Document
advertisement

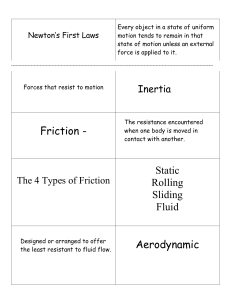
Velocity Definition: the speed and direction of motion of an object. meters per second (m/s) Example: The car moved at a velocity of 20 m/s toward the east. Acceleration Definition: the rate of change in velocity as a function of time. meters per second squared (m/s2) Example: The falling rock accelerated at a constant rate of 9.8m/s2. Velocity 1s | Acceleration 2s | 3s | 4s | Mass Definition: how much the object will resist change to velocity. kilograms (kg) Example: The table was hard to move because it had a large mass. Weight Definition: the force of gravity on an object. Example: Your weight is less on the Moon than on Earth. Force Definition: a “pushing” or “pulling” on an object. Newtons (N) Example: I applied a force to move the chair. Fnorm Fgrav Normal Force Definition: a force perpendicular to the object’s contact surface. Fnorm Fnorm Fnorm Ffrict F grav Friction Definition: the force that acts opposite to the motion of one object in contact with another object. Example: the force of friction opposed the motion of the sliding box, slowing it down. Fnorm F frict Fgrav Fapp Net Force Definition: the vector sum of forces. Fnet = 15 N up Static Friction Definition: friction that prevents the sliding motion between two objects. Newtons (N) Example: the static friction between the basketball player’s sneakers and the floor kept him from sliding. f F norm static F grav Finish Line Kinetic Friction Definition: friction that occurs between two objects when when one object slides against another Newtons (N) Example: the kinetic friction from rubbing my hands together warmed them on the cold winter’s night. f F norm kinetic F grav Newton’s first law of motion The Law of Inertia an object at rest stays at rest an object in motion stays in motion with the same velocity unless acted upon by an unbalanced force Newton’s second law of motion The acceleration of an object produced by a net applied force is directly related to the magnitude of the force, and inversely related to the mass of the object The net force equals mass times acceleration Fnet = ma Newton’s third law of motion for every action (force) there is an equal and opposite reaction (force). Example: the angry bird exerts a force on the blocks and the blocks exert an equal and opposite force back.