Photosynthesis PPT
advertisement
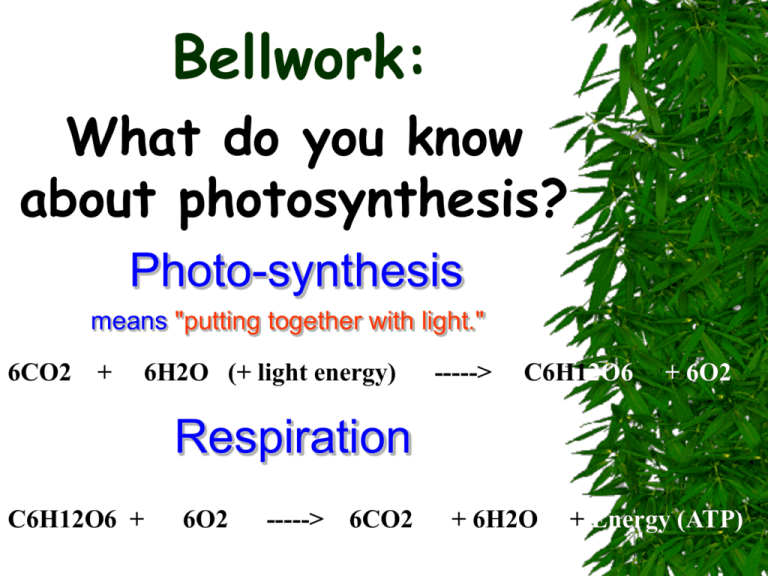
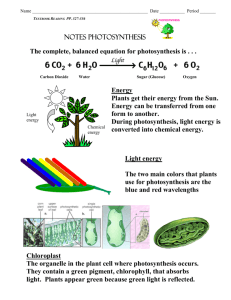
Bellwork: What do you know about photosynthesis? Photo-synthesis means "putting together with light." 6CO2 + 6H2O (+ light energy) -----> C6H12O6 + 6O2 Respiration C6H12O6 + 6O2 -----> 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy (ATP) Photosynthesis-starts the ecological food webs! What is photosynthesis? A chemical reaction in which light energy is converted to chemical energy in the form of glucose. It is how the energy in sunlight becomes usable to living things. Why is it so important? Two big reasons: 1. One product is glucose (sugar), which provides the basis for most food chains. 2. The second product is oxygen which is needed by aerobic organisms (require oxygen) for survival. Photosynthesis sunlight Carbon dioxide + water absorbed by chlorophyll glucose + oxygen 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 As can be seen from the equation for photosynthesis, the wood, bark, and root came from water and carbon dioxide. Where does photosynthesis occur? Most photosynthesis occurs in the oceans, the oceans occupy (70%) of the earth's surface! In terms of organisms, photosynthesis occurs in autotrophs that contain the green pigment chlorophyll. Review: What is an autotroph? Multicellular level: photosynthesis occurs in the leaves of plants. Cellular level: the reactions for photosynthesis occur in the chloroplasts of eukaryotes and in the cytoplasm of prokaryotes. Plant leaves have many types of cells! Chloroplasts make the sugars! Plants Leaves are green because they contain the pigment: chlorophyll Why do leaves have a broad surface area? "Thanks for the Glucose!" PHOTOSYNTHESIS • Why do we see green? • Green color from white light reflected NOT absorbed • Chloroplast: organelle responsible for photosynthesis • Chlorophyll: located within Chloroplast • Green pigment Plant Cells The photograph below is an elodea leaf X 400. Individual cells are clearly visible. The tiny green structures within the cells are chloroplasts this is where photosynthesis happens. What raw materials are needed? Chlorophyll Sunlight Water Carbon dioxide Biochemical Pathway Photosynthesis is a series of two reactions The products from the st 1 rxn are used in the 2nd PHOTOSYNTHESIS • 2 Phases • Light-dependent reaction • Light-independent reaction • Light-dependent: converts light energy into chemical energy; produces ATP molecules to be used to fuel light-independent reaction • Light-independent: uses ATP produced to make simple sugars. Summary of Photosynthesis carbon dioxide + water + light energy --> glucose + oxygen + water As a chemical formula: CO2 + H2O + light energy ---> C6H12O6 + O2 + H2O fsgjkshm k Extra Tidbits Important part of OxygenCarbon Dioxide Cycle. – pumps out oxygen – Removes CO2 from atmosphere of CO2 linked with ↑ global temp (think "Global Warming"). ↑levels Chloroplasts ½ of the chemistry occurs in a liquid inside the chloroplasts called STROMA ½ of photosynthesis occurs in stacks of membranes inside the chloroplast called GRANA. Chlorophyll Green pigment, which absorbs sunlight. 2 types of chlorophyll – chlorophyll a – chlorophyll b Chlorophyll a is the main, b is an accessory Chemical Reaction Occurs in two phases. Capture Energy #1 is called the "light reactions". It requires light! Convert Energy to Food #2 is called "carbon fixation" or the "dark reactions". Aka Calvin Cycle It does not require light. Start with CO2 End with Glucose Photosynthesis EQUATION FOR PHOTOSYNTHESIS WATER 6CO2 + 6H2O +ENERGY CARBON DIOXIDE OXYGEN C6H12O6 + 6O2 GLUCOSE Back to the Chloroplast The light reactions occur in the grana, which contain the chlorophyll for absorbing light. The dark reactions occur in the stroma. Detailed Light Reactions The light reactions use light & water, & produce the oxygen "waste product". The light energy is used to split the water molecule (photolysis), which produces e-’s. H+ & Oions. The oxygen is released from the plant into the air. ATP & NADPH2 are energy molecules. They will be used up during the dark reactions, as will the H+ ions. Electron Transport 1. 2. CONVERTS to useable Energy Light excites the electrons E-’s leave chlorophyll a and go to the primary electron acceptor (PEA) (in thylakoid membrane) Sun Light energy transfers to chlorophyll. • At each step along the transport chain, the electrons lose energy. Chlorophyll passes energy down through the electron transport chain. Energized electrons provide energy that splits H2 O H+ NADP+ oxygen released to ADP bonds P forming ATP NADPH for the use in light-independent reactions 3. PEA then donates the e’s to other molecules which pass them on over and over. (electron transport chain) 4. E’s join with a proton and NADP+ which forms NADPH Replacing the Electrons E-’s are taken from the chlorophyll to pass down the ETC. They must be replaced to be passed down again. E-’s accumulated during photolysis are given to the chlorophyll. Photosynthesis Rap Check it! EQUATION FOR PHOTOSYNTHESIS WATER 6CO2 + 6H2O +ENERGY CARBON DIOXIDE OXYGEN C6H12O6 + 6O2 GLUCOSE PHOTOSYNTHESIS • What affects photosynthesis? • Light intensity: as light increases, rate of photosynthesis _____________________ PHOTOSYNTHESIS • What affects photosynthesis? • Carbon Dioxide: As CO2 increases, rate of photosynthesis _________________ PHOTOSYNTHESIS • What affects photosynthesis? • Temperature: • Temperature Low = Rate of photosynthesis low • Temperature Increases = Rate of photosynthesis increases • If temperature too hot, rate drops Chlorophyll: A Light Absorbing Pigment The Solar Panel Chemical! Photosynthesis Glucose provides the energy and carbon needed to make other plant materials like wax and proteins. Oxygen and Sugar! • In plants and simple animals, waste products are removed by diffusion. Plants, for example, excrete O2, a product of photosynthesis. PHOTOSYNTHESIS • How did we get O2 as a byproduct?! • Photolysis: replaces lost electrons by splitting water Check it! 1. The process that uses the sun’s energy to make simple sugars is _____________. A. B. C. D. Cellular respiration Glycolysis Photosynthesis Photolysis Check it! 2. The function accomplished by the lightdependent reactions is ______________. A. B. C. D. Energy storage Sugar production Carbon fixation Conversion of sugar