Population Ecology Notes
advertisement

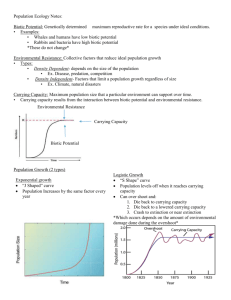
Population Ecology Notes Biotic Potential: • Defined: Genetically determined maximum reproductive rate for a species under ideal conditions. • Examples: • Whales and humans have low biotic potential • Rabbits and bacteria have high biotic potential *These do not change* Environmental Resistance: • Defined: Collective factors that reduce ideal population growth • Types: • Density Dependent- depends on the size of the population • Ex. Disease, predation, competition • Density Independent- Factors that limit a population growth regardless of size • Ex. Climate, natural disasters Carrying Capacity: Environmental Resistance Biotic Potential • Defined: Maximum population size that a particular environment can support over time. • Carrying capacity results from the interaction between biotic potential and environmental resistance. Population Growth: (2 types) 1. Exponential growth a. “J Shaped” curve b. Population Increases by the same factor every year Population Growth: (2 types) 2. Logistic Growth a. “S Shape” curve b. Population levels off when it reaches carrying capacity c. Can over shoot and: 1. Die back to carrying capacity 2. Die back to a lowered carrying capacity 3. Crash to extinction or near extinction *Which occurs depends on the amount of environmental damage done during the overshoot*