Unit: 00 Prologue
advertisement

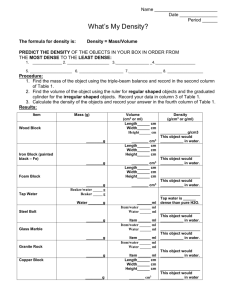
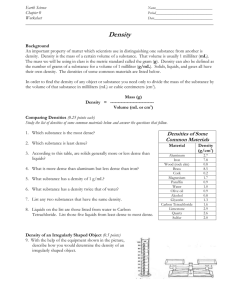
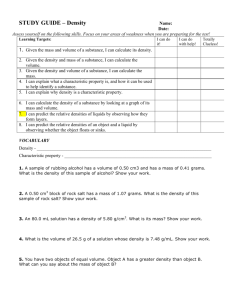
Unit: 01 Prologue New Test/ New Quiz A. Observation and Measurement 1. Observation a) def. using your senses to describe something b) use of instruments to extend our senses 2. Inference a) def. drawing a conclusion from your observations b) you must have prior knowledge 3. Classification a) def. grouping objects based on similarities (Organize) 4. Measurement a) def. a numerical value to describe something b) Basic dimensional quantities 1) Length – meter – m – use ruler 2) Volume a) liter – l – graduated cylinder for non-regular objects b) cm3 – ruler for regular objects 3) Mass – gram – g – triple beam balance 4) Time – second – s – clock 5) Temperature – oC -- thermometer 5. Basic terms to know in a laboratory a) Standard unit something used globally to make measurements easier to communicate b) Tool instrument that helps make observations more exact by extending your senses c) Volume amount of space an object has d) Mass amount of particles an object has (never changes due to position) e) Weight how much gravitational pull an object has (changes with respect to location) f) Matter anything that has mass and takes up space 6. Scientific Prefixes a) Milli – 1/1000 ex. There are 1000 milligrams in a gram b) Centi –1/100 ex. There are 100 centigrams in a gram c) Kilo – 1000x ex. There are 1000 grams in a kilogram B. Percent Deviation (Error) % Deviation = Difference from accepted accepted value x100 % = Difference from accepted accepted value x100 C. Graphs 1. Types a) Line (trends) b) Bar (comparisons) c) Pie (percentages) 2. Horizontal (x) axis is usually the independent variable 3. Vertical (y) axis is usually the dependent variable END OF QUIZ D. Density 1. Density a. def. the measure of the Concentration of matter (mass) in a given space (volume) 2. Finding density a. Density = mass (ESRT Front Volume Cover) b. ex. Mass = 270g Volume = 100 cm3 D = 270g / 100 cm3 D = 2.7 g/cm3 Density = mass Volume c. Finding Mass and Volume M D V 3. Rules ***a. If you break a sample, the density stays the Same b. Only true when temperature and pressure remain constant c. Same uniform material = same density 4. What happens to density if temperature changes? a) Increase in temperature cause molecules to move apart (Less dense) b) This is called an indirect relationship. when two variables are related in opposite directions D e n s i t y Temperature 5. What happens to density if pressure changes a) Increase the pressure, the molecules come closer together (more dense) b) This is called a DIRECT relationship when two variables both change in the same direction. D e n s i t y Pressure c) Compress = Increase in pressure 6. Which phase of matter is the most dense?(water is an exception) a) Solids (most dense) b) Liquids c) Gases (least dense) 7. Density and Water a) Density of water as a liquid is 1.0 g/ml or 1.0 g/cm3 b) Only substance found naturally in all three states c) Water as an exception maximum density of water occurs at 4 oC as a liquid d) Graph for the density of water Density -- 4o C S L temperature - G 8. Density Drawings of water 2/3 a) When ice floats, 2/3 of the ice is below the surface 9.Compare the densities of object A and B A B Both objects A and B are the SAME density because 50% of the objects are below the surface 10. Density of an object does NOT depend on the size or the shape, but on the material it is made of a) ex. Density of aluminum stays the same even if its size and shape changes (as long as pressure and temperature remain constant) 11. Density Comparisons a) If the density of an object is less than the density of the liquid, the object will float in the liquid b) If the density of an object is more than the density of the liquid, the object will sink in the liquid. c) If an object and a liquid have the exactly the same density, the object can remain stationary anywhere a) b) c) 12. Water Specialty a) Water expands when it Freezes (most other materials contract when cooled) b) Water in a pond 4oC 13. Special temperatures a) b) c) d) Water Boils = 212 F or 100 C or 373 K Body Temp. = 98.6 F or 37 C Room Temp.= 68 F or 20 C Water Freezes = 32 F or 0 C An empty 250 mL beaker has a mass of 60g. When 100 mL of oil is added to the beaker, the total mass is 140g. The density of the oil is approximately 8.O cm 4.0 cm 8.O cm 4.0 cm 4.0 cm #2 #3 #4 #5 #6 #7 AOC _______ AOB ________ BOC _______