Heat Capacity
advertisement

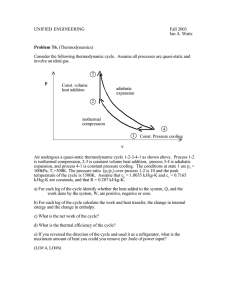
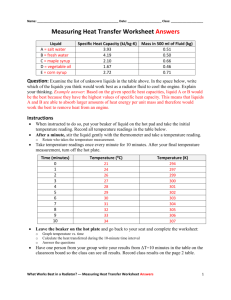
Heat Capacity Work In Work done on a system v1 K1 (1 / 2)mv12 v2 K 2 (1 / 2)mv22 The work - energy principle applies to all objects. • If an object speeds up it gains kinetic energy. • If an object slows down it loses kinetic energy. W K Heat In Heat into a system Temperature change is due to heat (Q). • If an object’s temperature increases it gains heat. T1 ,U1 T2 ,U 2 • If an object’s temperature decreases it loses heat. Q T Heat Capacity The ratio of the change in heat to the change in temperature is the heat capacity (C). • Depends on material • Depends on the mass • Measured in J/K Q CT Specific Heat The ratio of the change in heat to the change in temperature is the heat capacity (C). • Depends on material • independent of the mass • Measured in J/kg-K Q mcT Material Mercury Copper Steel Granite Aluminum Wood Ice Water Specific heat 140 J/kg-K 390 J/kg-K 500 J/kg-K 840 J/kg-K 900 J/kg-K 1400 J/kg-K 2100 J/kg-K 4200 J/kg-K Take a Shower You are last to use the shower today and the temperature in the water heater has dropped to 18 C from the normal temperature of 50 C. The heater holds 150 kg and has a 50 kW heating coil. How long should you wait before starting your shower? Find the heat required. Q = mcT = (150 kg) (4200 J/kg-K) ( 32 C) Q = 2.1 x 107 J Find the time from the power, and set the heat to the work. P = W/t t = Q / P (2.1 x 107 J) / (5 x 104 W) t = 4000 s = 1.1 hr Equilibrium Temperature Two systems in thermal contact will adjust to reach the same temperature - thermal equilibrium If they are thermally insulated, all the heat goes from the hot system to the cold system. 1 2 m1c1T1 m2c2T2 0 Doing Dishes A 1.5 kg aluminum pan is heated to 180 C then placed into a sink with 8 kg water at 20 C. Setup the equation for an unknown equilibrium temperature T. If no water boils, what is the equilibrium temperature? Solve for T. m p c p (T Tp ) mwcw (Tw T ) 0 T m p c pT p mwcwTw m p c p mw c w T = 26 C next