Banking Procedures and Control of Cash
advertisement

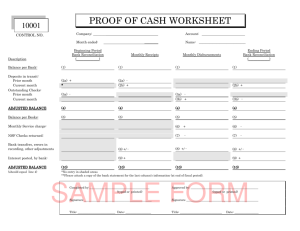
Banking Procedures and Control of Cash Chapter 6 6-1 Internal Control of Cash – – – – – – Internal Control Procedures separation and rotation of duties cash receipts deposited daily setting up a petty cash fund all other payments made by check authorization required for activities checks and other documents prenumbered 6-2 Learning Objective 1 Depositing, writing, and endorsing checks for a checking account. 6-3 Learning Unit 6-1 Opening a checking account A signature card is required for validation to protect against forgery and unauthorized signing. Duplicate deposit tickets are used. ATM cards and personal identification numbers are protected. 6-4 Learning Unit 6-1 Check endorsement What is a check endorsement? It is the signing or stamping of one’s name on the back left-hand side on the check. Checks must be signed by the person to whom the check is made out. 6-5 Learning Unit 6-1 Types of Endorsements Blank endorsement Full endorsement Restrictive endorsement 6-6 Learning Unit 6-1 The checkbook A check is a written order. The drawer is the one who writes the check. The drawee is the one who pays the money to the payee (bank). 6-7 Learning Unit 6-1 The checkbook The payee is the one to whom the check is payable. Write checks properly to ensure that amounts and payee cannot be changed. 6-8 Learning Unit 6-1 The bank reconciliation This is a process that verifies the cash balance in the business records to the ending bank balance for the month. Deposits in transit are deposits not recorded by the bank before the report (add to the bank balance). 6-9 Learning Unit 6-1 The bank reconciliation Outstanding checks are issued checks that have not yet cleared the bank (subtract from the bank balance). Service charges are fees charged by a bank (subtract from the bank balance). 6 - 10 Learning Unit 6-1 The bank reconciliation Nonsufficient funds (NSF) checks are those which are received, deposited in the bank, and returned because the drawer did not have funds in their account (subtract from bank balance). The check and a collection fee is charged back to the drawer. 6 - 11 Learning Unit 6-1 Terminology Bank credits are when a bank credits the account, which is an increase to the cash balance in the business. What are some examples? – bank errors – funds collected by the bank on behalf of the business 6 - 12 Learning Unit 6-1 Terminology Bank debits are a deduction from the cash balance in the business. What are some examples? – bank errors – NSFs – service charges 6 - 13 Learning Objective 2 Reconciling a bank statement. 6 - 14 The Bank Reconciliation Process On August 2, Clara J. Accounting Practice received the July’s bank statement. It indicated the following: The bank balance was $25,225. The bank had collected a note receivable from one of Clara’s customers in the amount of $1,000. 6 - 15 The Bank Reconciliation Process The bank paid the electric bill of $300. There was a $200 check returned for NSF. Interest earned on the account was $15. Bank service charges were $6. Da te P ay che c k fo r Joh De Pa yc he ck fo r Ja ne D p t. of T re a su re r n D oe D a te oe De p t. o f T re a su re r 6 - 16 The Bank Reconciliation Process Clara’s books indicates a cash balance of $26,647. A deposit of $3,250 was mailed to the bank on June 30. Checks issued in June for $1,319 have not yet been paid by the bank. 6 - 17 The Bank Reconciliation Process Balance per bank, June 30 $25,225 Add deposit in transit 3,250 $28,475 1,319 $27,156 Less outstanding checks Adjusted bank balance 6 - 18 The Bank Reconciliation Process Balance per books, June 30 Add: Note receivable collected by the bank Interest income Less: Payment of electric bill NSF check Service charge Adjusted book balance $26,647 1,000 15 $27,662 300 200 6 $27,156 6 - 19 The Bank Reconciliation Process Balance per books $27,156 Balance per bank $27,156 Amounts are the same 6 - 20 Learning Objectives 3 and 4 Establishing and replenishing a petty cash fund; setting up an auxiliary petty cash record. Establishing and replenishing a change fund. 6 - 21 Learning Unit 6-2 Petty cash fund This is an account used for paying small day-to-day expenses. The only time petty cash is entered in the journal is to establish the fund (or to change the level of cash in the fund). Expenses are debited and Cash credited to replenish the fund. 6 - 22 Learning Unit 6-2 What is the entry to record the establishment of a $150 petty cash fund? Petty Cash 150 Cash in bank 150 To open the petty cash fund 6 - 23 Learning Unit 6-2 Forty dollars were taken out of the petty cash fund for coffee and other miscellaneous expenses. What is the journal entry to record the replenishment of the fund? Miscellaneous expense 40 Cash in bank 40 To replenish the petty cash fund 6 - 24 Learning Objective 5 Handling transactions involving cash short and over. 6 - 25 Cash Short and Over How are small cash errors recorded? Beginning change fund + Cash register total = Correct amount of cash – Counted cash = Shortage or overage of cash 6 - 26 End of Chapter 6 6 - 27