Origins of Buddhism - Mrs. Lucas's Social Studies Site
advertisement

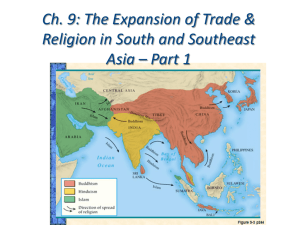
Origins of Buddhism Chapter 19, Section 3 Main Ideas 1. Siddhartha Gautama searched for wisdom in many ways. 2. The teachings of Buddhism deal with finding peace. 3. Buddhism spread far from where it began in India. Key Terms Fasting- going without food Meditation- the focusing of the mind on spiritual ideas Nirvana- a state of perfect peace Missionaries- people who work to spread their religious beliefs Siddhartha’s Search for Wisdom Not everyone in India was Hindu. Siddhartha Gautama was a prince who grew up in the Kshatriya caste. He felt something was missing from his life and began looking to answers to life’s meaning. He saw how hard people worked and how much grief they suffered. Siddhartha left his home and family to find answers to the meaning of life but could not find them. Siddhartha looks for answers… He did not give up. He wanted to free his mind from daily concerns to look for answers. He traveled from place to place He did not clean himself. He began to fast (go without food). He spent his time meditating (focusing the mind on spiritual ideas). He did this for six years. He sat down to meditate close to the Ganges River Suffering Comes From: Wanting what we like but do not have. Wanting to keep what we like and already have. Not wanting what we dislike but have. Tree of Wisdom/First Sermon Siddhartha meditated under the Tree of Wisdom and told his followers what he had determined in the First Sermon. From this point on, he became known as the Buddha, or “The Enlightened One”. The Buddha spent the rest of his life traveling across northern India and teaching people his ideas. Teachings of Buddhism: Four Noble Truths 1. Suffering and unhappiness are a part of human life. No one can escape sorrow. 2. Suffering comes from our desires for pleasure and material goods. People cause their own misery because they want things they cannot have. 3. People can overcome their desires and ignorance and reach nirvana, a state of perfect peace. Reaching nirvana would free a person’s soul from suffering and from the need for further reincarnation. 4. People can overcome ignorance and desire by following an eightfold path that leads to wisdom, enlightenment, and salvation. The Eightfold Path 1. Right Thought- Believe in the nature of existence as suffering and in the Four Noble Truths. 2. Right Intent- Incline toward goodness and kindness 3. Right Speech- Avoid lies and gossip 4. Right Action- Don’t steal from or harm others. 5. Right Livelihood- Reject work that hurts others. 6. Right Effort- Prevent evil and do good. 7. Right Mindfulness- Control your feelings and thoughts. 8. Right Concentration- Practice proper meditation Challenging Hindu Ideas The Buddha’s practices went against many Hindu beliefs. Buddha opposed the caste system. Because of this, many Hindus converted to Buddhism. Buddhism allowed people to feel in control of their lives. Buddhism Spreads Buddhism spread thoughout India. With the help of Indian king Asoka, Buddhist missionaries were sent to other countries to teach their religious beliefs. Missionaries introduced Buddhism to Sri Lanka and other parts of Southeast Asia, as well as Central Asia and Persia. It eventually spread to China, Japan, and Korea. In modern times, Buddhism has become a major global religion.