File
advertisement

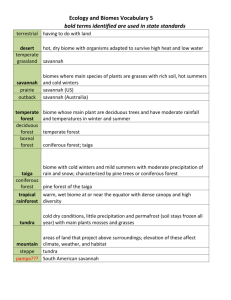
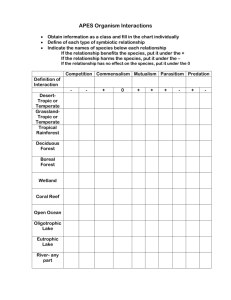
Intro to Ecology Part 2 Climate vs. Weather Weather Day-to-day conditions of Earth's atmosphere precipitation, humidity, temperature, etc. Changes every day Climate The average, year-after-year, conditions (temperature and precipitation) that prevail in a specific region Microclimate Climate in a specific area that varies from the surrounding climate region Ex. The burrow of a Kangaroo rat in the New Mexico desert (dark and cool) Biomes Terrestrial ecosystems that cover a large region of Earth Characterized by communities of plants and other organisms adapted to the climate and other abiotic factors Major Terrestrial Biomes Tropical Rainforest Tropical Dry Forest Tropical Savannah Desert Temperate Grasslands (Prairie) Temperate Woodland/shrubland (Chaparral) Temperate forest Northwestern Coniferous Boreal Forest/Taiga Tundra Tropical Rainforest Canopy: dense covering of tree tops Understory: 2nd story of shorter trees and vines under the canopy Fern Gully/Medicine Man Tropical Dry Forest Deciduous trees: broad leaves that fall Wet/Dry season “Jungle Book” forest Tropical Savannah In the tropics Wet/dry season Less rainfall than trop. Dry forest Think “Lion King” Desert Around 25-35o Latitude N and S Plants and animal adaptations Spines, waxy cuticles, scales Think “The Mummy” and “The Sahara” Temperate Woodland/Shrubland/Chaparral Dense shrubs Mediterranean, California coast Brush fires Temperate Grassland prairies Midwest (Kansas, Oklahoma, Missouri) Brush fires Think movie “Twister” “Wizard of Oz” and “Little House on the Prairie” Temperate Forest Mix of coniferous and deciduous trees Humus (HUE-Mus) material formed from decaying leaves….very fertile!!! Forests with leaves that change colors Think fairy tale forest “Snow White” and “Sleeping Beauty” Northwestern Coniferous “Rainforest” of the temperate climate zone…very DIVERSE vegetation Mild, moist temperatures Think “Twilight” “New Moon” “Eclipse” Boreal Forest/ Taiga Bitter cold winters Coniferous trees Make the timberline…border between taiga and the tundra Think “X-Men Origins”…Wolverine’s home Tundra Permafrost: layer of permanently frozen subsoil “Ice Age” Other interesting ecosystems… Mountain Ranges On all continents Abiotic and biotic factors change with ELAVATION (as u go up) Therefore plants and animals change VERTICALLY Grassland at base woodland/pines spruce/conifer forest tundra like open area at summit with wildflowers Polar Ice Caps Border the Tundra Cold year round Characterized by ice and snow Plants and algae are few but include Mosses and Lichens North Pole Sea ice and ice cap that covers Greenland Polar bears, seals, insects and mites South Pole 5 km thick layer of ice Penguins and marine mammals COPY!!! Define! Producer: Consumer: Autotroph: Heterotroph: Food Chain: Food Web: Trophic Level: Energy is transferred in ecosystems Producers give E to Consumers Food chains show flow of energy (arrows show where energy is going) Trophic levela single step in the food chain Primary ProducersAUTOTROPHSmake their OWN food A step in the transfer of energy and matter in an ecosystem Use Photosynthesis and Chemosynthesis to change inorganic chemicals into molecules that they use for ENERGY!!! Plants and bacteria Consumers HETEROTROPHS must eat different things to get their E…canNOT make their own GLUCOSE Primary consumers, secondary consumers, tertiary consumers Herbivores: eat plants Omnivores: eat plants and animals (bears, humans) Carnivores: eat other animals (wolves) Detritivores: eat dead plants and animals (earthworms, mites, crabs) Decomposers: get energy from decaying organic matter (bacteria and fungus aka mushrooms) Trophic Levels • Each link in a food chain is known as a trophic level. • Trophic levels represent a feeding step in the transfer of energy and matter in an ecosystem. Trophic Levels Tertiary E N E R G Y consumers- top carnivores Secondary consumerssmall carnivores Primary consumers- Herbivores Producers- Autotrophs Food chain- simple model that shows how matter and energy move through an ecosystem Food web- shows all possible feeding relationships in a community at each trophic level • Represents a network of interconnected food chains Food chain (just 1 path of energy) Food web (all possible energy paths) Biome Projects Tropical Rainforest Tropical Dry Forest Tropical Savannah Desert Temperate Grasslands (Prairie) Temperate forest Chaparral /shrub land North Western Coniferous Boreal Forest/Taiga Tundra Everglades Deep Sea Hydrothermal Vents Tropical Coral Reefs Biome Project Guide Lines Children’s book using your biome as a setting and showing interactions between organisms Must be NEAT, SIMPLISTIC, yet INFORMATIVE Report Abiotic Factors of biome Climate and Precipitation Countries in which biome can be found Dominant animals (at least 9) Dominant plants (at least 9) Problems/issues threatening this biome 3 interesting facts 3 different food chains Name of organism Primary producer, primary consumer, secondary consumer and tertiary consumer labeled in each Type of consumer (herbivore, carnivore, omnivore, detritivore, decomposer) labeled in each One of the food chains MUST be present in and numbered/labeled in 3D model 1 food web (pictures and names of organisms) Model 3-D CREATIVE model of biome Model must include one of the food chains listed in your Report Model must include accurate plants and animals No candy/edible items and No living organisms