and interventricular septum • Clinical name? • Left anterior descending artery (LAD) Left Marginal a Circumflex branch of Left Coronary a • Supply? • Left atrium and Left ventricle • Name the 2 descending branches.. • (More Superior) = Lt. posterior ventricular a • (Inferior branch) = Posterior interventricular a Posterior interventricular a • Which coronary artery does this most commonly originate from (right or left)? • Right • However, AP decided to use a Left coronary a. dominant pattern • =supplying most of the posterior wall Coronary Sinus Small Cardiac v Middle Cardiac v Great Cardiac v Anterior Cardiac vv (Right and Left) CT Imaging • • • • Right ventricle Ascending aorta Pulmonary vv Descending aorta CT imaging • Right Coronary Artery • Right Atrium • Left Coronary Artery