TAG MAGNET HIGH SCHOOL AP Macroeconomics Syllabus
advertisement

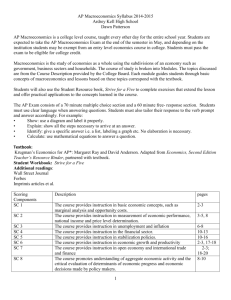
TAG MAGNET HIGH SCHOOL AP Macroeconomics Syllabus Description of Course Activities: Advanced Placement Macroeconomics is designed to engage students in intellectual, critical, and creative process of thinking skills from in class discussion, individual projects, and hands on problem solving. Advanced Placement Macroeconomics requires extensive reading, research, and problem solving responsibility from the student. The course will give students a thorough understanding of the principles of macroeconomics such as fiscal and monetary policy, aggregate demand and supply, output, price determination, national income, performance measures, and the global economy. The goal is for students to be prepared to take the college level examination and to make the student interested and excited about learning the field of Macroeconomics. Advanced Placement Macroeconomics follows the curriculum of the Advanced Placement Board and the Texas Education Agency. AP Macroeconomics taught at the TAG Magnet will include Gifted and Talented Strategies using real world applications and problem solving skills, and involve learning seminars with other disciplines. Course Objectives and Student Outcomes Students will be prepared to do acceptable work on the AP Macroeconomics Exam. Explain various economic models including Keynesian and Classical Explain government economic indicators and their application to the national economy Understand the various aggregate supply/demand to the national economy Cause and effect of how one countries economic polices has an impact on our country Understand the impact of the Federal Reserve Bank on economic policy Enrichment activities include: Group Research Project: Perform an analytical and critical analysis of released information data by the United States Government. Students will collect data, make hypotheses, identify patterns, and synthesize their released economic data. Examples of project analysis include current information on the United States gross domestic product, consumer price index, producer price index, business inventories, unemployment, trade deficits, and currency exchange. An oral presentation of the product will be presented to the class. Field Trip: Visit the Federal Reserve Bank in Dallas where students will be presented an overview of Government budget policies, interaction of fiscal and monetary policies, tools of central bank policy, and the definition of money and its creation. Stock Market Game: Students will have an allowance to buy and sell stocks and bonds of their choosing to make profit during the course. Main focus will be on the law of Supply and Demand and the ability to create and equilibrium price of their goods and services. Non Curricular Seminar: In class presentation of current tax laws including various retirement vehicles such as 401K, 403B, Traditional IRA, Roth IRA, and the use of Insurance Annuities. Presentation will also include the use of mutual funds: including the difference between no load and loaded funds, types of stock funds, types of bond funds, types of money market funds, and tax advantages of each type. Items of discussion will also include various types of life insurance including term, whole, universal and variable universal products. Text Book(s): McConnell, Campbell, Stanley Brue, Sean M. Flynn. Economics: Principles, Problems, and Policies, 19th ed. McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 2012. N. Gregory Mankiw, Principles of Economics, 2nd ed. South-Western Thompson Learning, 2001 Additional Student Reading Requirement Todd Buchholz, From Here to Economy, New York: Plume, 1995 Grading Policy - based on Dallas ISD school policy Grading Scale for Six Weeks Average Class work/Homework 40% * Major Tests 25% Projects/Products 20% * Six Weeks Test Grade 15% *Multiple choice exam questions and essays will be taken from released AP United States Government and Politics exams from the Advanced Placement College Board. If a Major Test is failed the student may retake and the higher score earned will be recorded as the grade. Late Homework assignments will receive a grade of 50 if turned in by the next two school days after due date. After that date a grade of 0 will be recorded. Homework assignment policy is determined by the TAG Social Studies Department. Course Outline Practice Diagnostic - 2000 releases Advanced Placement Macroeconomics Exam I. Basic Economic Concepts a. Define and Identify – scarcity and unlimited wants and limited recourses (land, labor, capital, entrepreneurships) b. Identify – tradeoffs and opportunity cost Mankiw short film – People face tradeoffs. What you give up to get it. c. Production Possibilities Curve – Identify concave or bowed out curve, identify points inside, along, and outside the PPC and their significance. d. Students will draw, graph, and interpret the PPC as it relates to tradeoffs, choices, historical conditions, and reaching points outside. e. Comparative and Absolute Advantage, Specialization, and Exchange: Distinguish and Illustrate between absolute and comparative advantage and calculate product exchange. f. Introduction to Demand, Supply, and Market Equilibrium: students will construct graphs illustrating demand, supply, and equilibrium price. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Distinguish between a change in demand and quantity demanded. Distinguish between a change in supply and quantity supplied. Graph a demand and supply curve showing price, quantity, equilibrium. Explain determinates of demand and supply, explain and show direction of curve shift of demand and supply and its importance. Students will draw, graph, and illustrate a correctly labeled demand and supply graph, showing changes in different economic conditions. g. Introduction to Macroeconomic Issues: business cycle, unemployment, inflation: Throughout course students will be responsible in gathering United States Government release of current event information showing course related economic data. Required Data and date of release will be posted on web site one week in advance. II. Measurement of Economic Performance a. b. National Income Concepts: Circular Flow Model, Measuring the GDP, and Components of the GDP, Business Cycles. 1. Students will identify, illustrate, and explain the Circular Flow Model showing the resource market, product market, business, households, and government 2. Students will identify and explain, graph, and calculate the Expenditure Approach of GDP: C + Ig + G + Xn. 3. Students will identify and explain the Income Approach of GDP: W + I + R + P 4. Students will identify and calculate the Nominal GDP and the Real GDP using a base year, students will also identify the GDP Deflator. Students will also be introduced to the Consumer Price Index as a comparison to the GDP. 5. Identify and calculate the net domestic product (NDP), national income (NI), personal income (PI), and disposable income (DI) 6. Students will graph and identify the four phases of the business cycle: Trough, Expansion, Peak, and Contraction. 7. Identify the Underground Economy 8. Introduction to Consumption Function Graph and Marginal Propensities of consumption and savings, Students will use MPC & MPS formulas to calculate equations. Inflation Measurement and Adjustment 1. 2. 3. Identify the Consumer Price Index and when released and by what government agency, and how it is calculated. Identify problems with the Consumer Price Index and compare with the GDP. Identify the Producer Price Index. 4. 5. c. Identify Demand-Pull and Cost Push Inflation, Hyperinflation, Deflation, Stagflation, and historical and current event examples. Identify: Who is Hurt by Inflation? Who is Helped by Inflation? Identify COLA. Unemployment 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Identify and Define types of Unemployment: frictional, structural, cyclical and seasonal. Identify measurement of unemployment: Who is counted and who is not? Identify full employment: Introduction to full employment and LRAS on AD/AS graph. Identify and define underemployment, discouraged job seekers, Identify the Natural Rate of Unemployment. REVIEW FOR SIX WEEKS FINAL 1st Six Weeks Final III. National Income and Price Determination Aggregate Demand, Aggregate Supply, Macroeconomic Equilibrium a. Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply – Students will graph, illustrate, and correctly label an Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply graph showing full employment, price level and output. b. Students will identify and graph Recession and Inflation on an AD/AS graph. c. Students will identify determinates of Aggregate Demand. d. Students will identify determinates of Aggregate Supply. e. Students will graph and identify short run and long run Aggregate Supply. f. Students will identify Crowding out effects on AD/AS and multipliers of: Introduction to Fiscal Policy and government spending. g. Students will identify the impact of Technological change and introduction of Supply Shocks. h. Introduction to Classical Theory and Keynesian Theory i. Students will graph AD/AS using three range Aggregate Supply Curve Start of Stock Market Game – Trading must include a No Load Mutual Bond Fund and a Stock Fund, Individual Stock, and Money Market Account – Stocks must be a minimum of $5. Unlimited trading but not allowed during class. IV. Financial Sector Money, Banking, and Financial Markets d. e. f. g. h. i. Students will identify functions of money: medium of exchange, standard of value, store of value. Identify Money Supply Definitions: M1, M2, and M3. Identify a Money Market, Stocks and ownership, Bonds and debts. Identify Banks and the creation of money. Discuss the present and future value of money. Introduction to the Loanable Funds Market. Central Bank and Control of the Money Supply a. b. c. d. Students will identify the Federal Reserve System (FED) and its current chairman. Students will research different branches and structures of system. Identify the importance of the FED: U. S. bank, local banks borrow from, regulation of banks, increasing and decreasing the money supply, clearing checks. How Does the FED control the Money Supply? Reserve Requirement, Discount Rate, Open Market Operations. Identify Real Interest Rate and Nominal Interest Rate – individual importance of staying ahead of inflation in savings. *** Time permitting: Tour of the Federal Reserve Bank with a speaker discussion the FED and Monetary Policy. V. Inflation, Unemployment, Stabilization Policies Fiscal Policy and Monetary Polices a. Students will identify Discretionary Fiscal Policy. 1. Changes in government spending in recession and high inflationary periods. 2. Changes in government tax rates in recession and high inflationary periods. 3. Identify the Laffer Curve. 4. Identify government deficits and debt. 5. Supply Side effects and Environmental Regulations. Review Classical and Keynesian Theory with historical significance. Review Crowding Out. Students will identify Monetary Policy. 1. Students will analyze Short Run and Long- Run effects of Monetary policy. 2. Review the three tools of the FED. 3. Identify Monetarist theory and MV=PQ. Students will graph crowing out effect and Laffer Curve. b. c. d. e. Inflation and Unemployment a. b. c. Review of types of inflation: Cost-Push and Demand Pull. Students will graph and interpret the short run and long run Phillips. Curve and identify its historical importance. Discuss Rational Expectations Theory. REVIEW FOR 2ND SIX WEEKS FINAL 2nd Six Weeks Final VI. Economic Growth and Productivity a. b. c. d. Investment of Human Capital – Knowledge and Skills to make a productive worker. Investment in Physical Capital – Machinery and Buildings. Research and Development, and Technological progress – Inventions and Products. Growth Policy – Importance of healthy Long-Run Growth. VII. Open Economy: International Trade and Finance Balance of Payments Accounts a. b. c. d. Review of Comparative and Absolute Advantage. Identify Balance of Trade in international trade and financial transactions. Identify Current Account. Identify Capital Account. Foreign Exchange Market, Net Exports and Capital Flows, Financial and Goods Market a. b. Students will graph currency changes and research current currency exchange rates. Identify the Demand for and Supply of Foreign Exchange. c. d. e. f. g. Identify current Currency appreciation and depreciation in the Foreign Exchange Market. Identify trade barriers, free trade and protectionism. Identify international trade agreements: NAFTA, EU, and WTO. Compare difference in international trading partners – Capitalist, Socialist, developed and developing countries. Discuss and identify outsourcing and the changing world economy. REVIEW FOR THE AP MACORECONOMICS EXAM