H- physl TUTORIAL 1_Solved_
advertisement

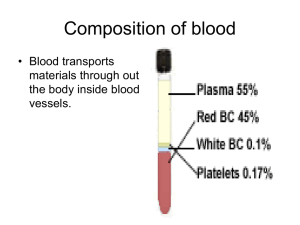
HMIM - 224 TUTORIAL - I DISCUSSION *SOLVED* •Dr. Zahoor 11 Topics Blood Plasma Hematocrit or PCV Plasma Protein Erythropoiesis Anaemia White Blood Cell (WBC) 2 2 1st lec Q.1 Give the composition of blood? 1. Plasma – 55% 2. Cells - 45% 2.Cells are -Erythrocytes [RBC - Red Blood Cells] - Leukocytes [WBC – White Blood Cells] - Platelets Q2. Define Hematocrit or PCV. It is ratio of cells [RBC, WBC, Platelet] to the plasma. PCV - 45% [40 to 47%] Plasma - 55% Q3. In blood, how much % is plasma? 55% 3 3 Q4. What is the composition of plasma? water – 90% - inorganic constituents – 1% E.g. Electrolytes – Na+, Cl-, K+, HCO3-,Ca2+ They play role in membrane excitability. Organic constituents - Plasma protein – 6 – 8% - Other organic substances present e.g. Glucose, amino acids, lipids and vitamins. Waste products – urea, creatinine, bilirubin. Dissolved gases – O2 and CO2 Hormones 4 Q5. Name the plasma protein. - Albumin - Globulin - Fibrinogen Q6. What is the function of albumin? Plasma osmotic pressure and Albumin binds to many substances for transport of like bilirubin Q7. What is the function of Globulin (alpha and beta)? Carry substances like thyroid hormones, cholesterol, iron, lipids, insulin, vitamins A, D, K. Many blood clotting factors are alpha or beta globulin. Angiotensinogin is alpha globulin. 5 5 Q8. What is gamma globulin? Gamma Globulins are antibodies and play important role in body defense mechanism Q9. What is the function of different gamma globulins? - IgG – work for defense of body present in plasma - IgM – work for defense of body present in plasma - IgA – present in secretion e.g. saliva, breast milk, intestinal secretion - IgD – recognize antigen - IgE – play role in allergic reaction 6 Q10. What is the function of fibrinogen? factor in blood clotting Q11. Give the causes of hypoprotenemia? less protein intake protein loss in kidney liver disease, decrease synthesis of protein intestinal disease, less absorption of protein Q12. What is edema? What is the cause of edema? in hypoproteinemia, there is decreased plasma osmotic pressure, therefore, there is Edema [collection of fluid in subcutaneous tissue]. 7 7 Q13. Blood viscosity depends on what? PCV and plasma protien Q14. How much blood volume in normal adult male/female? Men 5.5 litter women 5.5 litter 2nd lec Q15. What is life span of RBC? 120 days Q16. What is the difference between blood, plasma and serum? The same componants but the serum doesn't have clotting factor 8 8 Q17. What is normal RBC count? 5 million per cubic millimeter (mm3) of blood. Q18. What is the size of RBC and its shape? biconcave discs 7.5 - 8 micrometer (µm) in diameter and 2µm thick at outer edge and 1µm thick at the center Q19. What is the function of RBC? O2 transport O2, also CO2 transport. Q20. Why RBC is red? Contain hemoglobin and heme contain iron Q21. What is the composition of hemoglobin? heme+globin 9 9 Q22. If you see arterial blood and venous blood sample in the tube by naked eye, what difference in the color would you find? Arterial Red(oxygenated) ,Venous bluish deoxygenated Q23. In adult, where erythropoiesis takes place? Red Bone marrow Q24. What things are required for erythropoiesis Amino acid -Iron – Vitamin B12 and folic acid _ Hormones erythropoietin 10 1 Q25. What is the difference between red and yellow bone marrow yellow bone marrow fat red bone marrow production of erythropoiesis 11 Q26. In your hospital, you are asked to take the bone marrow sample of a patient who has decreased RBC, WBC, and platelet count, which site you will choose to take the bone marrow sample? Sternum – iliac crest (Flat bones) Q27. What is erythropoietin? Hormone erythropoietin is secreted in blood and stimulates erythropoiesis. 12 1 Q28. Where is erythropoietin formed? kidney Q29. What is the function of Erythropoietin? stimulates erythropoiesis in the bone marrow by acting on committed RBC. 13 Q30. A patient has kidney disease, what will be his hemoglobin, and RBC count? What treatment you will give him/her for his anemia? Decrease(Low) ,erythroprotien Q31. If reticulocyte count is increased, what does it signify? Active bone marrow, high rate of erythropoietic activity, Hemolytic anemia 14 1 Q32. When there is Hb breakdown, what happens? Give bilirubin= jaundice 3rd lec Q33. What is Anemia Decreased hemoglobin - Decreased RBC count - Decreased Hematocrit [PCV] Therefore, decreased O2 carrying capacity of blood. 15 Q34. What are different types of Anemia? Nutritional anemia - Pernicious Anemia-Aplastic Anemia- Hemolytic Anemia-Renal Anemia-Hemorrhagic Anemia Q35. If Hb decreased, RBC decreased, PCV decreased, MCV (Mean Cell Volume of a single cell) decreased, MCH [Mean Concentration of Hemoglobin of single cell] decreased, what type of anemia is it? Microcytic anemia [iron deficiency] small cell+ low Hemoglobin Q36. What will happen in Vit B12 deficiency anemia? Macrocytic [megloblastic] anemia MCV increase, Hemoglobin normal Q37. Define MCH. Mean Concentration of Hemoglobin 16 1 Q38. How much is normal Hb in adult person? 15 gram / dl Q39. Give two causes of Hemolytic anemia? -Hemolysis in newborn antibody – antigen reaction -Malaria -Sickle Cell Anemia -RBC is sickle shaped -Mismatched blood transfusion -Drugs Q40. Give two causes of Aplastic anemia( bone marrow suppression)? -Excessive exposure to X-ray -Exposure to radiation, e.g. bomb blast -Chemotherapy for Cancer -Drugs Q41. How much blood is taken when blood donation is done? 450-550ml 17 1 Q42.After how much time, blood donation can be given again, why? 3 months, cause the RBC produce every 36days 4th lec Q43. What are different types of WBC? Polymorpho nuclear granulocytes Mononuclear agranulocyte 18 1 - Q44. What is normal % of N, E, B, L, M? What is life span of different leukocytes? • N 60-70 / E 1-4 / B 0,5-1 / L 20-40 / M 2-8 Granulocytes 4-8 hours (1 day) Monocytes 10-20 hours (3 days) Lymphocytes months (100-300 days) Macrophages Months- years 19 Q45. How you will identify neutrophil in microscopic examination? Multilobed nucleus , Pink- purple granules Q46. What is function of Neutrophil phagocytosis Eosinophil Allergy Basophil Heparin -Histamine Lymphocyte immune deafens Monocyte phagocytosis 20 2 Q47. What is normal total leukocyte count? 4000-11000/mm3or µL ( same units) Q48. What is Leukocytosis? Increase in WBC Q49. In what condition, Leukocytosis will occur. bacterial infection Q50.What is Leukopenia. Give one cause. Decrease in WBC, Viral infection Q51. What is Leukemia? Increase in immature leukocyte 21