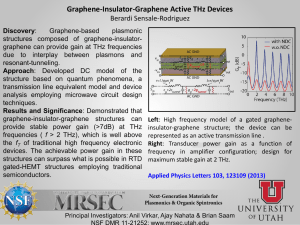
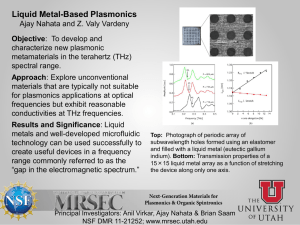
Development of high sensitive FIR detector
advertisement

Towards passive terahertz imaging using a semiconductor quantum dot sensor Vladimir Antonov Royal Holloway University of London http://www.teraeye.com Acknowledgments Royal Holloway, UK : H Hashiba Tokyo University&JST, Japan: Prof. S Komiyama, Drs. J Chen, O Astafiev (NEC) ISSP RAN, Russia: Dr. L Kulik NPL, UK: Dr A Tzalenchuk, Dr S Gibling and P Kleinschmidt Chalmers University, Sweden: Prof. P Delsing, Dr S Kubatkin Optisense LTD: M Andreo Passive Imaging with superconducting bolometer by VTT-NIST Nb superconducting bolometer Detection of hidden weapon Courtesy of VTT-NIST Some numbers for consideration Noise Equivalent Temperature Difference (NETD) imposed by the temperature contrast, or variation of spectral intensity (spectral fingertips) < 0.1K Background limited noise BLIP~ T(F/n)1/2 , where F - frame rate (10Hz), n - number of detected photons (108), ~0.05K Detector should have NETD better than 0.1K and counting rate around 108 photons/sec Some numbers for consideration Passive imaging 2 U, 10-21 J /(Hz m3) U, 10-19 J /(Hz m3) Plank’s law T=305K 1.5 1 T=300K 0.5 100 200 f , THz 300 400 500 2.25 2 1.75 1.5 1.25 0.75 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 f , THz There is a difference in ~1010 photons/sec (~10-23J) for black body radiation at 300K and 305K in bandwidth from 0.5 to 0.7 THz. Finger prints of explosives Complex materials has a unique fingerprints in spectrum T=300K JF Federici et all ’05 QD as a spectral sensitive detector Layout of the QD in 2DEG SEM images of the QD Resonance curve Frequency (/cm) Plasma resonance in QD QD in magnetic field 60 2 4neZero filed 0 ~ m 1R 2 40 0 20 0 APL ’02 0 1 c c c 2 0 2 2 2 2 B (Tesla) 3 4 5 QD-SET detector Energy diagram SET QD 0 EF e2 C1 Dark switches and photo-response SET response to QD excitation radiation is OFF Conductance DVg SET current, arb Log-periodic circular antenna (0.2-3Thz) coupled with QD sensor original peaks shifted radiation is ON peaks Vg 25 Gate voltage, 75 Time,sec Modeling of QD-SET SET SG1 CG Offset charge at SET QD SG2 VSD C CC C SD CCD C1 C 2 S S C1 R1 N S S S C VS CC C N D D S C2 R2 NSET S S C D S C1 R1 CC VS C SD VC CCD eN D C VC D C C NSET+1 QSET S QSET VS C SS VC CCS D D C2 R2 D -Vc Formation of QD Individual SET trace IS, arb. units -4.0 -3.8 -3.6 VS,V I S (pA) 200 Charging of the QD I 0 2D map of SET current -2.75 -2.70 VC (V) -3.4 Photosignal at 0.3K T=0.05K T=0.3K Photo response and dark counts Noise Equivalent Power~ 10-20 Watt/Hz1/2 NETD = NEP/(2hkBDnt1/2 ~0.01K Quantum Efficiency ~1% Spectral bandwidth ~ 1% Operation temperature is limited by SET (up to 4K) APL, JAP, PRB, IEEE ’04-07 Photosignal at 0.5-0.7K 120 T=0.5K 35 photoresponse 120 60 20 15 30 dark -1 Counts,s Counts,s 25 photoresponse 90 25 60 20 15 30 dark 10 0 30 10 0 -2.20 -2.15 -2.10 -2.05 -2.00 VC,V 5 -2.20 -2.15 -2.10 -2.05 -2.00 VC,V 5 Lifetime,ms 90 Lifetime,ms -1 30 35 T=0.7K 2D maps of QD-SET Emitter is OFF VS, V VS, V Emitter is ON VC, V VC, V Physica E ’06 PRB’06 Detector of different designs A lateral sensor with QD crossing the channel A lateral sensor with QD inside channel A lateral sensor with QD outside channel A vertical sensor QD outside of 2DEG channel QD-SET Gate QD inside the 2DEG channel QD in high magnetic field QD in high magnetic field SEM picture of the QD C1 Metal gates EF C12 C2 Vg 1m LL2 LL1 LL1 LL0 NATURE, 2000 QD in high B QD under illumination 0.4 Conductance (e /h) Conductance (e2/h) 0.6 Time traces of QD conductance 2 B=3.67 T T=0.05 K light off light on 0.2 0.0 -689 -688 Gate voltage (mV) -687 Spectral sensitivity of the detector 0.4 light on 0.2 light off 0.0 0 5 Time (sec) 10 QD in high B QD has three levels: Lifetime of excitations LL0,LL0, LL1 II I 4 10 3 2 7 5 1 6 10 10 9 1 10 -1 10 -2 10 -3 3.4 4 1 3 8 3.6 PRB, 2002 3.8 B (T) 4.0 4.2 I -660 I I I II II II I I I I II II II II II II I II II 1 -665 0 -670 3.5 3.6 B(Tesla) 3.7 Condactance (arb.units) 2 Control gate voltage (mVolt) Lifetime (s) 10 LT THZ microscope of Tokyo University Ikushima, Komiyama APL, 2006 LT THZ microscope of Tokyo University Future plans: Quantum Dot in DQW heterostructure Schematic view Inter-well excitation in asymmetric DQW ~1 THz Near-field antennae Near-field antenna Simulation of near-field antennae 50m Simulation of E-field Near-field antenna Challenges QD detector: which type? Room Temperature Imaging Source of THz radiation for in-situ calibration • Physics of isolated QD in DW heterostructures Vertical sensor in DQW heterostructure An et all, PRB’07