Document
advertisement

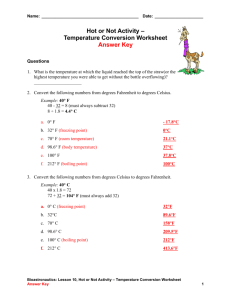
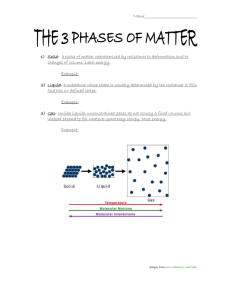
Physical Boot Camp 5.5B Identify the boiling and freezing/melting points of water on the Celsius scale. STAAR 2013 #14; RC 1; Supporting; 47 1. A student measures the temperature of water being heated on a hot plate. The student observes that the temperature of the water is 53ºC. How many more degrees Celsius must the temperature rise before it reaches the boiling temperature of water? STAAR 2013 #14; RC 1; Supporting; 47 1. A student measures the temperature of water being heated on a hot plate. The student observes that the temperature of the water is 53ºC. How many more degrees Celsius must the temperature rise before it reaches the boiling temperature of water? Boiling point of water: 100ºC So…..100 – 53 = 47 2. 2. 2004—#32 (70%) 3. When a chocolate bar is heated by the sun, all of the following are likely to be seen EXCEPT— F G H J boiling melting a liquid a change in shape 2004—#32 (70%) 3. When a chocolate bar is heated by the sun, all of the following are likely to be seen EXCEPT— F G H J boiling melting a liquid a change in shape 2006—#9 (72%) 4. Some students were studying properties of water. One student placed a cup containing 80 mL of water in a freezer. Another student placed an identical cup containing 40 mL of water in a different freezer. Which of the following will be the same for both cups of water? A B C D The temperature at which the water freezes The mass of the frozen water The time it takes the water to freeze The volume of the frozen water 2006—#9 (72%) 4. Some students were studying properties of water. One student placed a cup containing 80 mL of water in a freezer. Another student placed an identical cup containing 40 mL of water in a different freezer. Which of the following will be the same for both cups of water? A B C D The temperature at which the water freezes The mass of the frozen water The time it takes the water to freeze The volume of the frozen water 2009—#29 (84%) 5. Which two properties of a crayon will stay about the same after the crayon is melted? A B C D Shape and physical state Temperature and hardness Color and mass Thickness and texture 2009—#29 (84%) 5. Which two properties of a crayon will stay about the same after the crayon is melted? A B C D Shape and physical state Temperature and hardness Color and mass Thickness and texture 6. 6. 7. What is the approximate melting point of ice? A B C D 0ºC 32ºC 45ºC 100ºC 7. What is the approximate melting point of ice? A B C D 0ºC 32ºC 45ºC 100ºC 8. What is the approximate boiling point of water at sea level? A B C D 35ºC 55ºC 85ºC 100ºC 8. What is the approximate boiling point of water at sea level? A B C D 35ºC 55ºC 85ºC 100ºC 9. 9. 10. If the temperature of a sample of pure water is below 0°C, then the water is most likely – A B C D frozen a liquid a gas warm 10. If the temperature of a sample of pure water is below 0°C, then the water is most likely – A B C D frozen a liquid a gas warm 11. Ice melts because it has reached its – A B C D magnetism point melting point boiling point freezing point 11. Ice melts because it has reached its – A B C D magnetism point melting point boiling point freezing point 12. 12. 13. 13. 14. A student left a chocolate bar on the window sill on a sunny day. Which of the following would cause the chocolate to melt? A Electric energy passes through the chocolate and changes its form. B Different types of matter in the chocolate separate and change form. C The refraction of the light coming through the window changes its form. D Heat from sunlight causes the chocolate to reach its melting point. 14. A student left a chocolate bar on the window sill on a sunny day. Which of the following would cause the chocolate to melt? A Electric energy passes through the chocolate and changes its form. B Different types of matter in the chocolate separate and change form. C The refraction of the light coming through the window changes its form. D Heat from sunlight causes the chocolate to reach its melting point. 15. Some students filled a teakettle with water and put it on a hot plate. They heated it until there was nothing left in the teakettle. What happened to the water in the teakettle? A B C D The particles in the water melted from the heat. The hot metal in the teakettle dissolved the water. The water reached its boiling point and evaporated. The very hot air inside the kettle dried out the water. 15. Some students filled a teakettle with water and put it on a hot plate. They heated it until there was nothing left in the teakettle. What happened to the water in the teakettle? A B C D The particles in the water melted from the heat. The hot metal in the teakettle dissolved the water. The water reached its boiling point and evaporated. The very hot air inside the kettle dried out the water. 16. Ice changes to liquid water when it reaches its – A B C D magnetism point melting point boiling point freezing point 16. Ice changes to liquid water when it reaches its – A B C D magnetism point melting point boiling point freezing point 17. What is the boiling point of water on the Celsius scale? A B C D 0°C 100°C 212°C 1,535°C 17. What is the boiling point of water on the Celsius scale? A B C D 0°C 100°C 212°C 1,535°C 18. If the temperature of a sample of water is above 100°C, then the water is most likely – A B C D frozen a liquid a gas warm 18. If the temperature of a sample of water is above 100°C, then the water is most likely – A B C D frozen a liquid a gas warm 19. According to the passage, which of the following has the higher melting point? A B C D Ice at 0°C Water at 100°C Iron at 1,535°C Tin at 2,270°C 19. According to the passage, which of the following has the higher melting point? A B C D Ice at 0°C Water at 100°C Iron at 1,535°C Tin at 2,270°C 20. 20. 21. A student adds 50 mL of boiling water to 100 mL of ice water. If the 150 mL of water is then put into a freezer, at what temperature will the water freeze? A B C D 0°C 15°C 37°C 50°C 21. A student adds 50 mL of boiling water to 100 mL of ice water. If the 150 mL of water is then put into a freezer, at what temperature will the water freeze? A B C D 0°C 15°C 37°C 50°C 22. At which temperature does ice begin to melt? A B C D -10°C 0°C 10°C 100°C 22. At which temperature does ice begin to melt? A B C D -10°C 0°C 10°C 100°C 23. 23. 24. Which of the following is a characteristic property that could be used to identify a substance as water? A B C D Water is always a liquid. Organisms need water to live. Things dissolve in water. Water boils at about 100ºC. 24. Which of the following is a characteristic property that could be used to identify a substance as water? A B C D Water is always a liquid. Organisms need water to live. Things dissolve in water. Water boils at about 100ºC. 25. 25. 26. The process where a solid changes to a liquid is called— A B C D melting evaporating freezing condensing 26. The process where a solid changes to a liquid is called— A B C D melting evaporating freezing condensing 27. The picture shows a pan of boiling water. What process is taking place as the water boils? A B C D A gas changing to a liquid A gas changing to a solid A solid changing to a gas A liquid changing to a gas 27. The picture shows a pan of boiling water. What process is taking place as the water boils? A B C D A gas changing to a liquid A gas changing to a solid A solid changing to a gas A liquid changing to a gas 28. 28. M.S. ?’s 29. What unit of measurement is used when recording the temperature of boiling water? A B C D milliliter degrees Celsius gram millimeter M.S. ?’s 29. What unit of measurement is used when recording the temperature of boiling water? A B C D milliliter degrees Celsius gram millimeter 30. A glass beaker is placed on a hot plate. Five hundred milliliters of room temperature water are added to the beaker. If the temperature continues to increase, the water in the beaker will most likely— A B C D turn into a solid become more dense turn into a gas show no change in temperature 30. A glass beaker is placed on a hot plate. Five hundred milliliters of room temperature water are added to the beaker. If the temperature continues to increase, the water in the beaker will most likely— A B C D turn into a solid become more dense turn into a gas show no change in temperature 31. Each of the following hypotheses explain freezing point EXCEPT— A a liquid changing into a solid B the temperature reaching 100º Celsius C liquid precipitation turning into freezing rain D the temperature reaching 0º Celsius 31. Each of the following hypotheses explain freezing point EXCEPT— A a liquid changing into a solid B the temperature reaching 100º Celsius C liquid precipitation turning into freezing rain D the temperature reaching 0º Celsius 32. An ice cube was placed in a plastic cup on the lab table. Students recorded the mass of the ice cube and the plastic cup at 5 grams. One hour later the ice cube completely melted, turning into liquid water. Then the students recorded the mass of the water and the cup. What was the mass of the water and the plastic cup? 32. An ice cube was placed in a plastic cup on the lab table. Students recorded the mass of the ice cube and the plastic cup at 5 grams. One hour later the ice cube completely melted, turning into liquid water. Then the students recorded the mass of the water and the cup. What was the mass of the water and the plastic cup? 5 grams 33. Water changes its state of matter when heat is added or taken away. When water reaches its boiling point the particles— A B C D are closer together stay the same are moving more rapidly are moving more slowly 34. Water changes its state of matter when heat is added or taken away. When water reaches its boiling point the particles— A B C D are closer together stay the same are moving more rapidly are moving more slowly 34. Which of the following is an example of water reaching its melting point? A A cup of water sitting outside on a sunny day B Water simmering on a hot stovetop C An ice cube left on the counter D A cup of water placed in the refrigerator 34. Which of the following is an example of water reaching its melting point? A A cup of water sitting outside on a sunny day B Water simmering on a hot stovetop C An ice cube left on the counter D A cup of water placed in the refrigerator 35. 0ºC is water’s… A B C D freezing point melting point boiling point both freezing point and melting point 35. 0ºC is water’s… A B C D freezing point melting point boiling point both freezing point and melting point 36. Students completed this chart during an experiment. They heated water to find the boiling point: Time it Takes for Water to Change State Beginning temp After 1 minute After 3 minutes After 4 minutes After 5 minutes 20ºC 42ºC 87ºC 100ºC 100ºC According to this chart, when did the water begin to boil? A B C D After 1 minute After 5 minutes After 4 minutes After 3 minutes 36. Students completed this chart during an experiment. They heated water to find the boiling point: Time it Takes for Water to Change State Beginning temp After 1 minute After 3 minutes After 4 minutes After 5 minutes 20ºC 42ºC 87ºC 100ºC 100ºC According to this chart, when did the water begin to boil? A B C D After 1 minute After 5 minutes After 4 minutes After 3 minutes 37. The temperature of water in a beaker measures 87ºC. How many more degrees must the temperature increase to reach the boiling point? A B C D 23ºC 13ºC 212ºC 100ºC 37. The temperature of water in a beaker measures 87ºC. How many more degrees must the temperature increase to reach the boiling point? A B C D 23ºC 13ºC (100-87=13) 212ºC 100ºC 38. A science class performs a temperature experiment. Groups measure the temperatures of items in cups. If the temperature of the cup of water measures 100ºC, which statement correctly describes the water? A B C D The water is boiling The water is cool. The water is freezing. The water is warm. 38. A science class performs a temperature experiment. Groups measure the temperatures of items in cups. If the temperature of the cup of water measures 100ºC, which statement correctly describes the water? A B C D The water is boiling The water is cool. The water is freezing. The water is warm. 39. Students made ice cream to investigate matter and its properties. The students added salt to the ice cream maker so that the mixture would change from a liquid to a solid. Which conclusion provides the most important reason salt was used to make the ice cream solidify? A B C D Salt dissolves in water. Salt adds flavor to the ice cream. Salt evaporates in water. Salt lowers the freezing point of water. 39. Students made ice cream to investigate matter and its properties. The students added salt to the ice cream maker so that the mixture would change from a liquid to a solid. Which conclusion provides the most important reason salt was used to make the ice cream solidify? A B C D Salt dissolves in water. Salt adds flavor to the ice cream. Salt evaporates in water. Salt lowers the freezing point of water. 40. Four students were experimenting with the boiling point of water. Measuring Boiling Point of Water Student Tools Needed Student A Thermometer, beaker, timer, goggles, hot plate Student B Hot plate, goggles, thermometer, tongs Student C Tongs, hot plate, timer, graduated cylinder Student D Beaker, pan balance, goggles, thermometer Which student gathered the correct tools for determining the boiling point of water? A B C D Student A Student B Student C Student D 40. Four students were experimenting with the boiling point of water. Measuring Boiling Point of Water Student Tools Needed Student A Thermometer, beaker, timer, goggles, hot plate Student B Hot plate, goggles, thermometer, tongs Student C Tongs, hot plate, timer, graduated cylinder Student D Beaker, pan balance, goggles, thermometer Which student gathered the correct tools for determining the boiling point of water? A B C D Student A Student B Student C Student D 41. A student put a cup of water in the freezer and left it there overnight. The next morning the student observed that the water in the cup had changed to ice. Which of the following statements best concludes why the water changed to ice? A B C D The water gained energy. The water reached its boiling point. The volume of the water decreased. Heat was taken away from the water. 41. A student put a cup of water in the freezer and left it there overnight. The next morning the student observed that the water in the cup had changed to ice. Which of the following statements best concludes why the water changed to ice? A B C D The water gained energy. The water reached its boiling point. The volume of the water decreased. Heat was taken away from the water. 42. A glass of water is placed in a very cold freezer. Every 5 minutes the temperature of water is measured and recorded: Time Elapsed Temperature 5 minutes 18ºC 10 minutes 12ºC 15 minutes 6ºC 20 minutes ? If the pattern continues, which statement correctly describes the water after 20 minutes? A B C D The water temp is 2ºC and the water is still liquid The water temp is 1ºC and the water is still liquid The water temp is 1ºC and the water is freezing The water temp is 0ºC and the water is freezing 42. A glass of water is placed in a very cold freezer. Every 5 minutes the temperature of water is measured and recorded: Time Elapsed Temperature 5 minutes 18ºC 10 minutes 12ºC 15 minutes 6ºC 20 minutes ? If the pattern continues, which statement correctly describes the water after 20 minutes? A B C D The water temp is 2ºC and the water is still liquid The water temp is 1ºC and the water is still liquid The water temp is 1ºC and the water is freezing The water temp is 0ºC and the water is freezing 43. A student is given an unknown liquid to rest in the laboratory. The student thinks the liquid is water. Which of the following is most helpful to determine if the liquid is water? A B C D boiling point of the liquid color of the liquid mass of the liquid volume of liquid 43. A student is given an unknown liquid to rest in the laboratory. The student thinks the liquid is water. Which of the following is most helpful to determine if the liquid is water? A B C D boiling point of the liquid color of the liquid mass of the liquid volume of liquid