File - Jacqueline Meier's ISM online portfolio
advertisement

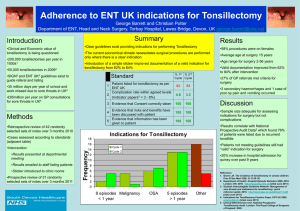
Health Science ISM By Jacqueline Meier Mrs. Click Spring 2014 • Mentor: Dr. Deborah Miller • Career: Ear, Nose, and throat specialist • Mentorship site: 250 Blossom St. • Project Topic: Comparing different removal options and procedures for tonsillectomy Dr. Miller’s Background Current education level: Doctorate (M.D) total of 8 years of school Typical schedule: Seeing patients in office Monday, Wednesday, and Friday. Tuesday and Thursday are surgery days Decided to become an ENT after doing rotations in med school Studied at Virginia Tech for 4 years & later finished up school at University of Texas for another 4 years What is an ENT Specialist? “Otolaryngologists diagnose and manage diseases of the ears, nose, sinuses, larynx (voice box), mouth, and throat, as well as structures of the neck and face.” Ears• Earing loss and earing disorders • Middle ear infection Nose• Chronic sinusitis • Nasal polys Throat• Swollen tonsils • Tonsillectomy What does it take to be an ENT? Educational requirements- Undergraduate degree- 4 years Medical Degree- 4 years Residency- 3- 8 years According to globalpost.com “ear, nose and throat doctors must complete a 5-year residency when studying at Loyola University in Chicago.” Total of at least 11 years at least and a maximum of 16 Salary- Average annual income 411,689 Project topic Comparing different procedures and techniques that can be utilize in order to perform tonsillectomy Product: Tri-fold board Tonsillectomy What is tonsillectomy? Surgical removal of tonsils, glands in the throat that help fight infection. Why should you get them removed? Constantly getting strep throat or other infections of the mouth, blocking breathing passage way, foul order or taste in mouth. Brief animation of tonsillectomy procedure http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zzXzr-zDLX8 Main ways to perform tonsillectomy Electrocauterization • - Burns tonsils and surrounding tissue Harmonic Scalpel • Also knows as Ultrasonography this uses energy from an ultrasound to vibrate the blade Bipolar Radiofrequency Ablation • Disrupts the molecular bonds of tonsil tissue. Electrocauterization • A device that burns tonsils and surrounding tissue in order to remove tonsils and cause less bleeding Use During Surgery This technique may be used in surgery to cut through soft tissue and completely remove the tonsils this is done so that the surgeon can gain access to the site and seal off blood vessels that are bleeding during surgery. Harmonic Scalpel • Uses hot ultrasonic energy to vibrate a special blade. The blade cuts tonsil tissues and stops bleeding. Used during surgery: This action cuts tissue with a fraction of the heat and trauma as compared to electrical cutting currents. The intense vibration also causes the blood in the immediate area to coagulate, so there is virtually no blood loss during the operation. Bipolar Radiofrequency Ablation • Uses radiofrequency energy to destroy tonsil tissue Used during surgery: As the energy is transferred to the tissue, ionic dissociation occurs. This mechanism can be used to remove all or only part of the tonsil. This causes removal of tissue with a thermal effect of 45-85 C°. The advantages of this technique are less pain, faster healing, and less post operative care. Data: Blood Loss 17% 70 50% 60 33% 50 40 Electrocauterization 30 Harmonic Scalpel Bipolar Radiofrequency Ablation 20 10 0 over all return to normal complaction diet Electrocauterization Bipolar Radiofrequency Ablation Harmonic Scalpel Conclusion: Coblation tonsillectomy results in decreased postoperative pain compared to electrocautery and Harmonic tonsillectomy. This is based on pain scores analysis and on faster return to normal diet. patients undergoing cold steel tonsillectomy have less pain than patients undergoing electrocautery. However, intraoperative blood loss and operative time are decreased cautery tonsillectomy. The Harmonic Scalpel tonsillectomy offers advantages of early return to diet and activity over standard electrocautery tonsillectomies. Dr.Miller Mrs.Click Mrs.Randall Kelsi Smith My mom Citations Ahmed, A., I. Aliyu, and E. Kolo. "Indications for Tonsillectomy and Adenoidectomy: Our Experience." Nigerian Journal of Clinical Practice 17.1 (2014): 90. Academic OneFile. Web. 10 Apr. 2014. http://go.galegroup.com/ps/i.do?id=GALE|A354977565&v=2.1&u=leag775 73&it=r&p=AONE&sw=w&asid=77b916f5648722a546d8467390aa3663 Fallon, L. Fleming. "Tonsillectomy." The Gale Encyclopedia of Surgery. Ed. Anthony J. Senagore. Vol. 3. Detroit: Gale, 2004. 1423-425. Gale Virtual Reference Library. Web. 10 Apr. 2014. <http://go.galegroup.com/ps/i.do?id=GALE|CX3406200448&v=2.1&u=leag 77573&it=r&p=GVRL&sw=w&asid=751d1777e8a99015105e082f3317e3d9>. Ibekwe, Titus, Godwin Obasikene, and Ekeng Offiong. "Tonsillectomy: Vasoconstrictive Hydrolytic Cold Dissection Method." African Journal of Paediatric Surgery 10.2 (2013): 150. Academic OneFile. Web. 4 Apr. 2014. <http://go.galegroup.com/ps/i.do?id=GALE|A340351123&v=2.1&u=leag77 573&it=r&p=AONE&sw=w&asid=38b7a665eda08d43338f3d63aca6e0e7>. Citations Continued Skolnik, Neil, and Jennifer Thuener. "Tonsillectomy in Children." Family Practice News 1 Aug. 2011: 98. Academic OneFile. Web. 6 Apr. 2014. <http://go.galegroup.com/ps/i.do?id=GALE|A266941036&v=2.1&u=leag77573 &it=r&p=AONE&sw=w&asid=2c0631a9e4b68b8a306b77d70279e5e3>. Chang, Christopher Y., and Richard Thrasher. "Coblation Cryptolysis to Treat Tonsil Stones: A Retrospective Case Series." Ear, Nose and Throat Journal June 2012: 238. Academic OneFile. Web. 10 Apr. 2014. <http://go.galegroup.com/ps/i.do?id=GALE|A294894492&v=2.1&u=leag77573 &it=r&p=AONE&sw=w&asid=f04a5e3d28b33588dd4930e29d46d876>. Ali, Naeem Sultan, Dr, and Mubasher Ikram, Dr. "Harmonic Scalpel versus Electrocautery Tonsillectomy: A Comparative Study in Adult Patients." Harmonic Scalpel versus Electrocautery Tonsillectomy: A Comparative Study in Adult Patients. N.p., n.d. Web. 04 May 2014.